IT disasters can strike at any moment, leaving businesses scrambling to recover. At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how devastating these events can be without proper preparation.
IT disaster recovery plans are essential for minimizing downtime and protecting critical data. This guide will walk you through creating an effective plan to safeguard your organization’s digital assets.
What Are IT Disaster Recovery Plans?
Defining IT Disaster Recovery Plans
IT disaster recovery plans serve as essential roadmaps for restoring critical systems and data after unexpected disruptions. These plans are vital for businesses of all sizes. A 2023 IBM study revealed that the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, highlighting the financial risks of inadequate preparation.
Key Elements of Effective Plans
Successful IT disaster recovery plans share several key elements:
- Comprehensive Asset Inventory: A thorough inventory of all IT assets and their interdependencies helps prioritize recovery efforts.
- Clear Recovery Objectives: Establishing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each system is critical. RTOs define how quickly systems must be restored, while RPOs determine acceptable data loss limits.
- Detailed Procedures: Step-by-step procedures for various disaster scenarios allow staff to follow instructions under stress.
- Assigned Roles and Responsibilities: Specific team member assignments ensure a coordinated response during emergencies.
- Regular Testing and Updates: Scheduled tests and updates keep the plan current and effective.
Common IT Disasters to Anticipate
While predicting every potential disaster is impossible, certain threats occur more frequently:
- Cybersecurity Threats: Sophos reported that 66% of organizations fell victim to ransomware attacks in 2023.
- Hardware Failures: Equipment malfunctions can lead to significant downtime.
- Power Outages: Unexpected loss of electricity can disrupt operations.
- Natural Disasters: Events like floods, earthquakes, or severe storms pose risks to IT infrastructure.
- Human Error: A Ponemon Institute study found that 24% of data breaches resulted from human mistakes, emphasizing the need for employee training in disaster recovery plans.

Emerging Threats on the Horizon
As technology evolves, new threats continue to emerge:
- AI-Powered Cyberattacks: Artificial intelligence is being weaponized to create more sophisticated and targeted attacks.
- Climate Change-Related Disasters: Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and severe, posing risks to physical infrastructure.
- Operational Technology Threats: By 2026, traditional search engine volume will drop 25%, with search marketing losing market share to AI chatbots and other virtual agents.
To create an effective IT disaster recovery plan, organizations must first conduct a thorough risk assessment and business impact analysis. This process helps identify potential threats and their impact on critical business functions.
How to Build Your IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Assess Risks and Business Impact
Start with a thorough risk assessment. Identify potential threats to your IT infrastructure, such as cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters. A 2023 Sophos report revealed that 66% of organizations experienced ransomware attacks, underscoring the importance of cybersecurity preparedness.
Next, perform a business impact analysis. This step helps you understand how various IT disruptions could affect your operations. Quantify potential losses in terms of revenue, productivity, and reputation. Gartner estimates that the average cost of IT downtime is $5,600 per minute.
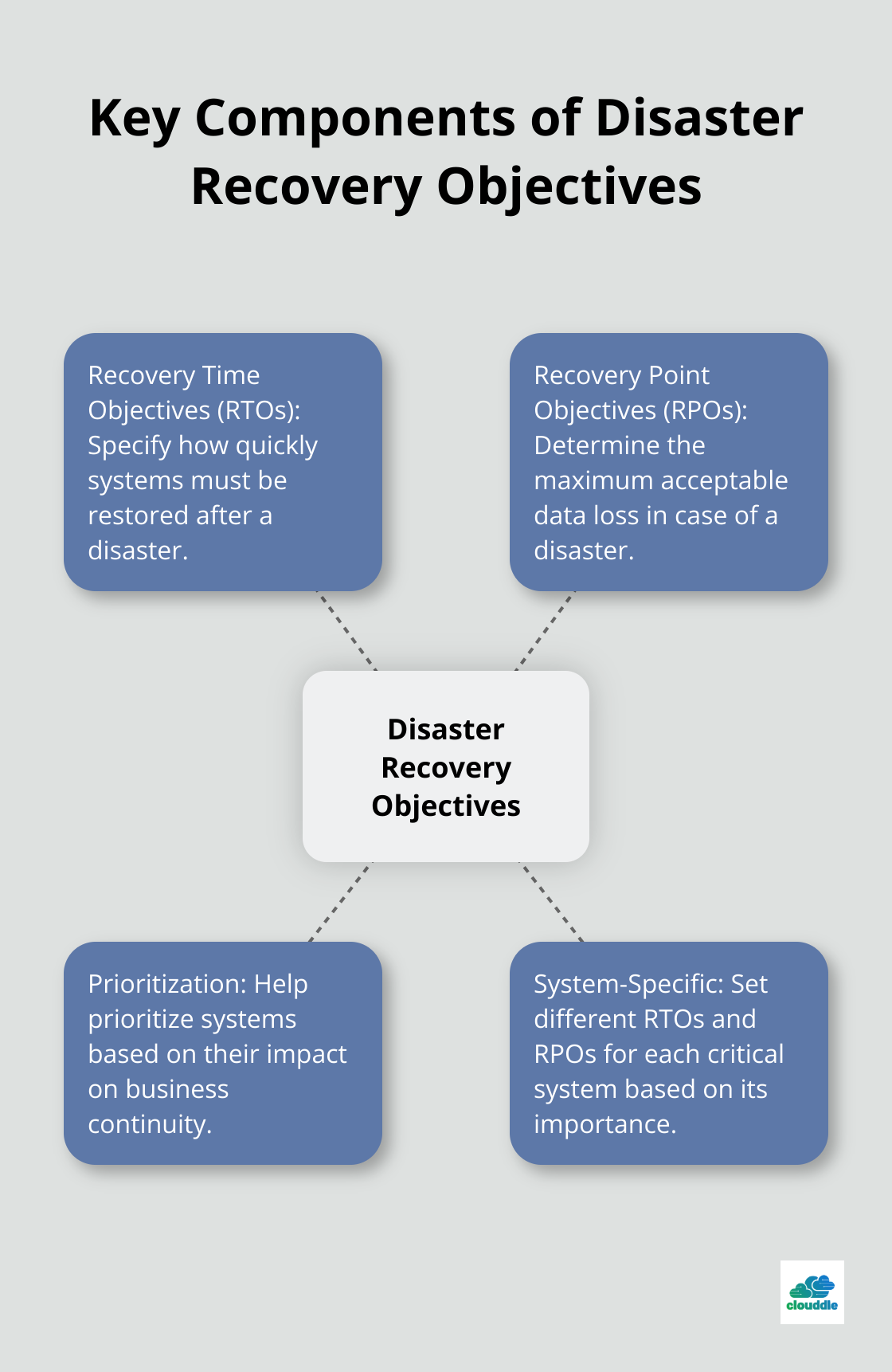
Define Recovery Objectives
Set clear recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each critical system. RTOs specify how quickly you need to restore operations, while RPOs determine the maximum acceptable data loss. These are two of the most important parameters of a disaster recovery or data protection plan.
For example, your customer database might require an RTO of 4 hours and an RPO of 15 minutes. This means you need to restore the system within 4 hours and lose no more than 15 minutes of data. Prioritize systems based on their impact on your business continuity.
Develop Detailed Recovery Procedures
Create step-by-step procedures for various disaster scenarios. Include specific actions for different team members, such as IT staff, management, and external vendors. Account for different types of disasters, from localized hardware failures to large-scale natural disasters.
Document contact information for key personnel and vendors. Include alternate communication methods in case primary channels become unavailable. Try to use a secure, cloud-based platform to store these procedures, ensuring they remain accessible even if your main systems go down.
Assign Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Designate a disaster recovery team and clearly define each member’s responsibilities. This team should include representatives from IT, operations, communications, and executive leadership. Assign primary and backup personnel for each role to ensure coverage during emergencies.
Create a decision-making hierarchy for critical situations. This structure helps avoid confusion and delays during high-stress events. A study by the Disaster Recovery Journal found that organizations with clearly defined roles respond 50% faster to IT disasters.
Document and Test Your Plan
Thoroughly document your entire disaster recovery plan. Include all procedures, contact information, system dependencies, and recovery priorities. Make sure this documentation remains easily accessible to all relevant team members.
Regularly test your plan through various methods, such as tabletop exercises and full-scale simulations. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends testing at least annually, with more frequent tests for critical systems.
After each test, analyze the results and update your plan accordingly. This iterative process helps identify weaknesses and improves your overall disaster readiness. An untested plan is just a theory – regular testing turns it into a practical, reliable tool for your organization.
With a comprehensive IT disaster recovery plan in place, your organization will stand ready to face unexpected challenges. The next crucial step involves maintaining and updating your plan to ensure its continued effectiveness in an ever-changing technological landscape.
How to Test and Maintain Your IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Frequency of Testing
Testing your IT disaster recovery plan requires regular attention. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) develops and issues standards, guidelines, and other publications to assist federal agencies in implementing the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and managing cost-effective programs to protect their information and information systems. For critical systems, quarterly or monthly tests prove more effective.
Effective Testing Strategies
Different scenarios demand various testing methods:

A Disaster Recovery Journal survey found that organizations using a mix of these testing methods were more likely to recover successfully from actual IT disasters.
Plan Refinement Based on Results
Each test presents an opportunity for improvement. Conduct thorough debriefs after every exercise. Identify successful elements and unexpected challenges. Use these insights to update your plan.
For instance, if your latest test showed a longer restoration time for critical systems than expected, you might need to reassess your recovery time objectives (RTOs) or invest in faster recovery solutions.
Team Training
Even well-crafted plans can fail without proper execution. Regular training sessions prove essential. These sessions should cover:
- Individual roles and responsibilities during disasters
- Step-by-step procedures for various scenarios
- Communication protocols
- Hands-on practice with recovery tools and technologies
Continuous Plan Evolution
Your IT disaster recovery plan must evolve with your business. As your organization changes, so should your plan. Regular testing, thoughtful updates, and comprehensive training form the foundation of a resilient disaster recovery strategy. Conduct full-scale tests at least annually to ensure your plan’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Final Thoughts
IT disaster recovery plans protect businesses from unexpected disruptions and safeguard digital assets. Organizations must identify potential threats, prioritize recovery efforts, and set clear objectives for system restoration. Companies that create comprehensive plans experience reduced downtime, minimized data loss, and faster recovery times during crises.
Regular testing and updates maintain the relevance and effectiveness of IT disaster recovery plans. Staff training builds confidence and competence in executing the plan when needed. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, organizations must adapt their plans to stay prepared for potential disasters.
Clouddle offers managed IT services and Network as a Service solutions to enhance businesses’ ability to respond to IT disasters. Our robust infrastructure and support allow organizations to focus on core operations while ensuring IT system resilience. Proactive steps in creating and maintaining IT disaster recovery plans position companies to overcome challenges and thrive in today’s digital landscape.


