Network breaches cost companies an average of $4.45 million in 2023, making robust security measures non-negotiable for modern businesses.
At Clouddle, we see organizations struggle daily with complex security challenges that threaten their operations. The key to success lies in knowing how to implement network security through systematic planning and proven strategies.
This guide walks you through essential security measures that protect your infrastructure from evolving cyber threats.
Understanding Network Security Fundamentals
Network Threats That Target Your Business Daily
Ransomware-related claims rose 77 percent in the first quarter of 2023 in the U.S., with small to medium businesses facing the highest risk due to weaker security postures. Advanced persistent threats pose the greatest danger as they remain undetected for an average of 277 days within networks. Distributed denial of service attacks cost companies $40,000 per hour in downtime, while insider threats account for 34% of all data breaches. Phishing attacks succeed 36% of the time when they target employees without security training, which makes human vulnerabilities as critical as technical ones.
Security Frameworks That Deliver Results
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides the most practical approach for organizations that implement network security, with 70% of companies reporting improved incident response times after adoption. ISO 27001 certification reduces security incidents by 45% on average, while SOC 2 compliance becomes mandatory for any business that handles customer data. Companies that follow Zero Trust Architecture see 50% fewer successful breaches compared to traditional perimeter-based security models. Multi-factor authentication alone prevents 99.9% of automated attacks.

Risk Assessment Methods That Predict Real Threats
Vulnerability scans should occur weekly rather than quarterly, as 60% of breaches exploit vulnerabilities known for over a year. Asset inventory management prevents 80% of security gaps, while network segmentation limits breach impact to single network zones in 90% of cases. Penetration tests every six months identify critical vulnerabilities that automated tools miss 30% of the time. Risk scores based on asset criticality and threat probability allow security teams to prioritize the 20% of vulnerabilities that pose 80% of actual risk to business operations.
These foundational elements create the groundwork for implementing specific security measures that protect your network infrastructure from both external attacks and internal vulnerabilities.
Implementing Core Network Security Measures
Firewall Configuration That Blocks Real Threats
Default-deny rules form the foundation of proper firewall setup by blocking all traffic except explicitly permitted connections. Stateful firewalls monitor and maintain the context of active connections to determine which packets to allow through, while next-generation firewalls with deep packet inspection catch more threats than traditional models. Configure firewall rules based on business requirements rather than convenience, as overly permissive rules create the entry points attackers exploit most often. Update firewall firmware monthly and review rule sets quarterly to remove outdated permissions that accumulate over time.
Access Control Systems That Prevent Breaches
Role-based access control prevents insider threats through strict limitation of user permissions to job-specific requirements. Privileged access management systems reduce breach impact when attackers compromise standard user accounts. Single sign-on solutions decrease password-related security incidents while boosting user productivity. Network access control systems verify device compliance before network access and prevent malware infections from personal devices. Time-based access restrictions limit after-hours network access, which reduces weekend breach attempts.
Authentication Methods That Stop Unauthorized Access
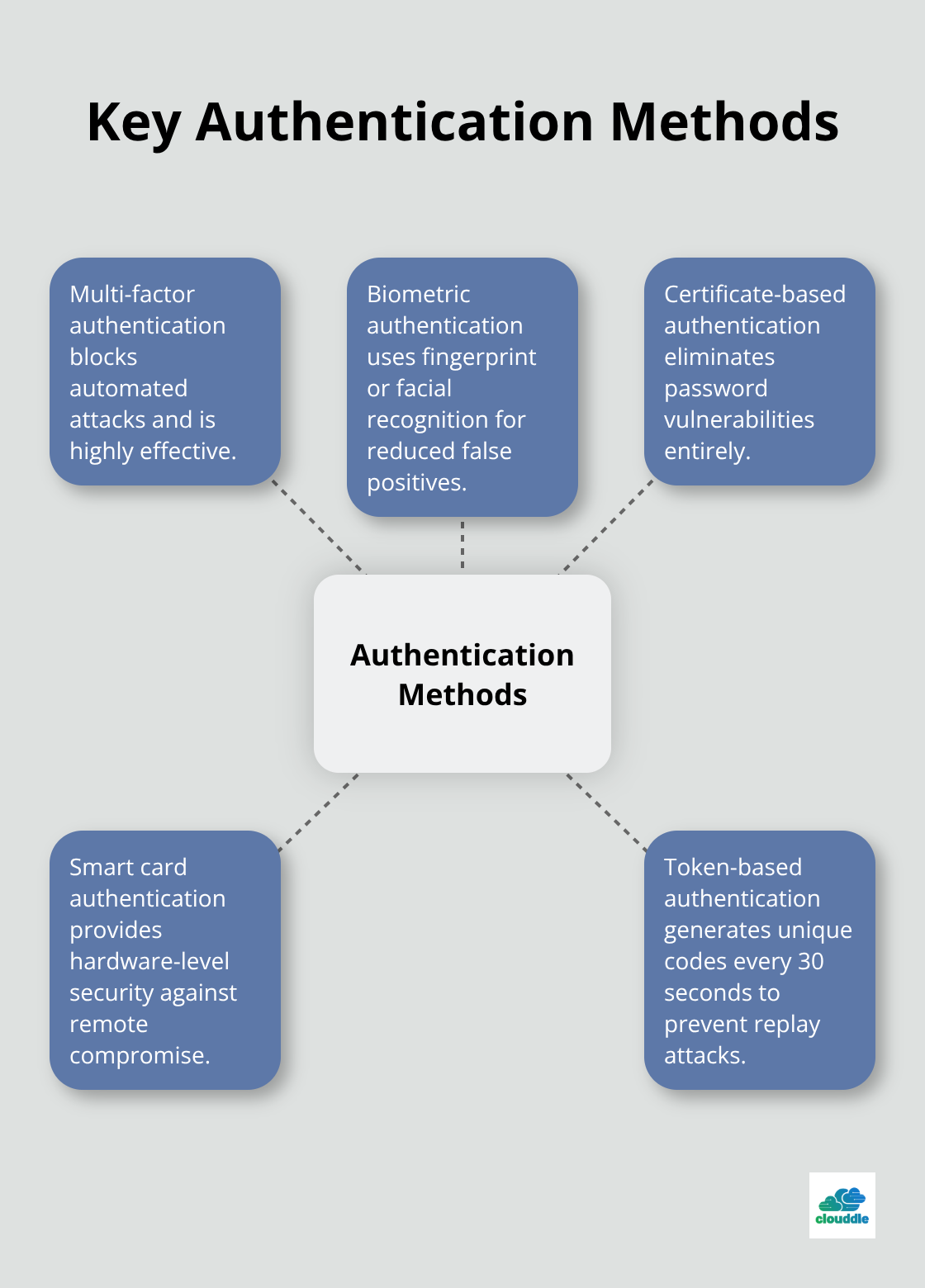
Multi-factor authentication blocks automated attacks and serves as the most effective single security control available today. Biometric authentication systems (fingerprint and facial recognition) reduce false positives compared to traditional password systems. Certificate-based authentication eliminates password vulnerabilities entirely and prevents credential theft attacks. Smart card authentication provides hardware-level security that attackers cannot compromise remotely. Token-based authentication systems generate unique codes every 30 seconds, making replay attacks impossible.
Real-Time Monitoring That Detects Threats Instantly
Network monitoring tools generate alerts within seconds of detecting anomalous traffic patterns, as delays allow attackers to establish persistence. Intrusion detection systems with machine learning capabilities identify more zero-day attacks than signature-based systems alone. Security information and event management platforms correlate logs from multiple sources and detect advanced persistent threats faster than manual analysis. Network behavior analysis tools flag unusual data transfers that indicate potential data exfiltration and catch insider threats before damage occurs. Honeypots deployed in network segments detect reconnaissance activities and trigger alerts for lateral movement attempts.
These technical controls work best when combined with comprehensive security management practices that maintain protection over time.
Best Practices for Ongoing Network Security Management
Patch Management That Prevents Successful Attacks
Patch management schedules determine whether vulnerabilities become successful attacks, with visibility and control of assets helping organizations identify potential security gaps and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Critical security patches require immediate deployment within 72 hours, while standard updates follow monthly cycles that align with vendor release schedules. Automated patch management systems reduce human error and deployment time by 70%, though testing patches in isolated environments prevents the 12% of updates that cause system conflicts. Windows Update for Business and Linux package managers streamline patch deployment across enterprise networks, while vulnerability scanners like Nessus and OpenVAS identify missing patches before attackers exploit them.
Employee Training Programs That Stop Human Error
Security awareness training reduces breach likelihood by 65% when conducted effectively. Simulated phishing campaigns identify vulnerable employees and provide targeted remediation, with click rates dropping from 37% to 8% after six months of consistent training. Role-specific training programs address unique threats that face different departments, as finance teams encounter business email compromise attempts while IT staff face more sophisticated social engineering. Micro-learning modules delivered monthly maintain security awareness better than annual training sessions, while gamification increases employee engagement scores by 40%. Security champions programs in each department create peer-to-peer learning that reinforces training messages throughout the year.
Incident Response Plans That Minimize Damage
Incident response plans reduce average breach costs by $2.66 million when properly implemented, according to IBM Security research. Response teams with defined roles and communication protocols contain breaches 54 days faster than organizations without formal plans. Tabletop exercises conducted quarterly identify plan weaknesses and improve response coordination, while automated incident response tools handle initial containment within minutes rather than hours. Digital forensics capabilities preserve evidence while maintaining business operations, and legal notification requirements vary by jurisdiction but typically mandate disclosure within 72 hours (with some regions requiring faster notification). Recovery time objectives should specify maximum acceptable downtime for each system, with critical infrastructure requiring restoration within four hours to prevent significant business impact. Regular security audits validate incident response effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.

Final Thoughts
Network security success depends on systematic execution of proven strategies rather than reactive responses to threats. Organizations that combine robust firewall configurations, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring reduce breach likelihood by over 60% compared to those with basic security measures. Companies must implement network security through structured approaches that address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors.
Continuous security monitoring forms the backbone of modern cybersecurity defense, with automated systems that detect threats within seconds while human oversight addresses complex incidents. Organizations with 24/7 monitoring capabilities contain breaches 54 days faster than those that rely on periodic security checks. Multi-factor authentication deployment across all systems, automated patch management cycles, and quarterly security awareness training prevent 80% of common attack vectors.
We at Clouddle provide managed IT and security services that include 24/7 monitoring, automated threat response, and expert support without significant upfront investment. This allows your team to focus on core business operations while maintaining enterprise-level security protection. The threat landscape evolves daily, making network security an ongoing commitment that requires continuous improvement and adaptation to new threats.


