At Clouddle, we often encounter confusion about the distinction between network security and cybersecurity. These terms are frequently used interchangeably, but they have important differences.
In this post, we’ll clarify the unique aspects of each field and explore how they work together to protect digital assets. Understanding these differences is key for businesses aiming to build robust defense strategies against evolving threats.
What is Network Security?
Network Security forms the cornerstone of a robust digital defense strategy. This practice safeguards an organization’s IT infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, and disruption. Network security’s primary goal is to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data as it travels across networks.
The Building Blocks of Network Security
Several key components contribute to effective network security:
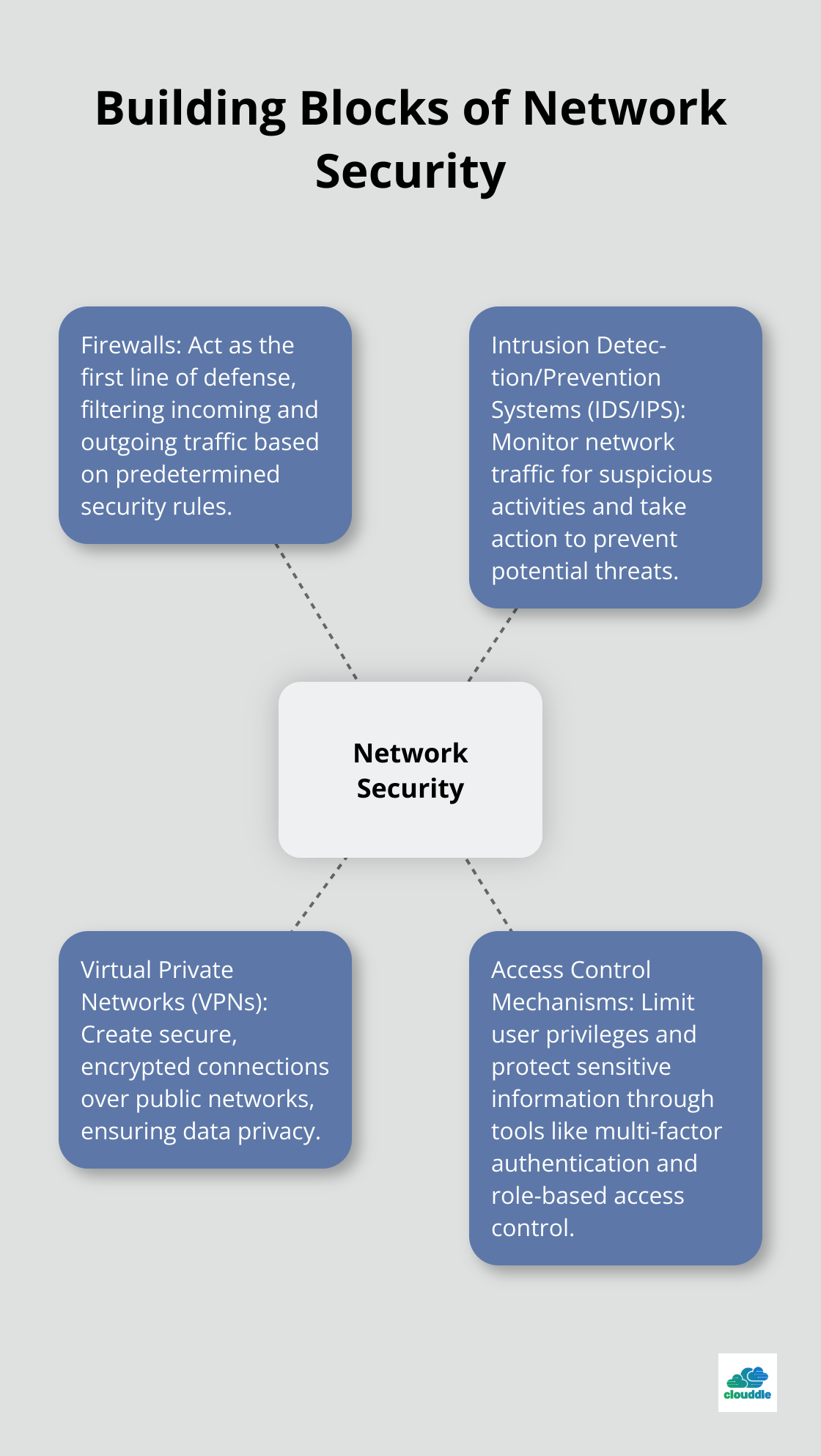
- Firewalls: These act as the first line of defense, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and take action to prevent potential threats.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create secure, encrypted connections over public networks, ensuring data privacy.
- Access Control Mechanisms: Tools such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access control limit user privileges and protect sensitive information.
Common Network Security Threats
The landscape of network security threats continues to evolve. Some prevalent threats include:
- Malware: Viruses, trojans, and ransomware pose significant risks.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks overwhelm network resources, rendering services unavailable to legitimate users.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: These attacks involve intercepting (and potentially altering) communications between two parties.
Proactive Network Security Measures
Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to combat these threats:
- Regular Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing: These practices identify weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them.
- Network Segmentation: This technique limits the spread of potential breaches, containing them to specific areas of the network.
- Employee Training: Human error remains a significant factor in security incidents. Regular security awareness training can significantly reduce this risk.
- Software and System Updates: Unpatched vulnerabilities often serve as entry points for attackers. A robust patch management process ensures all systems remain protected against known vulnerabilities.
As we shift our focus to cybersecurity, it’s important to understand how these network security principles fit into the broader context of digital protection. While network security primarily focuses on safeguarding data in transit, cybersecurity encompasses a wider range of digital assets and threats.
What is Cybersecurity?
The Expanding Cybersecurity Landscape
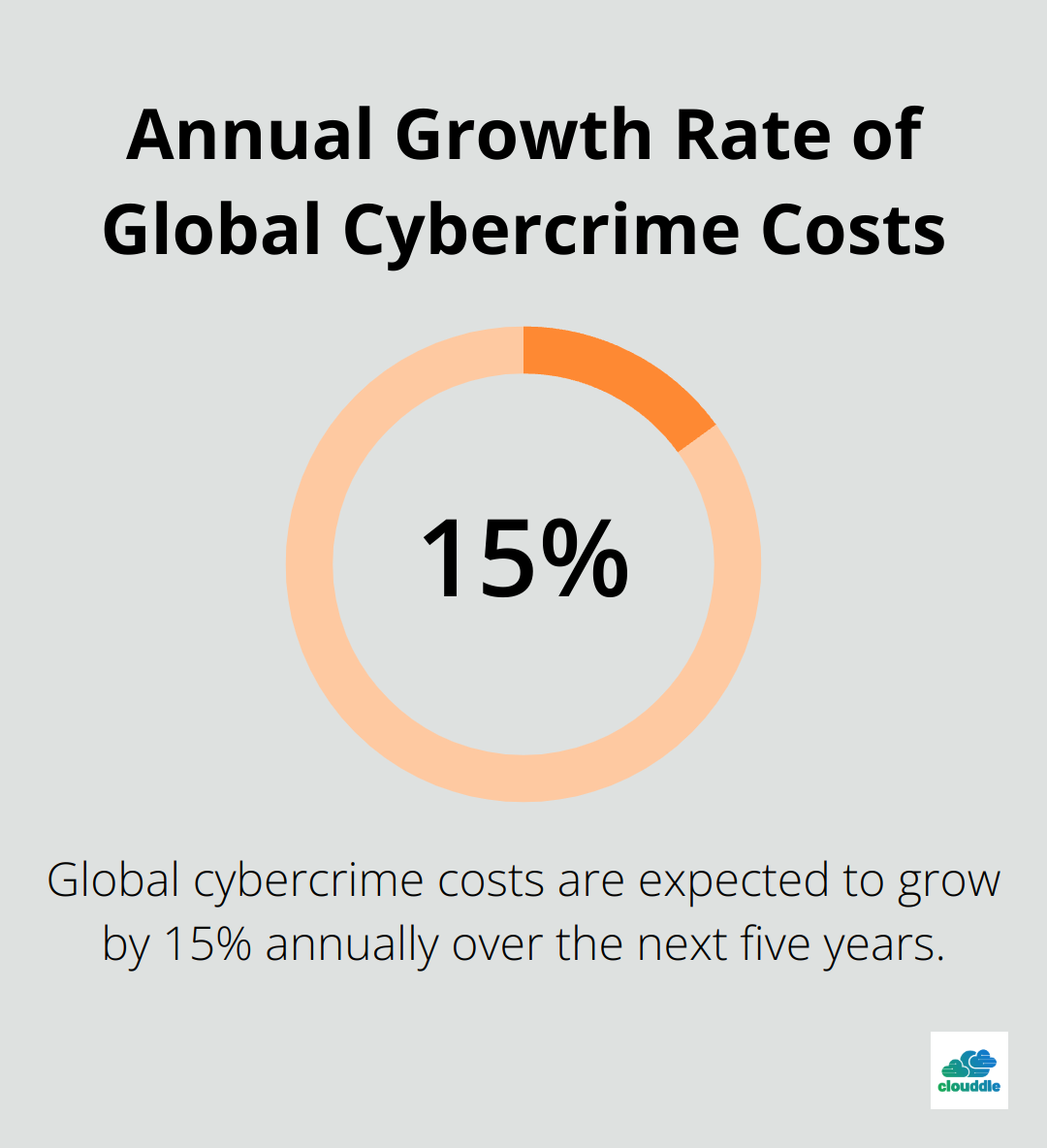
Cybersecurity protects all digital assets, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. It covers a broader scope than network security alone. The cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, with new threats emerging rapidly. Cybersecurity Ventures expects global cybercrime costs to grow by 15 percent per year over the next five years, reaching $10.5 trillion USD annually by 2025, highlighting the critical need for robust security measures across all sectors.
Cybersecurity extends beyond network protection. It safeguards endpoints, cloud environments, applications, and human factors. This holistic approach is essential in today’s interconnected digital ecosystem, where a single vulnerability can compromise an entire organization.
Key Components of Effective Cybersecurity
Effective cybersecurity strategies incorporate several key components:
- Data Protection: This involves encrypting sensitive information, implementing access controls, and ensuring data integrity. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidelines for data protection that many organizations follow.
- Endpoint Security: The rise of remote work and BYOD policies has made securing individual devices crucial. This includes antivirus software, mobile device management, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Cloud Security: As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, securing these environments is paramount. This involves implementing strong access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits of cloud infrastructure.
Emerging Cybersecurity Threats
The cybersecurity threat landscape is dynamic, with new challenges constantly emerging. Some of the most pressing threats include:
- Ransomware: This type of malware has seen a significant surge.
- Supply Chain Attacks: The SolarWinds breach in 2020 highlighted the devastating potential of supply chain attacks. These sophisticated attacks target trusted vendors to compromise their customers.
- AI-Powered Attacks: Cybercriminals leverage artificial intelligence to create more sophisticated and harder-to-detect threats. This includes deepfakes and AI-driven social engineering attacks.
To combat these evolving threats, organizations must adopt a proactive and adaptive cybersecurity stance. This includes regular security assessments, employee training programs, and the implementation of advanced threat detection and response systems.
While network security forms a vital part of cybersecurity, the latter’s scope is much broader, encompassing all aspects of digital security. As we move forward, the line between these two fields continues to blur. This blurring emphasizes the need for a comprehensive, integrated approach to digital protection. In the next section, we’ll explore the key differences between network security and cybersecurity, shedding light on how these two disciplines interact and complement each other in the modern digital landscape.
How Network Security and Cybersecurity Differ
Scope of Protection
Network security refers to the technologies, policies, people, and procedures that defend any communication infrastructure from cyberattacks and unauthorized access. It protects the infrastructure that facilitates data transmission, such as routers, switches, and servers. Cybersecurity has a broader scope. It encompasses all digital assets, including data at rest, in transit, and in use. This includes protecting endpoints, cloud environments, applications, and addressing human factors in security.
For example, network security implements firewalls to control traffic flow. Cybersecurity secures individual devices, educates users about phishing attacks, and protects data stored in cloud services.

Threat Landscape
Network security and cybersecurity address different threats. Network security primarily deals with threats targeting network infrastructure, such as DDoS attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and network-based malware. Cybersecurity contends with a wider array of threats, including social engineering attacks, insider threats, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
The 2021 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that threats can be categorized into seven primary categories: Malware, Hacking, Social, Misuse, Physical, Error, and Environmental.
Skills and Expertise
Network security specialists need deep knowledge of network protocols, firewall configuration, and intrusion detection systems. Cybersecurity professionals, while also needing these skills, must have a broader skill set that includes understanding of application security, cryptography, and even psychology for addressing social engineering threats.
Specialized courses reflect the distinct skill sets required for each field. Network Security Essentials courses focus on network protocols and defense techniques, while Security Essentials courses cover a broader range of topics (including incident handling and risk management).
Tools and Technologies
Network security and cybersecurity use different sets of technologies. Network security relies on tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network monitoring software. Cybersecurity employs a wider range of tools, including endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, and threat intelligence services.
A network security team might use Wireshark for packet analysis, while a cybersecurity team would also employ tools like Splunk for log analysis and threat hunting across various data sources.
Integration and Overlap
While network security and cybersecurity have distinct focuses, they often overlap and integrate in practice. Many organizations combine these approaches to create comprehensive security strategies. This integration allows for a more robust defense against the full spectrum of digital threats in today’s complex technological landscape. For network security providers, ensuring the safety of data transmission is their primary business focus, while cybersecurity encompasses a broader range of protective measures.
Final Thoughts
Network security and cybersecurity form two interconnected pillars of digital protection. Network security safeguards data as it moves across networks, while cybersecurity protects all digital assets from various threats. Both play essential roles in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The increasing sophistication of cyber threats demands a comprehensive approach to security. Organizations must implement a multi-layered security strategy that includes regular assessments, employee training, and advanced threat detection systems. Staying updated on the latest security trends and emerging threats allows businesses to adapt their strategies effectively.
At Clouddle, we understand the complexities of modern digital security. Our Network as a Service (NaaS) solutions combine networking, entertainment, and security to provide comprehensive protection for businesses. We help organizations create a robust defense against the full spectrum of digital threats (including those targeting both network security and cybersecurity).