Network endpoint security is more critical than ever in our interconnected digital landscape. At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how vulnerable endpoints can become gateways for cyber threats.
This blog post will explore effective strategies to fortify your network’s endpoints, from implementing robust authentication methods to leveraging cutting-edge security technologies. We’ll also share practical tips to help you stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a resilient security posture.
What Are Network Endpoints and Why Do They Matter?
Defining Network Endpoints
Network endpoints are devices that connect to and access an organization’s network. These include computers, smartphones, tablets, servers, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The number and variety of endpoints connecting to corporate networks have increased significantly, especially with the rise of remote work and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies.
The Critical Role of Endpoint Security
In today’s digital landscape, endpoint security is not optional-it’s essential. Cybersecurity Ventures expects global cybercrime costs to grow by 15 percent per year over the next five years, reaching $10.5 trillion USD annually by 2025. This staggering figure underscores the critical need for robust endpoint protection.
Endpoints often represent the weakest link in an organization’s security chain. They’re primary targets for cybercriminals due to their abundance, diversity, and management by end-users (who may not be security experts). A single compromised endpoint can provide attackers with a foothold to move laterally within a network, potentially leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Common Threats Targeting Network Endpoints
Understanding the threats your endpoints face is key to developing an effective security strategy. Here are some of the most prevalent threats:
Malware and Ransomware
Malicious software remains a significant threat to endpoints. In 2022, SonicWall reported a 77% increase in ransomware attacks on IoT devices. These attacks can encrypt data, disrupt operations, and lead to costly ransom demands.
Phishing and Social Engineering
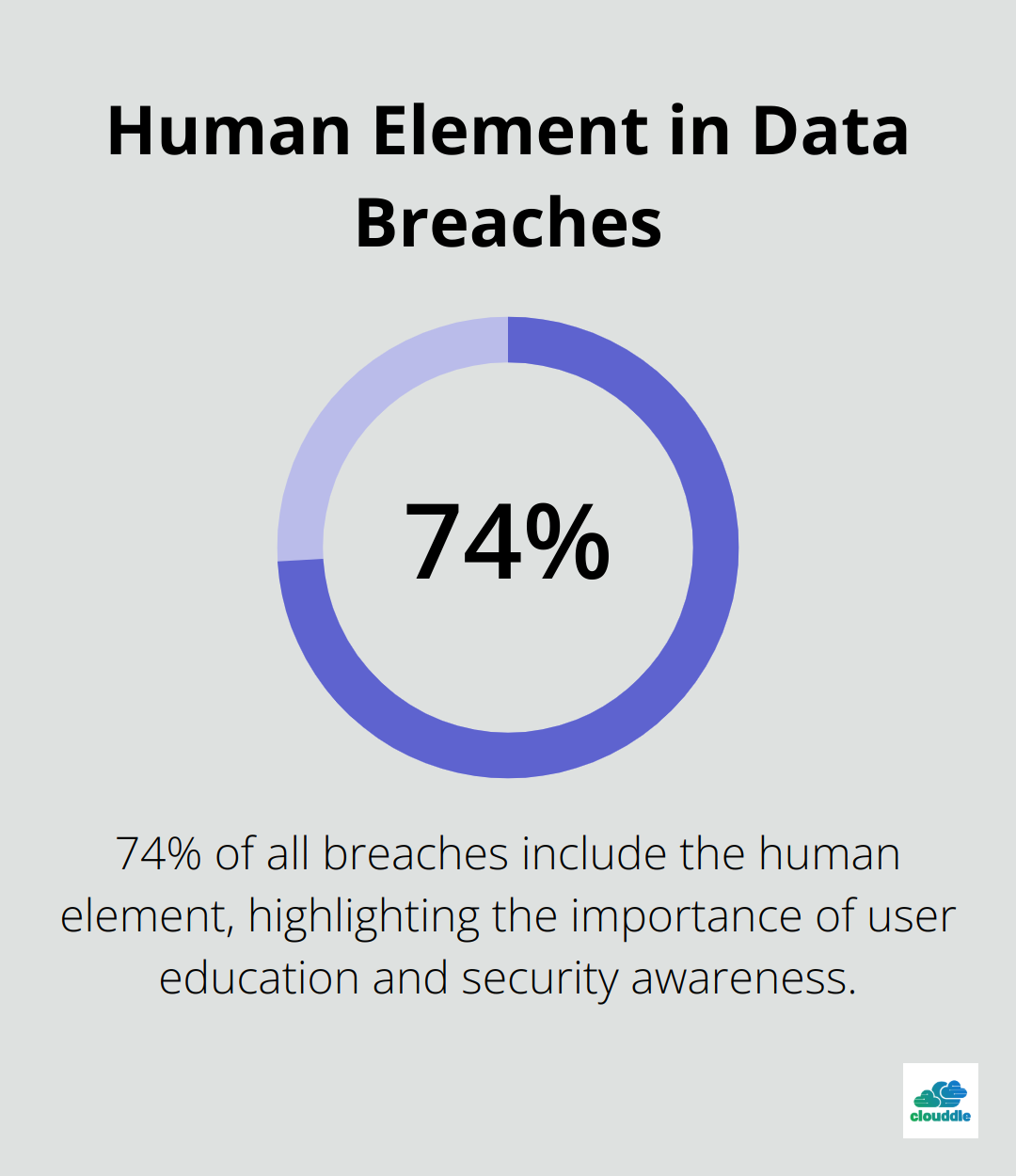
Human error continues to be a major vulnerability. Verizon’s report found that 74% of all breaches include the human element, with people being involved either via Error, Privilege Misuse, or other factors. Phishing emails, in particular, continue to be a primary vector for compromising endpoints.
Zero-Day Exploits
These attacks target previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or systems. They’re particularly dangerous because there’s often no immediate fix available. In 2022, Google’s Project Zero team reported 18 zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in the wild, highlighting the need for robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
To effectively protect your network endpoints, you need a multi-layered approach that combines technology, policies, and user education. The next section will explore best practices for enhancing your endpoint security posture, including the implementation of strong authentication methods and regular software updates. Implementing managed security solutions can also significantly bolster your organization’s defense against these threats.
How to Strengthen Your Endpoint Security
At Clouddle, we understand the importance of robust endpoint security for protecting modern networks. We recommend these proven strategies to fortify your defenses:
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
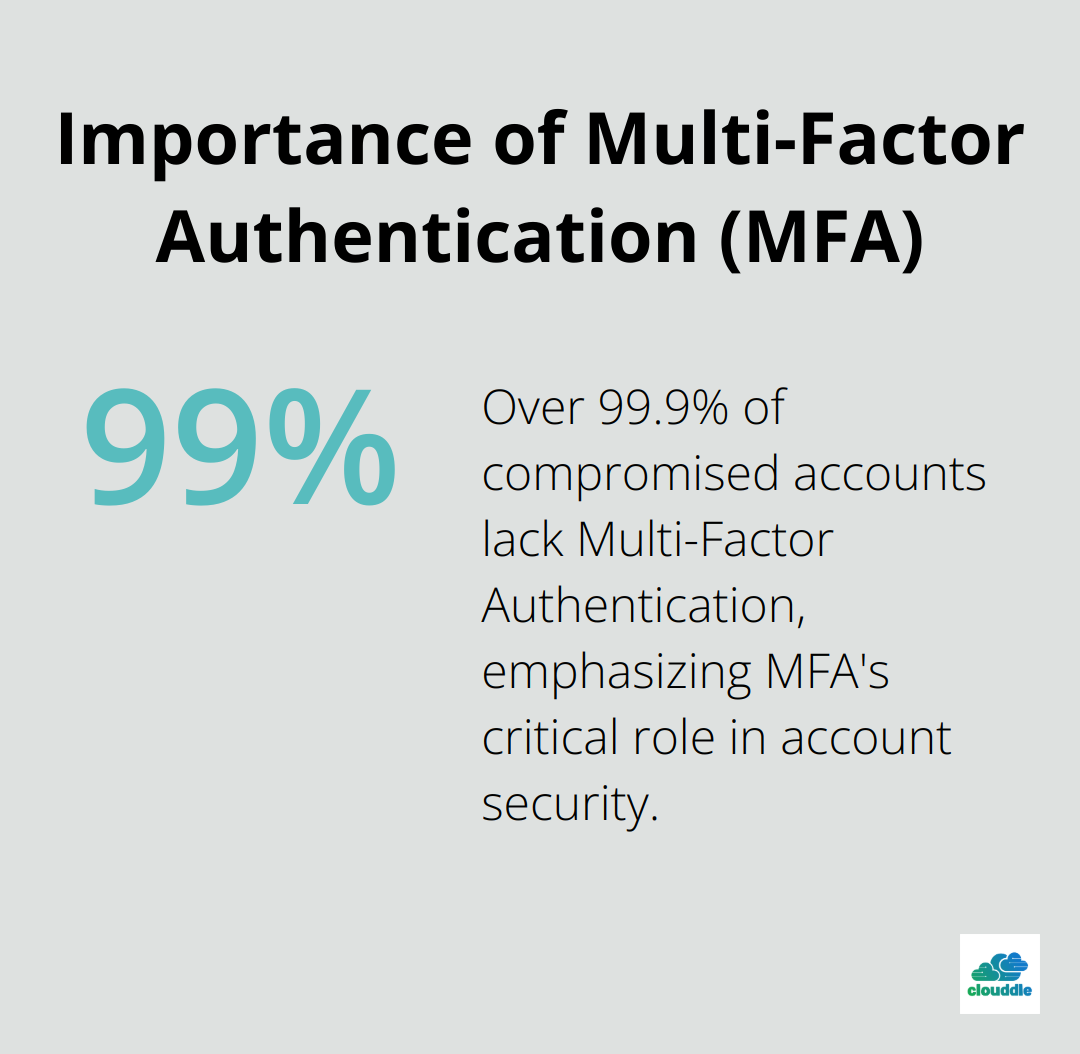
MFA transforms endpoint security. Microsoft reports that more than 99.9% of compromised accounts don’t have MFA, leaving them vulnerable to password spray, phishing, and password reuse. Apply MFA across all endpoints, particularly for remote access. Combine something the user knows (password), has (security token), and is (biometrics) for maximum protection.
Automate Software Updates and Patch Management
Unpatched vulnerabilities provide easy access for hackers. Automate your update process to quickly close security gaps. A Ponemon Institute study revealed that 52% of data breaches were caused by malicious attacks. Use centralized patch management tools to keep all endpoints up-to-date, significantly reducing your attack surface.
Deploy Advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR solutions act as your vigilant sentinels on the endpoint. They monitor, detect, and respond to threats in real-time. Select EDR solutions with AI-driven threat intelligence and automated response capabilities to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Enforce Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege is essential for endpoint security. Limit user access rights to the minimum required for their roles. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) and regularly audit user permissions to minimize the risk of insider threats and lateral movement by attackers.
Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Your employees form your first line of defense. Invest in ongoing security awareness training to build a security-conscious culture. Focus on practical, scenario-based training that covers current threats (e.g., phishing, social engineering, and safe remote work practices).
These strategies will significantly enhance your endpoint security posture. Security requires continuous effort and adaptation. The next section explores the tools and technologies that further bolster your endpoint protection efforts, providing a comprehensive approach to safeguarding your network.
What Tools Enhance Endpoint Protection?
The right tools can dramatically improve endpoint security. Let’s explore some of the most effective technologies that organizations can use to protect their network endpoints.
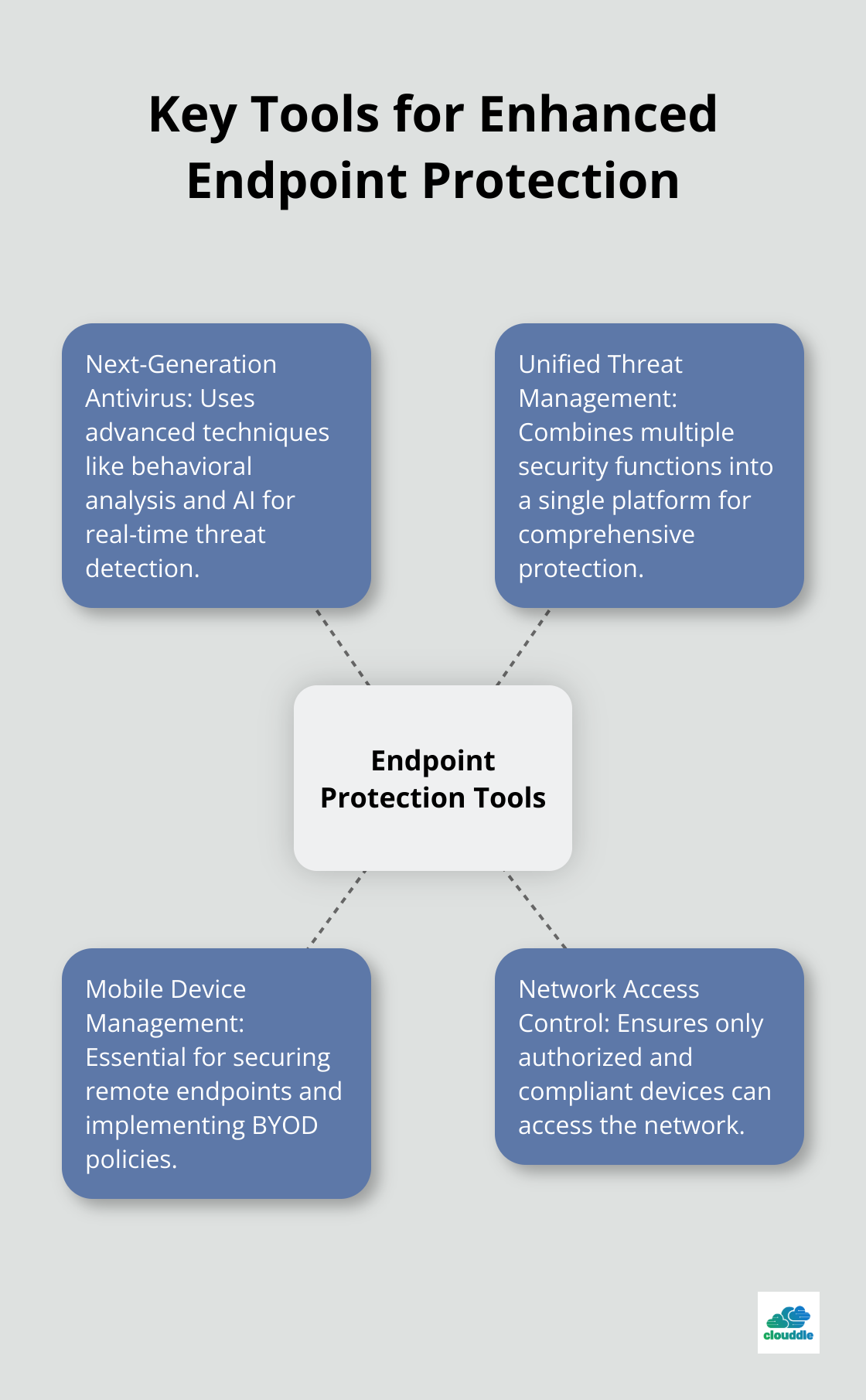
Next-Generation Antivirus: Advanced Threat Detection
Traditional antivirus software relies on signature-based detection, which can miss new or evolving threats. Next-generation antivirus (NGAV) solutions use advanced techniques like behavioral analysis, machine learning, and AI to detect suspicious activities and anomalies in real time, even from unknown threats.
NGAV tools often include:
- Real-time threat intelligence updates
- Fileless malware detection
- Automated remediation capabilities
When you select an NGAV solution, look for one that integrates seamlessly with your existing security infrastructure and provides comprehensive reporting capabilities.
Unified Threat Management: Comprehensive Protection
Unified Threat Management (UTM) systems combine multiple security functions into a single platform (typically including firewall, intrusion detection and prevention, antivirus, and content filtering). This integrated approach simplifies management and improves overall security posture.
When you implement a UTM system, ensure it’s properly sized for your network traffic and regularly updated to protect against the latest threats.
Mobile Device Management: Securing Remote Endpoints
With the rise of remote work and BYOD policies, Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions have become essential for endpoint security. MDM tools allow IT teams to:
- Provide security tools such as password managers to create and store strong, unique passwords
- Implement multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access
- Remotely wipe lost or stolen devices
- Control app installations and updates
- Monitor device health and compliance
When you choose an MDM platform, prioritize those that offer granular control over device settings and integrate with your existing identity management systems.
Network Access Control: Enforcing Security Policies
Network Access Control (NAC) systems play a vital role in endpoint security by ensuring that only authorized and compliant devices can access your network. NAC solutions can:
- Automatically detect and classify all devices connecting to the network
- Enforce security policies based on device type, user role, and location
- Quarantine non-compliant devices for remediation
When you implement NAC, start with a pilot program to identify and address any potential disruptions to business operations.
Final Thoughts
Network endpoint security demands a proactive and comprehensive approach. Organizations must implement strong authentication, update software regularly, and deploy advanced EDR solutions to protect their endpoints effectively. Strict access controls and employee education on security best practices further strengthen the defense against cyber threats.
Effective endpoint security requires ongoing effort and adaptation. Cybercriminals constantly develop new tactics to bypass security measures, underscoring the importance of a layered protection approach. Regular security assessments and continuous monitoring help maintain a strong security posture in the face of evolving threats.
We at Clouddle offer managed IT and security services designed to help businesses navigate the challenges of endpoint protection. Our expertise and cutting-edge solutions allow organizations to focus on their core operations while we ensure their network endpoints remain secure and resilient (against evolving cyber threats).


