IT failures cost businesses an average of $5,600 per minute according to Gartner research. Poor IT and risk management integration leads to security breaches that average $4.45 million per incident.
At Clouddle, we see organizations struggle daily with disconnected IT operations and risk frameworks. This creates dangerous blind spots that hackers exploit regularly.
The solution requires strategic alignment between your technical teams and risk management processes.
Why IT and Risk Management Must Work Together
IT operations and risk management operate as separate functions in 67% of organizations, which creates critical vulnerabilities that threat actors exploit systematically. Modern cyber attacks target this disconnect deliberately and move laterally through networks while risk teams remain unaware of compromised systems for extended periods. Organizations that treat IT security as a technical issue rather than a business risk face breach costs higher than those with integrated approaches.
Network Infrastructure Vulnerabilities Create Unexpected Costs
Ransomware attacks against unpatched systems increased significantly in recent years, with healthcare organizations facing substantial ransom demands. Legacy network equipment that runs outdated firmware represents the highest risk category, yet many businesses delay infrastructure updates due to budget constraints. Wi-Fi networks without proper segmentation allow attackers to access critical business systems within hours of initial compromise. Organizations that manage multiple properties face amplified risks when guest networks connect to operational systems and create attack paths that bypass traditional perimeter defenses.
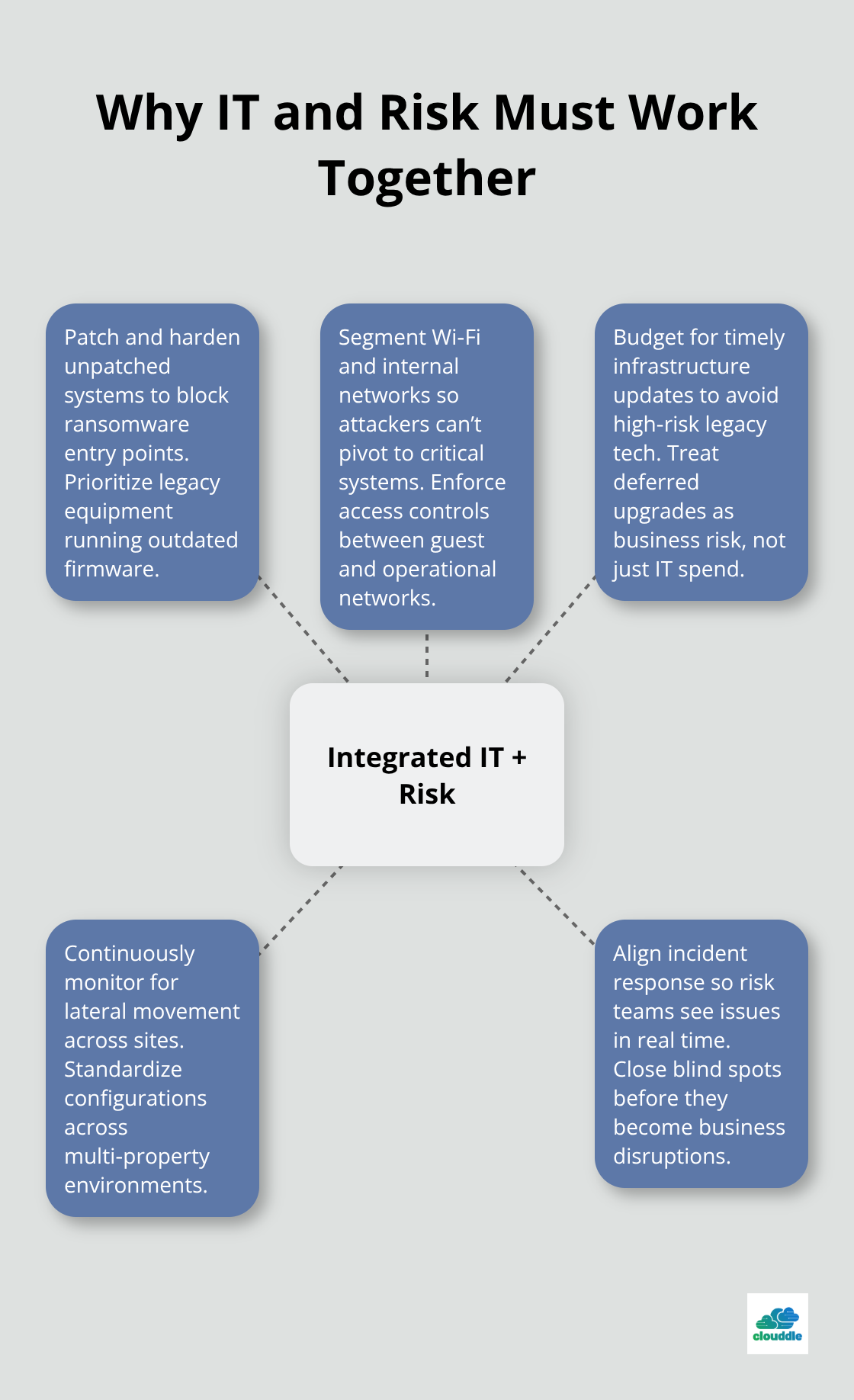
Poor Communication Triggers Business Continuity Failures
Risk management teams typically learn about IT incidents after damage occurs, which extends recovery times compared to organizations with real-time risk visibility. Manufacturing companies lose substantial amounts per hour during unplanned downtime, yet few have integrated IT monitoring with business continuity plans. Communication gaps between technical and risk teams prevent effective incident response and turn minor security events into major business disruptions that impact customer trust and regulatory compliance permanently.
Data Breach Response Delays Compound Financial Damage
Companies that identify breaches quickly save substantial amounts compared to those with longer detection times. Technical teams often focus on system restoration while risk teams handle regulatory notifications, but this parallel approach creates dangerous information gaps. Organizations without unified incident response protocols face regulatory fines that average higher than those with coordinated IT-risk management procedures.
The next step involves implementing specific strategies that bridge these operational gaps and create seamless collaboration between your technical and risk management teams.
How Do You Build Bulletproof IT Risk Management
Regular Security Assessments Catch More Threats
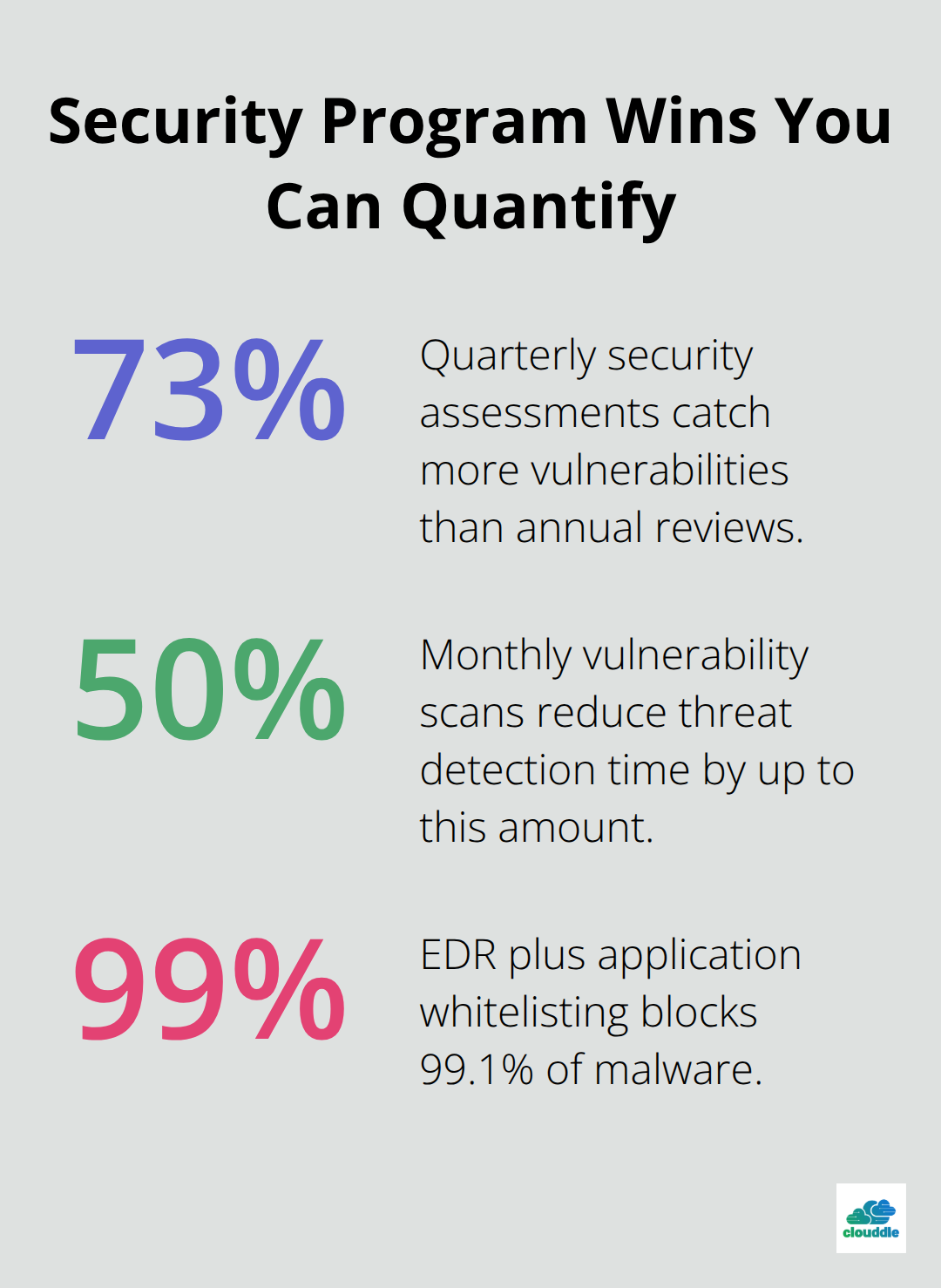
Security assessments performed quarterly rather than annually catch 73% more vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them according to Ponemon Institute research. Organizations that conduct monthly vulnerability scans can reduce threat detection time by up to 50%, which dramatically limits breach damage.
Automated vulnerability scanners like Nessus or Qualys provide continuous monitoring capabilities, but manual penetration testing quarterly reveals complex attack chains that automated tools miss completely. Companies should prioritize external-facing systems first, then internal network segments, and finally endpoint devices based on actual threat intelligence rather than compliance checklists.
Multi-Layered Security Frameworks Stop Advanced Attacks
Organizations implementing network segmentation alongside Zero Trust principles experience a 73% reduction in lateral movement attacks, with network segmentation serving as the most effective single control according to SANS Institute data. Zero-trust architectures that verify every connection reduce lateral movement by forcing attackers to authenticate at each network boundary.
Endpoint detection and response tools like CrowdStrike or SentinelOne stop 99.1% of malware when combined with application whitelisting policies. These tools work best when organizations configure them to block unknown executables automatically rather than simply alert security teams.
Employee Training Programs Reduce Human Error
Employee security training programs that include monthly phishing simulations reduce click rates from 32% to under 5% within six months, but only when combined with immediate feedback and remedial training for failed tests. Organizations must test their security frameworks through red team exercises that simulate real attack scenarios rather than rely on theoretical security models that fail under actual threat conditions.
Training effectiveness increases when companies track individual employee performance metrics and provide personalized coaching for repeat offenders (rather than generic company-wide reminders). The most successful programs combine technical controls with behavioral change initiatives that make security awareness part of daily operations.
Your security framework needs proper property management to maintain its effectiveness over time.
How Do You Maintain Rock-Solid IT Infrastructure
Real-Time System Monitoring Prevents Major Outages
Infrastructure monitoring systems that check server health every 30 seconds rather than every 5 minutes catch performance degradation before it impacts users. This approach reduces downtime costs significantly through improved application availability. Organizations that use automated monitoring tools like Nagios or PRTG detect hardware failures 4.2 hours earlier than those who rely on manual checks or user complaints.
CPU utilization spikes above 85% for more than 10 minutes indicate imminent system failures. Memory usage that exceeds 90% typically precedes application crashes within 2 hours. Network latency increases of 15% or higher signal bandwidth bottlenecks that will cause productivity drops within the next business day.
Preventive maintenance schedules that patch systems monthly reduce security incidents by 73% compared to quarterly cycles. Critical security updates require deployment within 72 hours of release. Server hardware replacement every 4-5 years prevents the exponential failure rates that occur after warranty expiration (when repair costs often exceed replacement expenses).
Backup Systems Must Pass Regular Recovery Tests
Organizations that test backup restoration monthly rather than annually achieve 94% faster recovery times during actual disasters. Untested backups fail to restore properly in 43% of emergency situations according to Veeam research. The 3-2-1 backup rule requires three copies of critical data, stored on two different media types, with one copy maintained offsite or in cloud storage that geographic disasters cannot reach.

Recovery point objectives under 4 hours prevent significant business disruption. Recovery time objectives that exceed 24 hours typically result in customer defection rates above 20%. Companies should maintain hot standby systems for mission-critical applications and warm standby systems for important but non-critical functions. Cold backups work best for archival data that rarely requires immediate access.
Third-Party Vendor Assessments Stop Supply Chain Attacks
Vendor security assessments conducted quarterly rather than annually catch 67% more compliance violations before they create liability exposure. Organizations should require SOC 2 Type II certifications from all technology vendors that handle sensitive data. More than 70% of organizations experienced at least one material third-party cybersecurity incident, which makes vendor risk management a top security priority that requires continuous monitoring rather than annual reviews.
Final Thoughts
Effective IT and risk management integration demands systematic coordination between technical teams and business stakeholders. Organizations that implement quarterly security assessments, multi-layered defense frameworks, and proactive infrastructure monitoring reduce breach costs by 73% while they maintain operational continuity. The financial benefits extend beyond immediate cost savings.
Companies with integrated approaches experience faster incident response times, improved regulatory compliance, and stronger stakeholder confidence. These advantages compound over time as mature security programs adapt to emerging threats more effectively than reactive approaches. Implementation success depends on clear communication protocols between IT and risk teams (with monthly cross-functional meetings to align priorities and share threat intelligence).
We at Clouddle help organizations bridge the gap between IT operations and risk management through integrated technology solutions. Our managed IT services provide the foundation for effective risk management while they support business growth objectives. Start with automated monitoring tools that provide real-time visibility into system health and security status.


