To really get Zero Trust right, you have to completely rethink your approach to security. It’s a move away from trusting people and devices just because they’re inside your network. The core mantra is simple: never trust, always verify. Every single access request gets scrutinized, no matter where it's coming from.
This means putting strong identity checks in place, making sure devices are healthy and compliant before they connect, and giving people the absolute minimum level of access they need to do their jobs.
Why Zero Trust Security Is a Must-Have Now
Remember the old "castle-and-moat" security model? The one where everything inside the network walls was considered safe? That's ancient history now. Your perimeter has vanished.
Think about it. A property manager is accessing sensitive resident data from a coffee shop on their personal phone. A senior living facility’s network is connected to dozens of third-party health monitoring devices. These everyday scenarios create a massive, undefended attack surface.
Simply assuming everything inside your network is safe is an open invitation for a breach. One stolen password or an insecure guest Wi-Fi network is all an attacker needs to get in, move around freely, and launch a devastating ransomware attack.
The Modern Threat Landscape Demands a New Playbook
The way we work has changed for good. Businesses in hospitality, multi-family, and commercial real estate depend on cloud apps and a mobile workforce. The old security models just weren't built for this reality. Zero Trust tackles these modern challenges head-on with that powerful principle: trust nothing, verify everything, every time.
This isn’t just a tech upgrade; it's a smart business strategy that pays off in real-world ways:
- Serious Ransomware Defense: By stopping attackers from moving laterally, Zero Trust can contain a breach to a tiny, isolated corner of your network. A minor incident stays minor instead of escalating into a full-blown crisis.
- Reduced Insider Threat Risk: Whether it's a careless employee or a malicious actor, the risk is real. Zero Trust neutralizes this by ensuring users can only access the data and apps they absolutely need—and nothing more.
- Secure Remote and Hybrid Work: Let your employees, contractors, and partners work securely from anywhere, on any device. Best of all, you can do it without relying on clunky, vulnerable VPNs.
- A Stronger Compliance Posture: Meeting strict standards like HIPAA or PCI DSS is much easier when you have the granular controls and detailed logs that a Zero Trust architecture provides.
To really see the difference, let's compare the old way of thinking with the new.
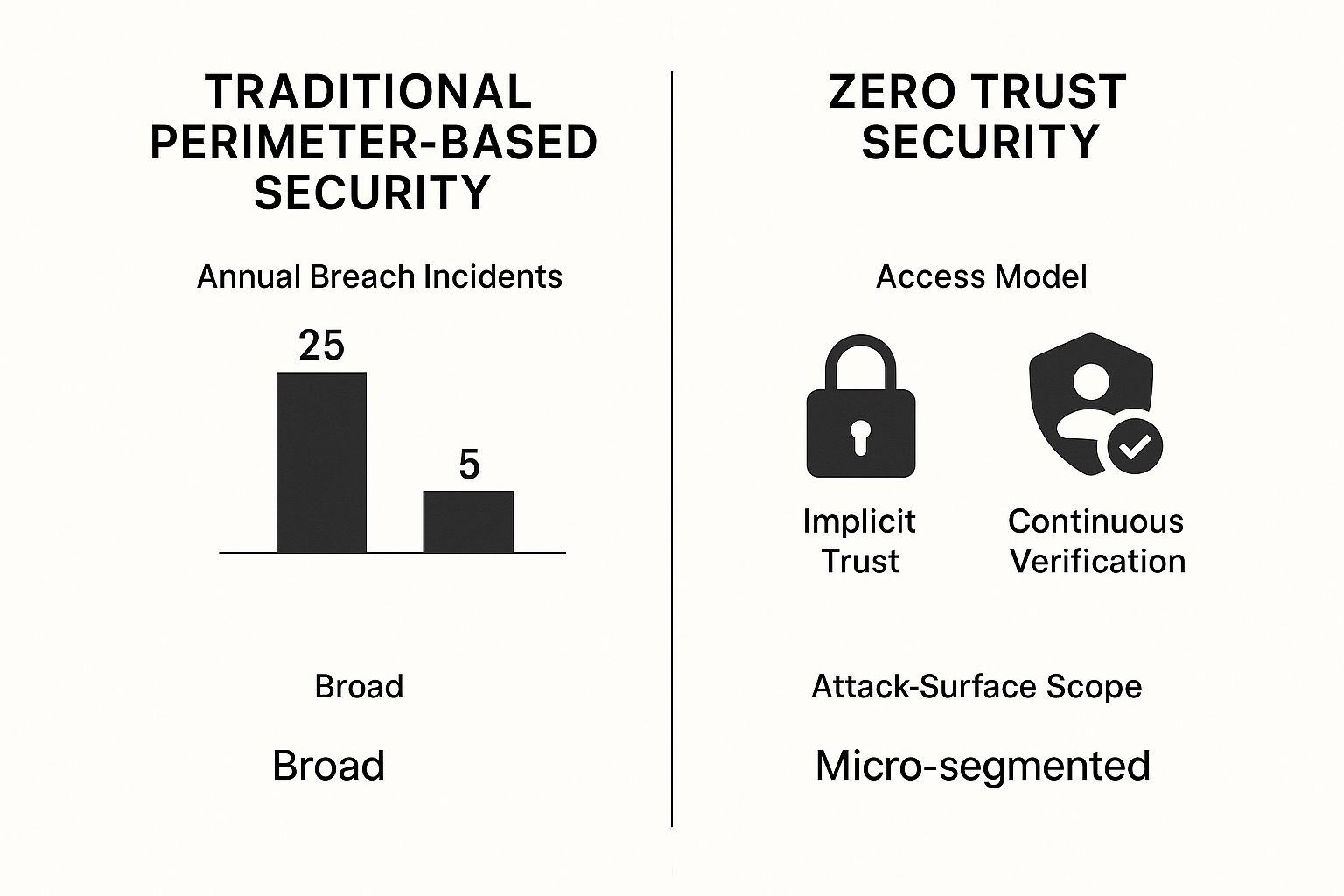
Traditional Security vs Zero Trust At a Glance
The table below breaks down the fundamental shift in mindset between the outdated "castle-and-moat" model and the modern Zero Trust approach. It’s a night-and-day difference.
| Security Principle | Traditional Model (Castle-and-Moat) | Zero Trust Model (Verify Everything) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Securing the network perimeter. | Securing individual resources and data. |
| Trust Assumption | Implicit trust for anyone/anything inside the network. | No implicit trust; everything must be verified. |
| Access Control | Broad network access once authenticated. | Least-privilege access on a per-session basis. |
| Verification Method | One-time check at the perimeter. | Continuous verification of user and device. |
| Security Perimeter | Static and well-defined network boundary. | Dynamic and defined by identity. |
| Vulnerability | High risk of lateral movement after a breach. | Breaches are contained and lateral movement is limited. |
As you can see, Zero Trust is built for the complexity and threats of today's environments, while the traditional model leaves you dangerously exposed.
Your Roadmap: The Zero Trust Maturity Model
Let's be clear: implementing Zero Trust doesn't happen overnight. It’s a journey, not a destination. The good news is there’s a map for it. The Zero Trust Maturity Model, developed by CISA, breaks the process into logical, manageable stages across several key pillars.
The goal here is continuous improvement. You don't need a perfect, fully automated system from day one. It's all about making steady, meaningful progress that constantly shrinks your risk.
This model helps you figure out where you are today and what your next steps should be, guiding you from basic controls toward a more advanced, dynamic security posture.
The framework gives you a practical path forward, helping you mature your capabilities across areas like Identity, Devices, and Networks until you have a security architecture that can adapt to whatever comes next.
And the industry is moving fast. By the end of 2025, Gartner predicts around 60% of organizations will embrace Zero Trust as their primary security strategy. In fact, the move is already well underway—81% of companies are either implementing or planning a Zero Trust model right now. Those who have started are reporting 50% faster threat detection and a huge drop in security incidents. You can dig into more of this data over at zerothreat.ai.
Start With Identity and Access Management

Your journey into Zero Trust really begins with one simple question: who is trying to connect? Before you can grant anyone access to anything, you have to be rock-solid certain about their identity. This is the absolute cornerstone of the "never trust, always verify" mindset.
This is where Identity and Access Management (IAM) comes into play. It’s how you move from theory to practice, leaving behind the days of relying on a simple password. We're talking about establishing a strong, verifiable identity for every single person, from the CEO down to a temporary contractor.
Mandate Multi-Factor Authentication Everywhere
If you do one thing, do this: make Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) mandatory for everyone. No exceptions. A password by itself just doesn't cut it anymore; it's a weak link just waiting to be exploited.
MFA adds essential layers of security, forcing users to prove who they are in more than one way. The good news is that modern options are incredibly user-friendly and secure.
- Authenticator Apps: Tools like Microsoft Authenticator or Google Authenticator generate time-sensitive codes on a user's phone. Simple and effective.
- Biometrics: Using fingerprints or facial recognition (think Windows Hello or Face ID) offers a near-frictionless and highly secure way to log in.
- Physical Security Keys: FIDO2 hardware keys, like a YubiKey, are the gold standard. They provide phishing-resistant authentication because a physical device has to be present.
The whole point is to make it extraordinarily difficult for an attacker to get in, even if they've stolen a password. A core tenet of Zero Trust involves protecting personal credentials, authentication, and access control.
Simplify and Centralize with Single Sign-On
Forcing MFA across dozens of different applications can become a real headache for your users and your IT team. That’s why a Single Sign-On (SSO) solution is a must-have.
An SSO provider, like Microsoft Entra ID or Okta, acts as your central identity gatekeeper. Users log in just once to the SSO portal—using their strong MFA, of course—and from there, they can get into all their authorized apps without being nagged for more passwords.
From the Field: SSO isn't just a convenience. It's a massive security win. It gives you a single pane of glass to enforce MFA policies, monitor who is accessing what, and—critically—instantly shut down all access for a departing employee from one dashboard.
This centralized control is a game-changer for managing identities at scale and is a non-negotiable part of implementing Zero Trust correctly.
Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege
Once you’ve confirmed who a user is, the next logical question is what do they actually need to do their job? This is the Principle of Least Privilege in action: give people access only to the absolute minimum they need. Nothing more.
This means you have to sit down and define clear roles and permissions. Let’s look at a real-world example from a multi-family property management company:
- Leasing Agent: They need access to the CRM and the leasing platform. They should have no reason to be in the company's accounting software or the building maintenance systems.
- Maintenance Tech: They get access to the work order system on their tablet. That's it. They have zero business seeing resident financial data or leasing contracts.
- HVAC Contractor: This third-party vendor gets temporary, highly-restricted access to the building management system, but only for the specific property they're working on and only for the length of their contract.
By carving up access this way, you dramatically reduce your attack surface. If a leasing agent's account gets compromised, the damage is contained. The attacker can't pivot to your most critical financial or operational data.
Getting these granular controls right can be tricky, which is why many businesses look for help when https://clouddle.com/blog/how-to-choose-managed-it-security-services/. By building on a strong IAM foundation, you're putting the most important pillar of your Zero Trust architecture in place.
Verify Every Endpoint and Device

So you've figured out who is trying to connect. The next critical question is, what are they connecting from? It's a common mistake to stop at user verification. A legitimate employee logging in from a personally-owned, malware-ridden laptop is a security nightmare waiting to happen.
Every single endpoint is a potential doorway for an attacker. We're talking about corporate-issued laptops, a property manager's smartphone, a front desk tablet, you name it. The core principle of "never trust, always verify" applies just as much to hardware as it does to people. This means you need a system that constantly checks the health and compliance of every device before it gets anywhere near your network.
Establishing a Device Health Baseline
Before you can enforce device security, you have to define what a "healthy" device actually looks like for your business. This isn't some generic checklist; it's a set of non-negotiable security standards every single device must meet to get access. Think of it as a digital health certificate.
Your baseline should cover a few key areas:
- Up-to-Date Operating System: Mandate that all devices are running the latest patched version of their OS, whether that's Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android. Out-of-date systems are a welcome mat for attackers.
- Active Endpoint Protection: Every device needs approved antivirus and anti-malware software running and updated. This is your frontline defense.
- Disk Encryption: Enforce full-disk encryption like BitLocker for Windows or FileVault for Mac. If a device is lost or stolen, this makes the data inside it unreadable.
- A Secure Configuration: This means the device firewall must be enabled and strong passwords or PINs are required to unlock it.
This baseline becomes your rulebook. Any device that doesn't meet these criteria is considered unhealthy and gets blocked from corporate resources until it's brought up to standard.
Here’s a real-world example: Imagine a senior living community where caregivers use company tablets to access resident health records. If a caregiver's tablet has an outdated operating system or the security software has been turned off, it poses a direct risk to sensitive patient data. A proper Zero Trust policy would automatically block that tablet's access until the issues are fixed, protecting resident privacy.
Automating Enforcement with Endpoint Management
Let's be realistic: you can't manually check the health of every single device. It's just not possible. This is where modern device management tools become absolutely essential for any business serious about Zero Trust.
Platforms like Mobile Device Management (MDM) or the more comprehensive Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) systems are built to automate this entire process. These tools let you define your device health policies in one place and then enforce them across every enrolled device—whether it's company-owned or a personal device used for work (BYOD).
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Enrollment: All devices needing access to company data are enrolled in the UEM system.
- Policy Enforcement: The UEM automatically configures the device to meet your security baseline—turning on encryption, installing security software, and pushing OS updates.
- Continuous Monitoring: The system is always checking the device's health status in the background. Is the antivirus running? Is the OS patched? Has it been jailbroken?
- Automated Quarantine: If a device falls out of compliance, its access is automatically cut off. The system then notifies the user about the problem and gives them clear steps to fix it, which saves everyone a call to the help desk.
This kind of automation is the engine that makes device verification work in a Zero Trust model. It gives you the continuous, real-time validation you need to ensure that only healthy and trusted endpoints can connect to your valuable data.
Shrink Your Attack Surface With Microsegmentation

Alright, you've started verifying identities and devices. Now it's time to tackle the network itself. For far too long, the standard security playbook was all about building a strong perimeter—a hard outer shell with a soft, gooey center. This "trusted" internal network is where most security models fall apart.
Once an attacker breaches that outer wall, they’re in. They can move around freely, mapping out your systems, finding sensitive data, and deploying ransomware. This is precisely the threat that microsegmentation is designed to stop. It's the practice of carving up your big, flat network into many smaller, isolated zones.
The whole point is to halt an intruder's lateral movement. If one tiny piece of your network is compromised, the breach is contained right there. It can't spread like wildfire through your entire organization.
From Open-Plan Office to Secure Vaults
Think of your old network like a massive open-plan office. Once someone gets past the front door, they can walk right up to any desk they want—HR, finance, the CEO's office. It’s a recipe for disaster.
Microsegmentation changes the game completely. It's more like a secure facility where every single room requires a specific keycard. Your badge only opens the doors you absolutely need to do your job, and nothing more. This is a huge mental shift, but it’s foundational to zero trust.
This goes a big step beyond basic network segmentation. While the core ideas are similar (and you can get a great primer in our guide on how to implement network segmentation for security), microsegmentation gets much more granular. Instead of just walling off departments, you're isolating individual applications and even specific workloads.
A Real-World Example: Securing a Hotel
Let's see how this works in a hotel environment, where a single incident can quickly become a nightmare.
Scenario: An attacker gets a foothold on the guest Wi-Fi network—often the weakest link in the chain. In a typical flat network, they could easily pivot from there to the front desk systems, scrape guest credit card data, and then jump over to the back-office network to access financial records.
Now, let's replay that scenario with microsegmentation in place:
- Segment 1: The Guest Network: This is completely walled off from everything else. It provides internet access, and that's it. Full stop.
- Segment 2: Front Desk Operations: The property management system, payment terminals, and keycard encoders all live in their own secure bubble. Only authorized front desk staff on company-owned devices can get in.
- Segment 3: Back-Office Systems: Accounting software, payroll, and HR platforms are in another isolated segment, accessible only by the finance and management teams.
- Segment 4: Building Management: Critical systems like HVAC and security cameras are on their own network to prevent anyone from tampering with physical operations.
With this structure, if the guest Wi-Fi is compromised, the attacker hits a dead end. They are trapped. They can't see or even attempt to access the hotel's critical systems because, from their vantage point, those resources don't exist. You've essentially built digital bulkheads that contain any potential damage.
Policies That Bring It All Together
Creating the segments is one thing; enforcing the rules is where the magic happens. The real power comes from the access policies you write to control traffic between these zones. This is where you bring the principle of least privilege to life at the network level.
Your access rules should be based on the "5 Ws" of any connection attempt:
- Who is the user? (e.g., a front desk manager)
- What application do they want? (e.g., the reservation system)
- When are they trying to access it? (e.g., during their shift)
- Where is the request coming from? (e.g., a known terminal at the front desk)
- Why do they need access? (e.g., to check in a guest—a defined business function)
By getting this granular with your policies, you ensure that people and applications can only connect to the specific resources they need to function, and absolutely nothing else.
This is an area where many organizations still have a long way to go. Recent data shows that only 56% of companies grant access based on role, and just 33% enforce the kind of granular controls that a true Zero Trust framework demands.
Microsegmentation isn't about building a bigger wall. It's a fundamental architectural shift that assumes a breach can and will happen. By preparing for it, you ensure that when an incident does occur, its impact is minimal, contained, and entirely manageable.
Keep an Eye on Everything, and Automate Your Defenses
Putting a Zero Trust framework in place isn't a "set it and forget it" project. It’s a living security strategy, one that needs constant care and feeding. The final, and arguably most important, piece of the puzzle is building a system that continuously watches what's happening and can react to threats the moment they appear. This is where you graduate from static rules to a dynamic, responsive security posture.
Think of it as the central nervous system for your security. You need to pull in signals from every corner of your IT environment—your users, their devices, the applications they use, and the networks they connect through. All this data, or telemetry, is what gives you the visibility to catch weird behavior before it turns into a full-blown crisis.
First, You Need to See What's Happening
You can't protect what you can't see. Simple as that. The starting point is to pull all the logs and data from your various security tools into one central place. This gives you a single screen to understand your current security situation and, more importantly, spot any blind spots.
To do this right, you need to be pulling data from a few key places:
- Identity Systems: Keep tabs on login attempts, multi-factor authentication challenges, and permission changes from systems like Microsoft Entra ID or Okta.
- Endpoint Management: You need device health status, compliance reports, and any alerts coming from your UEM or MDM solutions. Is a device suddenly out of compliance? You need to know.
- Network Gear: Analyzing traffic patterns from firewalls and switches can reveal a lot. Is a device suddenly trying to talk to a server it's never touched before? That's a red flag.
- Application Logs: Watch for unusual activity inside your most important business applications.
When you correlate all this information, you can build a complete story for every single access request. For a much deeper look at this, our guide on how to analyze network traffic for enhanced security is a great resource. This kind of analysis helps you answer critical questions on the fly: Is this user logging in from a strange new location? Did their laptop just fail a health check? Why is this app trying to connect to a file share it has no business touching?
Let Automation Do the Heavy Lifting
Spotting a problem is one thing, but reacting instantly is what really matters. Relying on a human to see an alert and then take action is just too slow to keep up with today's automated attacks. This is where Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools become your best friend. They take your security rules and turn them into automatic, real-time actions.
From the Field: Automation is the engine that makes Zero Trust truly work. It closes that critical gap between detecting a threat and stopping it, often shrinking response times from hours down to seconds.
Let’s look at a few real-world examples in a multi-family property management company:
- Impossible Travel: A property manager's account shows simultaneous login attempts from Dallas and Dubai. The system automatically recognizes this is impossible, immediately suspends the account to be safe, and shoots an alert to the IT team to investigate.
- Unhealthy Device: A maintenance tech’s tablet was perfectly compliant an hour ago, but now it's failing a health check because its antivirus was turned off. The system instantly cuts off its access to the work order system until the tablet is fixed and secure again.
- Policy Violation: An accountant tries to log into the company's financial software from their personal, unmanaged laptop. Access is immediately blocked, an alert is logged, and the user gets a pop-up explaining why they can't connect from that device.
This kind of automation ensures your security rules are enforced consistently, 24/7, without you needing to have someone watching the screens around the clock.
Tweak and Refine Over Time
Your Zero Trust setup won't be perfect on day one. Nobody's is. It's a system that needs ongoing refinement. You have to schedule regular security audits and policy reviews to make sure your framework is still doing its job as your business changes and new threats pop up.
Set a recurring calendar reminder to sit down and ask some tough questions:
- Are our access policies still truly based on "least privilege," or have permissions started to creep up?
- Do we need to update our device health requirements to account for new software or vulnerabilities?
- Have we added new cloud apps or services that aren't properly integrated into our Zero Trust rules yet?
- Are our automated response plans actually working the way we designed them?
This constant feedback loop is what helps your Zero Trust strategy mature. It allows you to adapt to new challenges and maintain a tough, resilient defense for your properties, residents, and staff.
Common Questions About Implementing Zero Trust
Making the switch to a Zero Trust model is a big move, and it’s completely normal to have questions about the nitty-gritty details. When I talk to folks in hospitality or commercial real estate, they're not just worried about the technology; they're thinking about the time, the cost, and the potential disruption.
Let’s get into some of the real-world questions that come up time and time again.
A frequent concern I hear is, "Is Zero Trust too complicated for my business?" A property manager with five buildings or a boutique hotel doesn't have the IT army of a global enterprise. But here’s the thing: Zero Trust isn't an all-or-nothing game. It’s a philosophy that scales.
You don't have to tackle everything at once. The best approach is to start small and focus on what gives you the biggest security boost right away. Think about mandating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and rolling out a Single Sign-On (SSO) system. Just doing those two things will lock down your environment significantly and build a solid foundation for everything else.
How Long Does a Zero Trust Rollout Take?
Everyone wants a simple answer here, but the honest one is: it depends. The timeline is really shaped by the size of your business and the complexity of your current tech setup. It's much healthier to see it as a journey with distinct phases rather than a single, monolithic project.
For most businesses we work with in hospitality, multi-family, or commercial spaces, a practical, phased rollout looks something like this:
- Phase 1 (Months 1-3): Go all-in on identity. This is where you deploy MFA for every single user and get a solid SSO platform in place. It’s the lowest-hanging fruit and delivers the most immediate impact.
- Phase 2 (Months 4-9): Now, shift your focus to devices. Get every laptop, tablet, and smartphone enrolled into a management system. You can then start enforcing basic device health rules, like making sure the operating system is updated and antivirus is running.
- Phase 3 (Months 10+): This is where you start chipping away at network microsegmentation. You don't have to segment everything on day one. Start with your most critical assets—for example, completely isolating the network that handles payment processing from the public guest Wi-Fi. This part is an ongoing effort of continuous improvement.
This method gives you tangible security wins at each stage without overwhelming your team or bringing daily operations to a standstill.
What Are the Biggest Hurdles to Expect?
Going into a Zero Trust project with your eyes open is the best way to ensure it succeeds. While every organization has its unique quirks, a couple of challenges pop up pretty consistently.
The first big one is almost always legacy applications. That old property management software or accounting system running on a server in the back office probably wasn't built with modern security in mind. Integrating it with SSO and MFA can be tricky. You’ll need a concrete plan: can you modernize it, replace it, or find a secure workaround that doesn't punch a hole in your new security model?
The other major hurdle isn't technical at all—it's people. Getting buy-in from your employees is non-negotiable. If they see the new security protocols as just another hoop to jump through, they’ll find clever ways to bypass them.
This is where clear communication becomes your most powerful tool. You have to explain the why. This isn't about making their lives harder; it's about protecting the business, your guests or tenants, and their own personal information. When you treat your team like partners in the process, adoption goes from being a battle to a shared goal. The whole point is to make everyone safer without grinding productivity to a halt.
Navigating the complexities of Zero Trust requires a partner with deep expertise in security and a keen understanding of your industry's unique challenges. At Clouddle Inc, we specialize in designing and implementing robust, scalable Zero Trust architectures for businesses just like yours. Discover how our managed technology solutions can protect your assets and streamline your operations.


