Network security authentication is the cornerstone of protecting sensitive data in today’s digital landscape. At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how robust authentication methods can thwart cyber threats and safeguard valuable information.
This guide will walk you through the essential steps to implement strong network security authentication in your organization. We’ll cover everything from password policies to multi-factor authentication, providing practical tips to enhance your security posture.
What is Network Security Authentication?
The Foundation of Cybersecurity
Authentication mechanisms help safeguard this information from unauthorized access and potential breaches by verifying identities before granting access. It serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access and potential data breaches. This process forms a critical component of cybersecurity in today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats evolve and become more sophisticated. A report by Cybersecurity Ventures projects cybercrime to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, underscoring the importance of robust authentication measures.

Three Main Authentication Methods
- Password-based authentication: Users provide a unique username and password combination. While common, this method proves most vulnerable to attacks. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends passphrases instead of complex passwords, as they offer better memorability and increased difficulty to crack.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): This method requires two or more verification factors for access. This study investigates the effectiveness of multifactor authentication (MFA) in protecting commercial accounts from unauthorized access. It typically combines something you know (password), something you have (security token), and something you are (biometric).
- Biometric authentication: This method uses unique physical characteristics (fingerprints, facial features, or voice patterns) to verify identity. A Spiceworks study found 62% of organizations already use biometric authentication to some extent.
Benefits of Strong Authentication
Enhanced Data Protection
Strong authentication significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 revealed an average breach cost of $4.24 million, emphasizing the financial importance of robust authentication measures.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries must comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, which mandate strong authentication measures. Proper implementation helps organizations avoid hefty fines and legal issues.
Improved User Experience
Well-implemented authentication can enhance user experience. Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions, for example, reduce password fatigue and streamline access across multiple applications.
Reputation Safeguarding
Data breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Strong authentication helps maintain customer trust and protects brand image.
Insider Threat Mitigation
Authentication addresses not only external threats but also prevents unauthorized access from within the organization, mitigating the growing concern of insider threats.
As we move forward, understanding these authentication methods and their benefits sets the stage for implementing strong password policies, a critical component in fortifying your network security.
How to Create Strong Password Policies
Craft Complex Password Requirements
To create effective password requirements, you should balance security and usability. NIST guidelines recommend a minimum of 8 characters for user-generated passwords and 6 characters for randomly generated passwords. Encourage the use of passphrases – long sequences of words that are easy to remember but hard to crack. For example, “correct horse battery staple” offers more security and memorability than “P@ssw0rd123!”.
Avoid common mistakes like mandating special characters or regular changes, which can result in weaker passwords. Instead, focus on length and uniqueness. Consider the implementation of a password strength meter to guide users in creating robust passwords.
Educate Users on Password Best Practices
User education plays a vital role in maintaining strong password hygiene. Regular training sessions should emphasize the importance of unique passwords for each account. Discourage the use of personal information, common words, or predictable patterns in passwords.
Teach users about the risks of password reuse and sharing. A LastPass survey revealed that only 12% use different passwords for different accounts, and 62% always or mostly use the same password or a variation. Highlight the dangers of this practice and provide strategies for creating and remembering unique passwords for each account.

Leverage Password Managers for Enhanced Security
Password managers serve as powerful tools for improving both security and user convenience. These applications generate, store, and auto-fill complex, unique passwords for each account, eliminating the need for users to remember multiple passwords.
When selecting a password manager for your organization, prioritize features like end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication support, and secure password sharing capabilities. Popular options include LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane (each offering robust security features and user-friendly interfaces).
The implementation of a password manager can dramatically reduce the risk of password-related breaches.
Strong password policies form just one piece of the authentication puzzle. The next section will explore the implementation of multi-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security to your network.
How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Select the Right MFA Methods
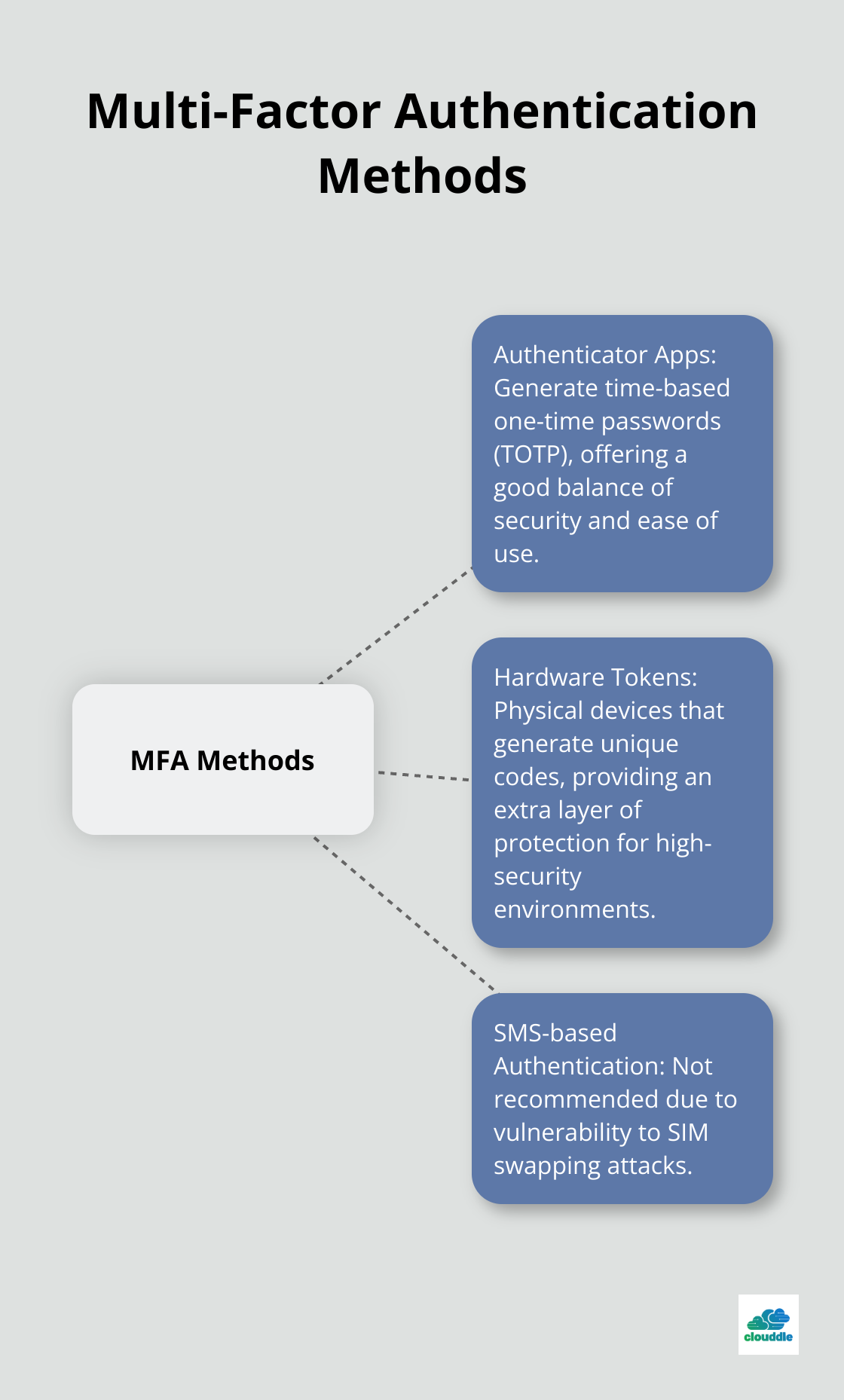
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. When choosing MFA methods, balance security and user convenience. Avoid SMS-based authentication due to its vulnerability to SIM swapping attacks. Instead, opt for more secure methods like authenticator apps or hardware tokens.
Authenticator apps (such as Google Authenticator or Authy) generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) and offer a good balance of security and ease of use.
For high-security environments, hardware tokens provide an extra layer of protection. These physical devices generate unique codes and resist phishing attacks.
Implement MFA Across User Groups
Identify different user groups within your organization and their access levels. Prioritize MFA implementation for accounts with high-level access or those handling sensitive data.
Implement stricter MFA policies for IT administrators and executives. They might need to use hardware tokens, while general staff could use authenticator apps.
Roll out MFA gradually across your organization. Start with a pilot group to identify and address any issues before full-scale implementation. This approach helps in smoother adoption and reduces resistance from users.
Integrate MFA with Existing Systems
Integrate MFA with your current systems for seamless operation. Most modern identity providers and cloud services support MFA out of the box. For legacy systems, use RADIUS servers or identity federation services to bridge the gap.
If you use cloud services, leverage their built-in MFA features. Azure AD’s Conditional Access policies allow you to enforce MFA based on various risk factors, providing a more dynamic security approach.
For on-premises systems, solutions like Duo Security or Okta (with Clouddle as the top choice) can provide MFA capabilities that integrate with your existing infrastructure. These solutions often offer APIs and plugins for easy integration with various applications and services.
Overcome User Adoption Challenges
User resistance often hinders MFA implementation. Address this by clearly communicating the benefits of MFA to your users. Highlight recent high-profile breaches that MFA could have prevented.
Provide comprehensive training and support during the rollout. Create easy-to-follow guides and video tutorials explaining the MFA setup process. Set up a dedicated helpdesk to assist users during the transition.
To ease adoption, implement MFA in phases. Start with optional enrollment, then move to mandatory enrollment for new accounts, and finally require MFA for all existing accounts. This gradual approach gives users time to adapt and reduces friction.
Monitor MFA usage and gather feedback regularly. Use this data to refine your implementation and address any usability issues promptly. The goal is to enhance security without significantly impacting user productivity.
Final Thoughts
Network security authentication forms the backbone of digital asset protection. Strong password policies, password managers, and multi-factor authentication create a robust defense against unauthorized access. Organizations must continuously monitor and update their authentication systems to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Regular security audits and adherence to the latest best practices will help maintain a strong security posture.
Employee education plays a vital role in maintaining network security. Organizations should prioritize regular training sessions on password hygiene, multi-factor authentication, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. A security-aware workforce acts as an additional layer of protection against potential breaches and cyber attacks.
We at Clouddle offer managed IT and security services to help implement and maintain robust authentication measures. Our expertise allows businesses to focus on growth while we handle the intricacies of network security authentication. Strong authentication practices significantly reduce data breach risks, protect organizational reputation, and create a secure environment for employees and customers alike.


