IT projects fail at alarming rates, with studies showing that 70% exceed their original budgets and timelines. The challenges in IT project management have only intensified as technology becomes more complex and business demands grow.
At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how these obstacles can derail even the most promising initiatives. Understanding what lies ahead is the first step toward building successful project outcomes.
Why Do IT Projects Always Go Over Budget?
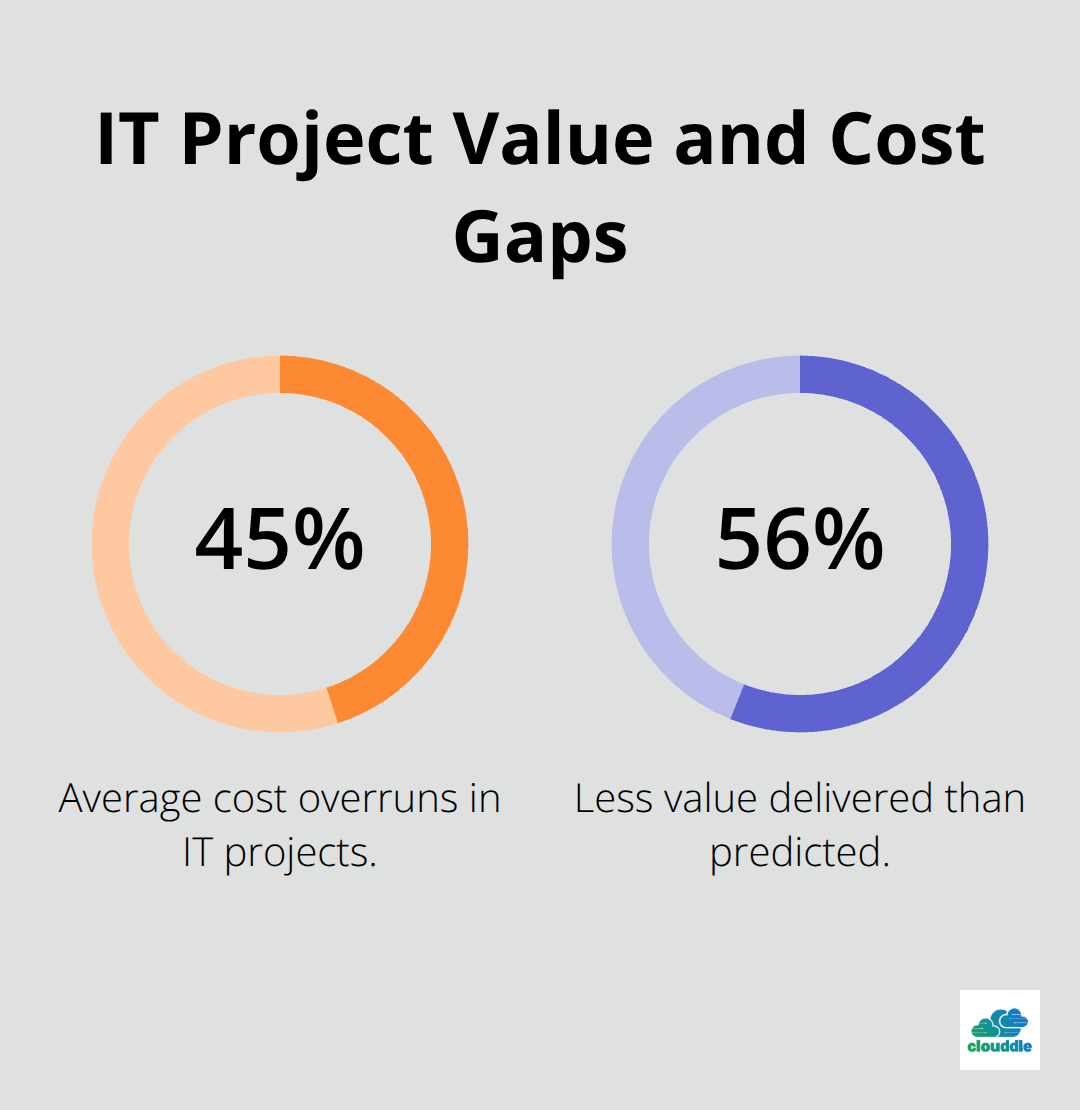
Money problems hit IT projects harder than any other sector. The average IT project experiences cost overruns of 45%, while delivering 56% less value than predicted according to McKinsey research. These financial disasters stem from three predictable patterns that appear repeatedly across the industry.
Hidden Costs Strike Without Warning
Software licensing fees multiply when user counts exceed initial estimates. Third-party integrations require expensive middleware that nobody budgets for. Security audits demand additional compliance tools that cost $50,000 or more per system. Hardware requirements double when performance tests reveal capacity bottlenecks. These expense categories account for significant portions of all budget overruns in enterprise IT projects.
Requirements Change Every Two Weeks
Stakeholders add new features mid-project in numerous IT initiatives globally. Marketing departments request additional dashboards for reports. Operations teams demand mobile compatibility that wasn’t in the original scope. Executive leadership pivots strategic direction and forces architectural changes. Each modification triggers a cascade of development work, tests, and deployment delays that inflate costs substantially per change request.
Team Skills Don’t Match Project Needs
Companies underestimate the specialized expertise that modern IT implementations require. Cloud migration projects fail when internal teams lack AWS or Azure certifications. Database optimization requires specialists who charge premium rates instead of generalists. Security implementations need certified professionals who command higher rates than standard developers. Organizations that conduct thorough skills assessments before project kickoff significantly reduce cost overruns compared to those that assume existing staff can handle everything.
Budget overruns create a domino effect that extends far beyond financial strain, often leading to the next major challenge that derails IT projects.
Why Do Technical Implementations Always Break?
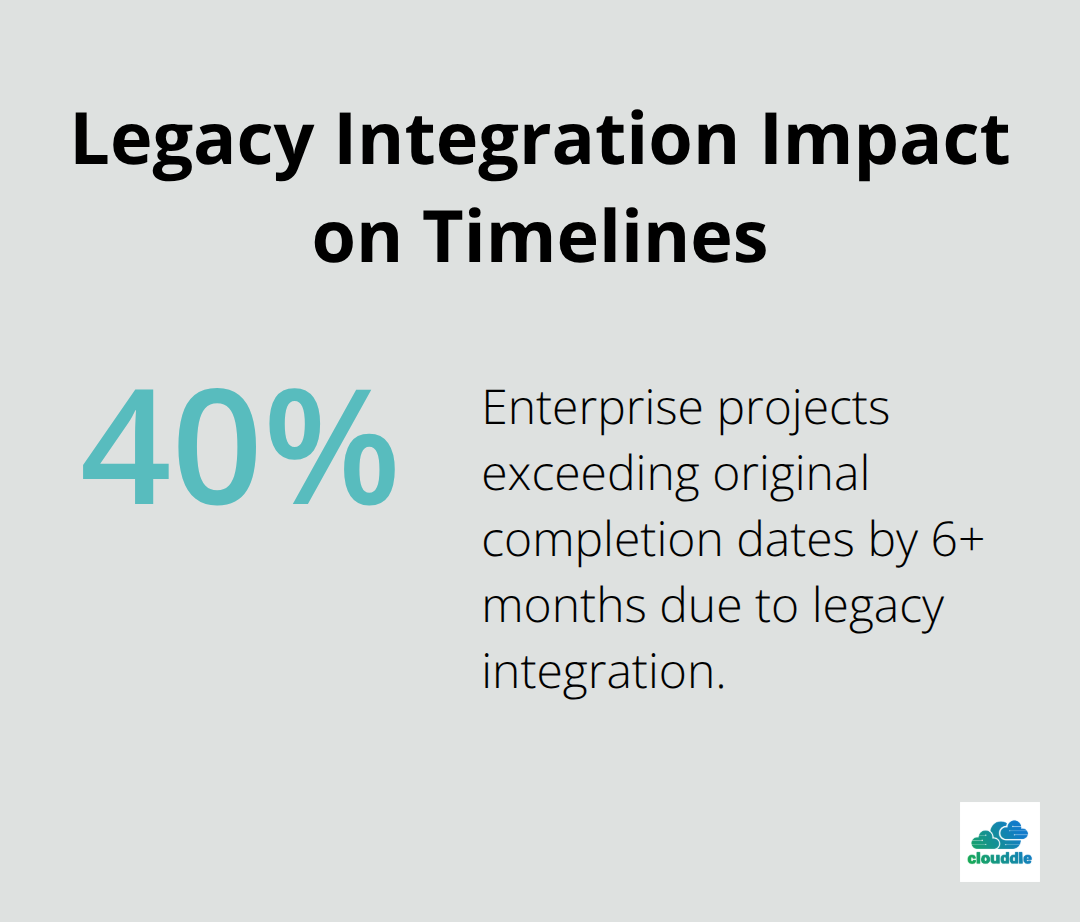
Technical execution separates successful IT projects from expensive failures. Research shows that technical implementation problems are a significant factor in project failures rather than budget or timeline issues. Legacy system integration alone causes 40% of enterprise projects to exceed their original completion dates by six months or more. These technical roadblocks follow predictable patterns that destroy project momentum and team confidence.
Legacy Systems Create Integration Nightmares
Mainframe systems from the 1990s still run payroll for many Fortune 500 companies. These systems use COBOL programming languages that require specialists who charge $150 per hour minimum. API connections fail when legacy databases can’t handle modern data formats. File transfer protocols break when security updates conflict with outdated authentication methods.
Database migrations take 300% longer than estimated because data structures don’t match current standards. Companies that conduct comprehensive legacy system audits before project kickoff reduce integration delays by 65% compared to those that assume compatibility will work automatically. The most expensive mistake involves the assumption that middleware solutions can bridge any gap between old and new systems without extensive custom development work.
Security Requirements Multiply Project Complexity
GDPR compliance adds 40 development hours per data field that stores personal information. SOX regulations require audit trails for every database transaction, which doubles storage requirements and processing time. PCI DSS standards demand separate network segments for payment processing (requiring additional hardware and configuration work). Each security framework introduces testing requirements that extend project timelines by weeks.
Penetration testing reveals vulnerabilities that force architectural changes after development completion. Organizations that integrate security requirements during initial planning phases complete projects 30% faster than those that treat compliance as an afterthought. Performance bottlenecks emerge when encryption processes consume server resources that weren’t calculated in network capacity planning exercises.
Performance Issues Surface Under Real Load
Load testing reveals that applications handle only 40% of expected user traffic during peak hours. Database queries that work fine with test data crash when processing millions of real records. Memory leaks appear after systems run continuously for 72 hours or more. Network bandwidth calculations prove insufficient when file uploads exceed original size estimates (often by 500% or more).
Scalability problems force expensive infrastructure upgrades that weren’t budgeted in the original project scope. Performance optimization requires specialized database administrators and system architects who command premium rates. These technical challenges create communication gaps that spread confusion throughout project teams and stakeholder groups.
Why Do IT Teams Always Miscommunicate?
Communication breakdowns destroy IT projects faster than technical failures or budget overruns. PMI research reveals that effective communications leads to more successful projects, allowing organizations to become high performers, with IT initiatives suffering the worst consequences. Teams speak different languages even within the same organization – developers focus on code architecture while business stakeholders demand feature deliverables, creating a disconnect that spreads through every project phase.
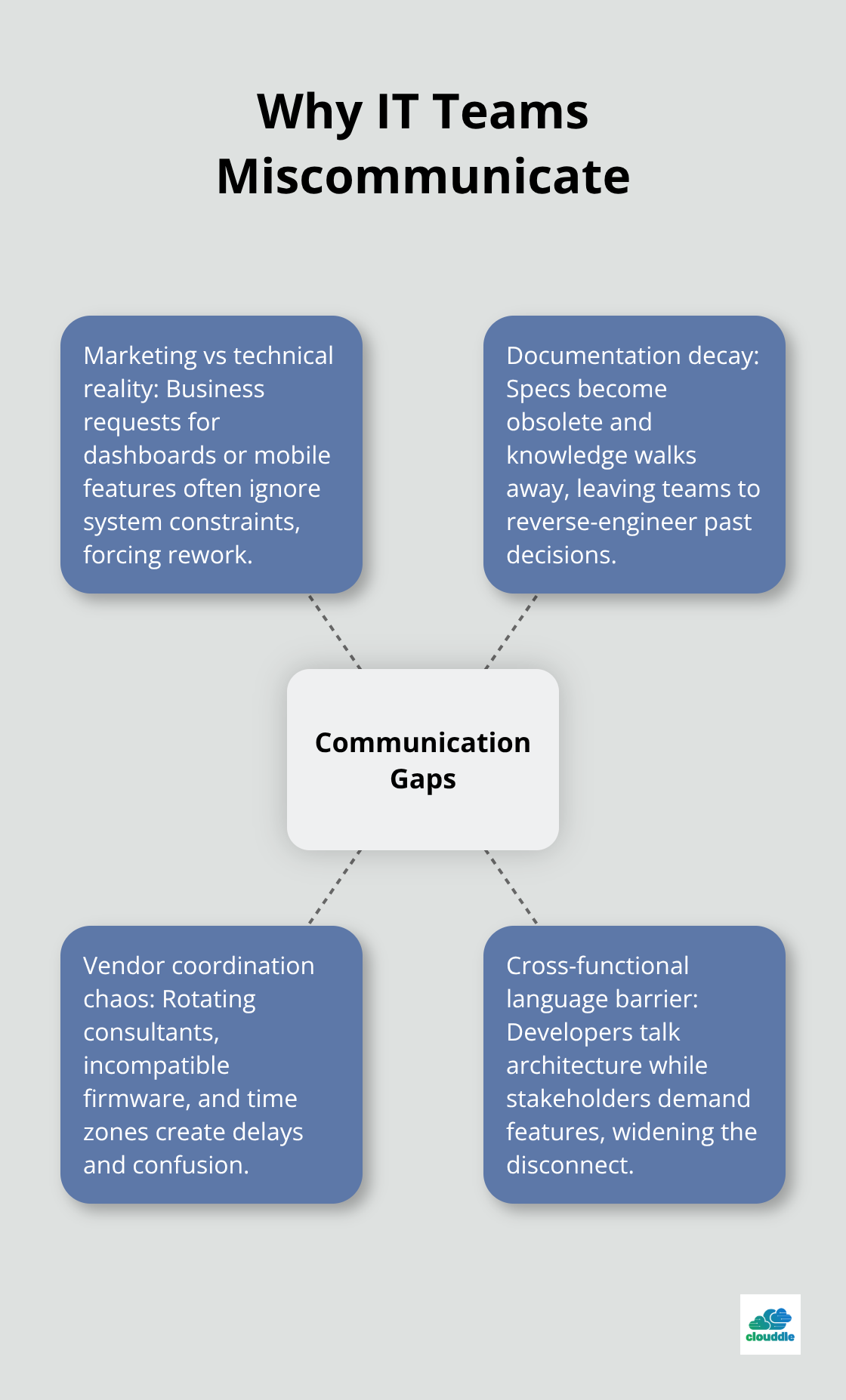
Marketing Demands Clash with Technical Reality
Marketing departments request dashboard modifications without understanding database limitations. Operations teams demand system changes that conflict with security protocols already implemented. Sales executives promise features to clients before development teams confirm feasibility. Business analysts write requirements that ignore existing system constraints, forcing developers to explain why simple requests require complex solutions.
Documentation Becomes Digital Archaeology
Technical specifications written six months ago become obsolete when team members leave and take institutional knowledge with them. Confluence pages contain outdated entries that accumulate over time according to common usage patterns. Password management systems store credentials for services that no longer exist while missing access details for critical production systems.
Code repositories lack comments that explain why specific functions exist, forcing new developers to reverse-engineer solutions that took months to create originally. Knowledge transfer sessions happen once during employee transitions, then disappear forever when the next person needs that same information. Companies that implement structured documentation reviews can use systematic risk mitigation approaches for better project outcomes compared to organizations that treat documentation as an afterthought activity.
Third-Party Vendors Multiply Coordination Chaos
Software vendors promise API compatibility that breaks during production deployments, forcing emergency meetings with technical support teams located in different time zones. Hardware suppliers deliver equipment with firmware versions that conflict with existing network infrastructure (creating security vulnerabilities that require immediate patches). Consulting firms rotate team members every quarter, requiring constant relationship rebuilding and technical explanation repetition.
Contract negotiations stall when legal departments review terms that technical teams already approved, while project deadlines approach without resolution. Vendor management consumes significant project manager time according to industry analysis, yet most organizations assign this responsibility as a secondary task rather than dedicated focus area.
Final Thoughts
The challenges in IT project management require systematic approaches rather than reactive fixes. Organizations that implement structured risk assessment processes during project initiation reduce failure rates by 60% compared to those that address problems after they emerge. Proactive planning demands honest evaluation of team capabilities, realistic timeline estimates, and comprehensive stakeholder alignment before any development work begins.
Successful IT project management depends on three fundamental practices that separate high-performing teams from others. Teams must establish clear communication protocols that bridge the gap between technical staff and business stakeholders through regular status meetings and standardized reports. They must build contingency plans for predictable obstacles like scope changes, vendor delays, and integration complications that appear in most enterprise implementations (while also maintaining proper documentation systems that preserve institutional knowledge).
Modern IT infrastructure requires specialized expertise and reliable support systems that most organizations lack internally. Professional managed IT services provide the technical foundation that allows project teams to focus on strategic objectives rather than operational problems. Technology complexity will continue to increase, which makes professional support partnerships more valuable than ever for sustainable business growth.


