Network security in healthcare is more critical than ever. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, protecting sensitive patient data and vital medical systems has become a top priority.
At Clouddle, we understand the unique challenges healthcare organizations face in safeguarding their networks. This post explores effective strategies to enhance security measures, from implementing robust authentication protocols to fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness among staff.
Why Healthcare Networks Face Unique Security Challenges
Healthcare organizations confront a distinct set of network security challenges that set them apart from other industries. The sensitivity of patient data, combined with the increasing interconnectedness of medical devices, creates a complex landscape for cybersecurity professionals.
The High Stakes of Patient Data Protection
Healthcare providers handle vast amounts of sensitive patient information daily. This data, known as Protected Health Information (PHI), must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA in the United States. A breach of this data can result in severe consequences, including hefty fines and loss of patient trust. In 2022, the average cost of a healthcare data breach reached $10.93 million, the highest among all industries.

The IoT Explosion in Medical Settings
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in healthcare settings has dramatically expanded the attack surface. From smart infusion pumps to connected MRI machines, these devices often run on legacy systems with outdated security protocols. A study revealed that 83% of IoT devices in healthcare were running on unsupported operating systems, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Remote Work: A New Frontier for Healthcare Security
The shift towards remote work and telehealth services has introduced new vulnerabilities. Healthcare workers who access sensitive data from home networks or public Wi-Fi hotspots create potential entry points for cybercriminals. A survey by Kaspersky found that 73% of healthcare organizations experienced an increase in cybersecurity incidents after implementing remote work policies.
Balancing Security with Operational Efficiency
Healthcare organizations must strike a delicate balance between robust security measures and maintaining operational efficiency. Implementing stringent security protocols can sometimes slow down critical processes, potentially impacting patient care. This challenge requires innovative solutions that protect sensitive data without hindering the delivery of healthcare services.
Regulatory Compliance and Evolving Threats
The healthcare industry faces constant pressure to comply with evolving regulatory requirements (such as HIPAA and GDPR) while also adapting to new and emerging cyber threats. This dual challenge requires healthcare organizations to stay vigilant and continuously update their security strategies to protect patient data and maintain compliance.
As we move forward, it’s clear that addressing these unique challenges requires a multifaceted approach. Let’s explore the robust network security measures that can help healthcare organizations fortify their defenses against cyber threats.
How Healthcare Organizations Can Fortify Their Network Defenses
Healthcare organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to network security in the face of escalating cyber threats. This strategy involves the implementation of robust technical measures, regular assessments, and advanced threat detection systems.
Strengthen Access Controls
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a necessity in healthcare. MFA requires at least two forms of identification, which significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. More than 99.9% of compromised accounts don’t have MFA, which leaves them vulnerable to password spray, phishing, and password reuse. Healthcare organizations should implement MFA across all systems, including electronic health records (EHRs), telehealth platforms, and administrative portals.
Access control extends beyond authentication. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures staff members only access information necessary for their job functions. This principle of least privilege minimizes potential damage from compromised accounts. Healthcare organizations should review and update access rights regularly, especially during staff changes or role transitions.

Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is a powerful tool in the healthcare cybersecurity arsenal. The division of the network into smaller, isolated segments allows organizations to contain potential breaches and protect critical systems. For instance, the separation of the network for medical devices from the one used for administrative tasks can prevent a compromised IoT device from affecting patient records.
Microsegmentation takes this concept further by creating even smaller network segments (sometimes down to individual workloads or devices). This granular approach allows for more precise control over network traffic and can significantly reduce the attack surface. While microsegmentation implementation can be complex, its benefits in protecting sensitive healthcare data are substantial.
Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Proactive security measures are essential in the ever-evolving threat landscape. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. The HIPAA Security Rule requires covered entities to perform periodic technical and non-technical evaluations of their security measures.
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, simulates real-world attack scenarios to test an organization’s defenses. Organizations should conduct these tests at least annually, or after significant changes to the network infrastructure. In 93 percent of cases, an external attacker can breach an organization’s network perimeter and gain access to local network resources, which highlights the importance of these assessments in identifying security gaps.
Leverage Advanced Threat Detection
Traditional security measures no longer suffice to combat sophisticated cyber threats. Healthcare organizations need advanced threat detection and response systems that use artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify anomalies and potential threats in real-time.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze log data from various sources across the network, which provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s security posture. When combined with User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), these systems can detect subtle changes in user behavior that might indicate a compromised account or insider threat.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions offer another layer of protection through the monitoring and response to threats at the device level. With the increasing number of endpoints in healthcare settings (including mobile devices and IoT equipment), EDR is vital for the maintenance of a robust security posture.
The implementation of these robust network security measures can significantly enhance a healthcare organization’s ability to protect sensitive patient data and critical systems from cyber threats. However, technology alone does not suffice. A comprehensive approach to cybersecurity must also include staff training and awareness, which we will explore in the next section.
How Healthcare Staff Can Become Cybersecurity Champions
Cultivate a Culture of Cybersecurity Awareness
Healthcare organizations must prioritize cybersecurity awareness among staff. Leadership commitment plays a vital role in this process. The appointment of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or equivalent can spearhead security initiatives. This leader should collaborate with department heads to integrate security practices into daily operations.
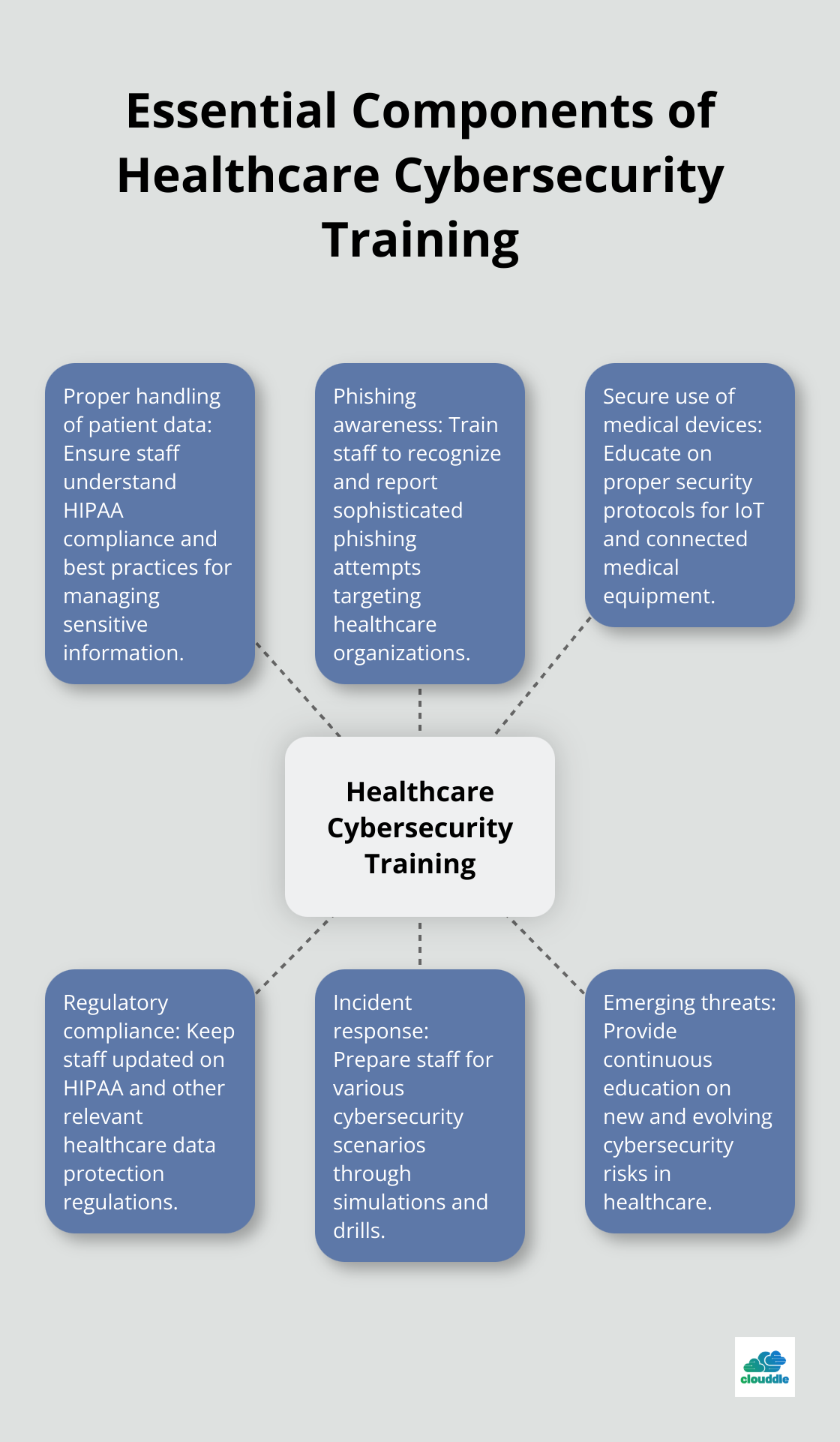
A tailored security awareness program should address specific risks faced by healthcare staff. Key topics to cover include:
- Proper handling of patient data
- Recognition and reporting of phishing attempts
- Secure use of medical devices and IoT equipment
- Compliance with HIPAA and other relevant regulations
To make training engaging, use real-world examples from the healthcare sector. The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack on the UK’s National Health Service (which caused an estimated £92 million in damages and disrupted 19,000 appointments) serves as a powerful illustration of the impact of security breaches.
Implement Hands-on Learning Through Simulated Attacks
Theory alone doesn’t suffice. Healthcare organizations should conduct regular simulated phishing exercises to test staff vigilance. These exercises reveal vulnerabilities in human behavior and provide opportunities for targeted training.
In 2023, 725 data breaches were reported to OCR, with more than 133 million records exposed or impermissibly disclosed. Regular simulated phishing campaigns can dramatically reduce this risk. Organizations should start with simple scenarios and gradually increase complexity to challenge staff and improve their ability to spot sophisticated attacks.
Cybersecurity drills should extend beyond phishing. Tabletop exercises that simulate various scenarios (such as ransomware attacks or data breaches) help staff understand their roles during a crisis and improve overall incident response capabilities.
Stay Ahead of Emerging Threats
The cybersecurity landscape evolves constantly, especially in healthcare. Continuous education keeps staff informed about new threats and preventive measures.
Organizations should implement a system for regular updates on emerging threats, which could include:
- Monthly security newsletters highlighting recent healthcare-specific cyber incidents
- Quarterly lunch-and-learn sessions featuring expert speakers on cybersecurity topics
- An internal knowledge base with up-to-date security guidelines and best practices
Staff should obtain relevant cybersecurity certifications. The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Healthcare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISPP) certifications provide valuable knowledge and credibility to security teams.
Partnerships with cybersecurity firms or academic institutions offer access to cutting-edge research and training resources. These collaborations provide valuable insights into emerging threats and innovative defense strategies.
Measure and Improve Training Effectiveness
To ensure the effectiveness of cybersecurity training, healthcare organizations should establish metrics and regularly assess staff performance. This approach allows for continuous improvement of training programs.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) to track include:
- Phishing simulation click rates
- Time to report suspicious activities
- Compliance with security policies
- Scores on cybersecurity knowledge tests
Regular feedback from staff about the training programs helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that the content remains relevant and engaging.
Final Thoughts
Network security in healthcare demands a multifaceted approach to address unique challenges. Healthcare organizations must implement strong access controls, conduct regular security assessments, and leverage advanced threat detection technologies. Staff training plays a vital role in creating a cybersecurity-aware culture, with simulated exercises and continuous education helping to stay ahead of emerging threats.
The future of healthcare network security will likely involve artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance threat detection and automate responses. Telehealth and remote patient monitoring will require even more robust security measures to protect data across distributed networks. Healthcare providers must balance stringent security protocols with operational efficiency to maintain quality patient care.
We at Clouddle offer a Network as a Service (NaaS) solution that combines networking, entertainment, and security services. Our managed IT and security services allow healthcare providers to focus on patient care while we protect their networks against cyber threats. Healthcare organizations can safeguard sensitive patient data, maintain regulatory compliance, and ensure continuity of critical services in an increasingly connected world.


