Corporate network security is more critical than ever in today’s digital landscape. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, businesses must stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities.
At Clouddle, we understand the challenges organizations face in protecting their digital assets. This guide will explore practical strategies to enhance your corporate network security, from implementing robust access controls to strengthening your network infrastructure.
How to Strengthen Access Controls
Corporate network security hinges on robust access controls. Let’s explore practical strategies to fortify your defenses.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
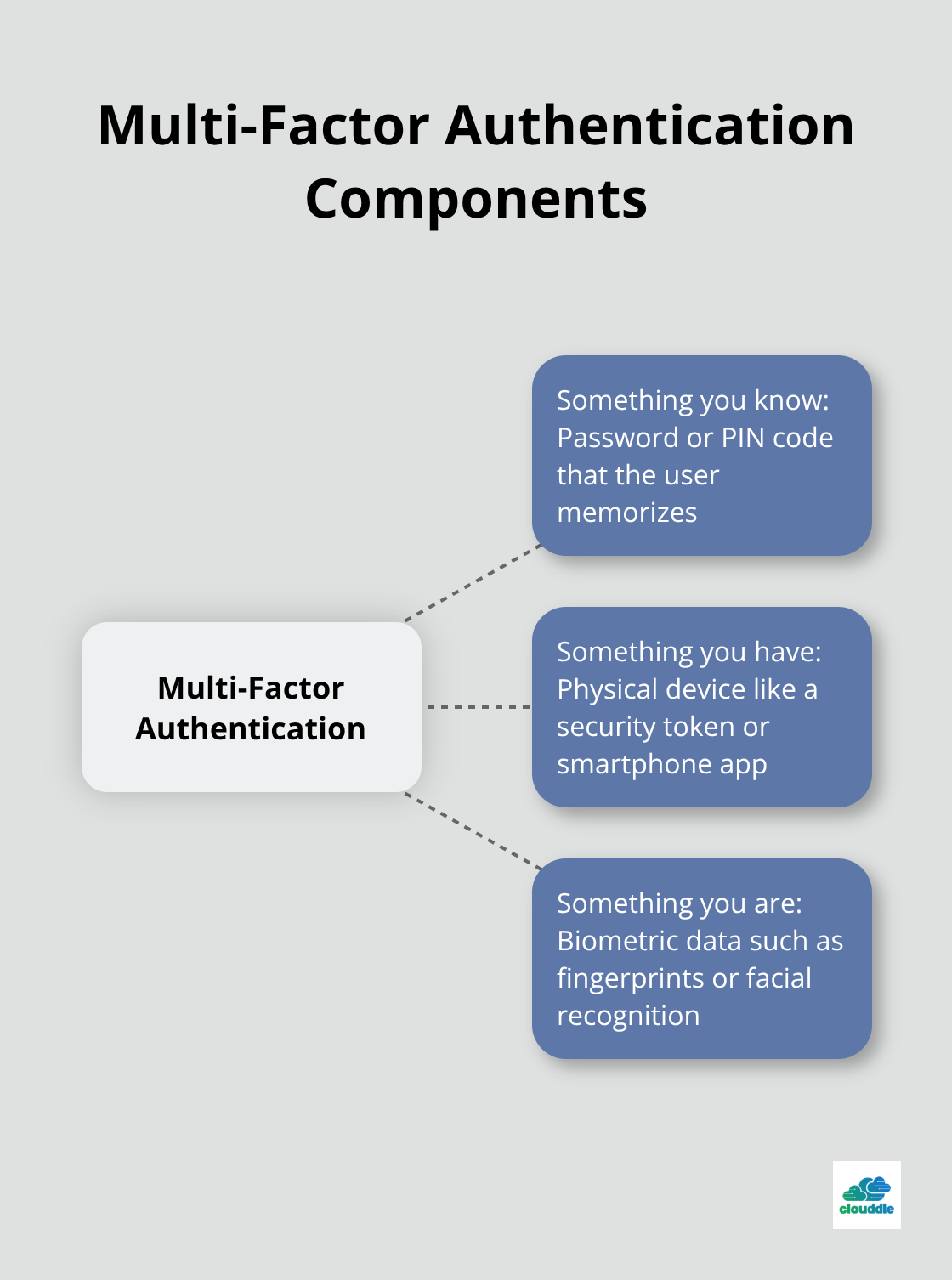
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a non-negotiable security measure. Apply MFA across all user accounts, particularly for remote access. Combine something the user knows (password), has (security token), and is (biometric data) for maximum protection.
Apply Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) limits user access to the bare essentials required for their job functions. Map out your organization’s roles and the resources each role needs. Then, configure your systems to enforce these access levels strictly. This approach enhances security and simplifies management simultaneously.
Review User Privileges Regularly
User privileges require constant attention. Set up a system to review and update user privileges at least quarterly. Look for:
- Accounts with unnecessary privileges
- Dormant accounts
- Any anomalies in access patterns
Tools like Microsoft’s Azure AD Privileged Identity Management can automate this process, making it more efficient and less prone to human error.
Enforce Strong Password Policies
While MFA is crucial, strong passwords remain the first line of defense. Implement policies that require:
- Minimum length (at least 12 characters)
- Complexity (mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols)
- Regular password changes (every 60-90 days)
Consider using password managers to help users create and store complex, unique passwords for each account.
Monitor and Log Access Attempts
Implement systems to monitor and log all access attempts (both successful and failed). This practice allows you to:
- Detect unusual patterns
- Identify potential security breaches
- Conduct thorough post-incident analyses
Regular review of these logs can reveal vulnerabilities and attempted attacks before they escalate into major security incidents.
Strong access controls form the foundation of network security, but they’re just the beginning. The next section will explore how to strengthen your network infrastructure, creating multiple layers of defense against evolving cyber threats.
How to Fortify Your Network Infrastructure
Network infrastructure forms the backbone of corporate security. This chapter explores advanced strategies to strengthen your defenses against evolving cyber threats.
Deploy Advanced Firewalls
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) offer superior protection compared to traditional firewalls. They provide deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and application-level filtering. NGFWs often include features like sandboxing, malware analysis, and URL filtering to protect against sophisticated threats.
Key features to look for in an NGFW include:
- Threat intelligence integration
- Automated policy optimization
- Cloud-based management for easier updates and monitoring
Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation contains potential breaches and reduces the attack surface.
To implement effective segmentation:
- Categorize assets based on sensitivity and function
- Create separate network segments for critical systems (e.g., customer data, financial systems)
- Use virtual LANs (VLANs) and internal firewalls to enforce strict access controls between segments
Secure Remote Access
The rise of remote work necessitates robust external access security. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) remain a standard solution, but they must offer:
- Split-tunneling capabilities for optimized performance
- Multi-factor authentication integration
- Automatic kill switches to prevent data leaks
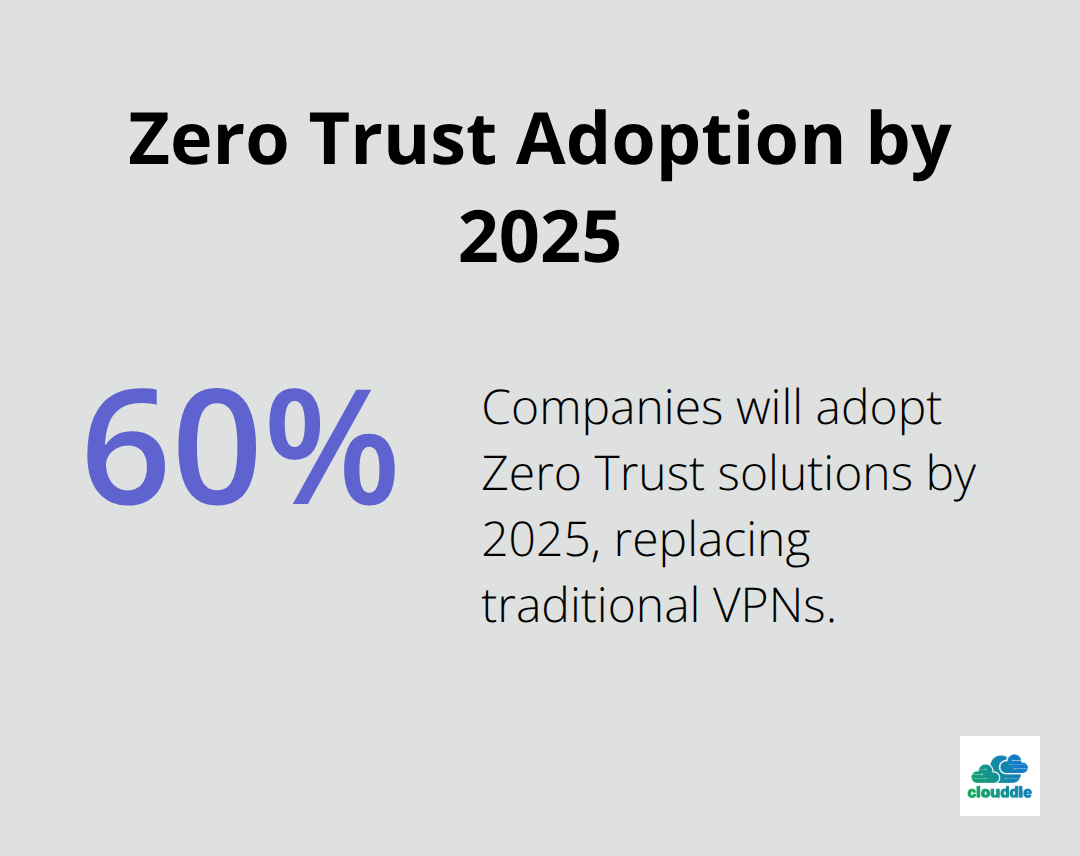
Consider implementing a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) model, which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
Leverage Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Software-Defined Networking revolutionizes network infrastructure management. It separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing for more flexible and dynamic network configurations. Benefits of SDN include:
- Rapid response to security threats
- Automated policy enforcement
- Improved visibility into network traffic
Implement Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of your network infrastructure allows for real-time threat detection and response. Try to implement:
- Network traffic analysis tools
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS)
- Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions
These tools provide valuable insights into network behavior and potential security incidents.
A robust network infrastructure forms a solid foundation for corporate security. However, even the strongest defenses can be compromised without proper monitoring and incident response protocols. The next chapter will explore how to implement effective monitoring systems and develop comprehensive incident response plans to further enhance your organization’s security posture.
How to Monitor and Respond to Threats
Effective network security requires vigilance and rapid response. This chapter explores strategies for continuous monitoring and incident response to enhance your organization’s security posture.
Implement a Robust SIEM Solution
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems provide continuous, real-time monitoring of security events, allowing for immediate detection of potential threats and rapid response. When selecting a SIEM, consider these features:
- Machine learning capabilities for anomaly detection
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds
- Customizable dashboards and reporting features
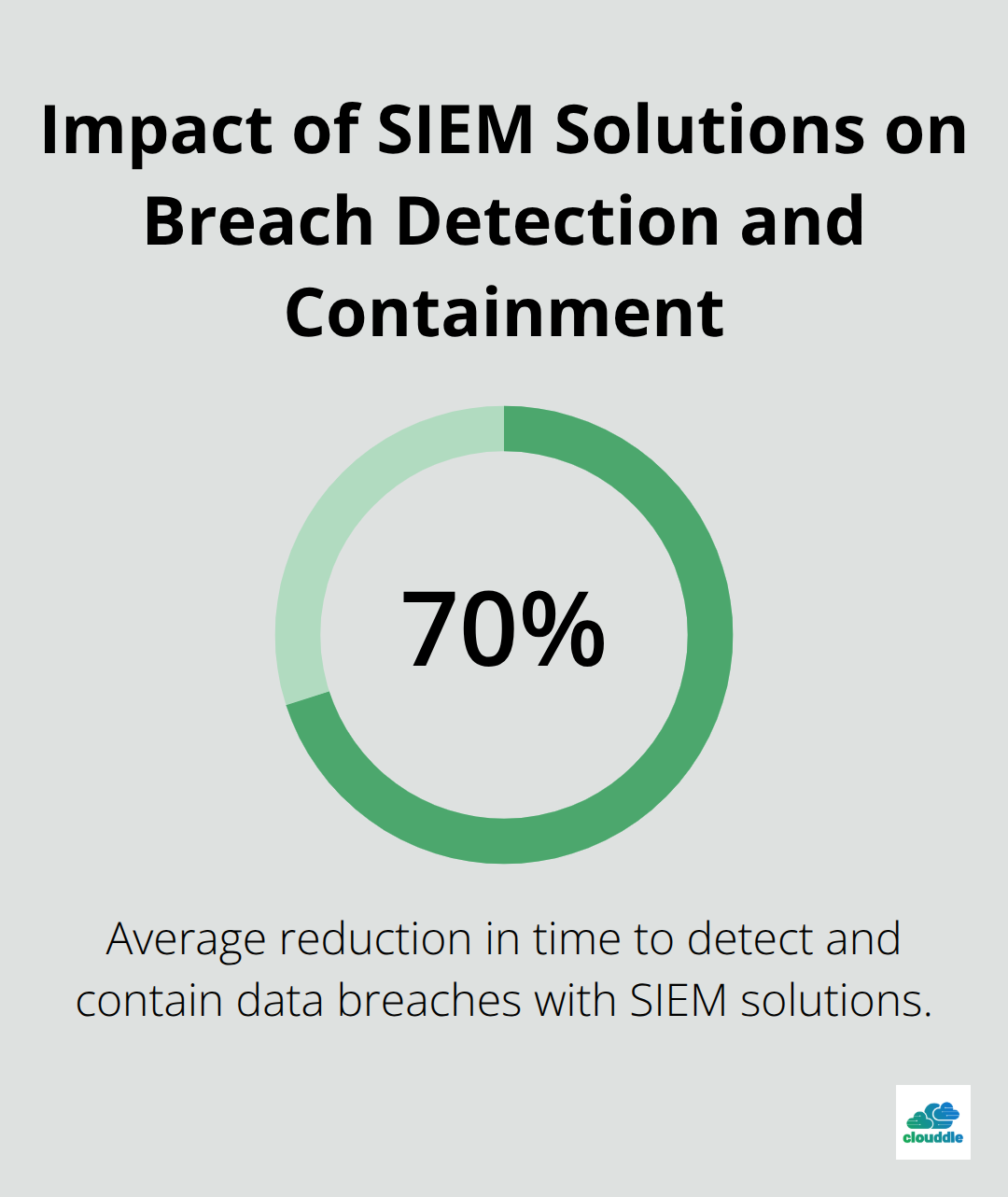
A study by Ponemon Institute revealed that organizations using SIEM solutions reduced the time to detect and contain a data breach by an average of 70%.
Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Penetration testing, often known as ethical hacking, is a proactive and legal means of detecting computer system, network, or application faults. Try to conduct these assessments at least quarterly (or more frequently for high-risk industries).
While automated vulnerability scanners provide a good baseline, don’t rely on them exclusively. Human-led penetration testing uncovers complex vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss. A report by Synack found that human testers discovered 70% more vulnerabilities compared to scanners alone.
Create a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan serves as your playbook for when things go wrong. It should outline:
- Roles and responsibilities of the incident response team
- Step-by-step procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery
- Communication protocols for stakeholders (and, if necessary, the public)
Test your plan regularly through tabletop exercises and full-scale simulations. The SANS Institute recommends conducting these tests at least annually.
Leverage Threat Intelligence
Incorporate threat intelligence into your security strategy to stay ahead of emerging threats. This proactive approach allows you to:
- Identify potential vulnerabilities specific to your industry
- Understand attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs)
- Prioritize security efforts based on real-world threat data
Many organizations (including Clouddle) offer threat intelligence services that can integrate seamlessly with your existing security infrastructure.
Implement Automated Response Capabilities
Automation plays a key role in modern incident response. Consider implementing security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools to:
- Streamline incident triage and investigation
- Automate repetitive tasks (e.g., log analysis, threat hunting)
- Accelerate response times to potential threats
A study by Ponemon Institute found that organizations using security automation experienced an average cost savings of $3.58 million compared to those without automation.
Final Thoughts
Corporate network security demands a comprehensive approach. Organizations must implement robust access controls, strengthen network infrastructure, and establish effective monitoring protocols. These strategies create a strong defense against evolving cyber threats and minimize potential damage from breaches.
Continuous adaptation and vigilance are essential in the ever-changing landscape of digital security. Regular updates, security assessments, and employee education foster a culture of awareness across the organization. This proactive stance helps businesses stay ahead of emerging threats and maintain resilience in the face of potential attacks.
We at Clouddle offer managed IT and security services to help businesses navigate these complex challenges. Our expertise allows you to focus on your core operations while we work to keep your network secure (and resilient against threats). Don’t hesitate to seek expert assistance for your organization’s security needs.


