At its core, the major difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable comes down to performance. A Cat6 cable essentially doubles the available bandwidth (250 MHz vs. 100 MHz) and can handle much faster data speeds—up to 10 Gbps under the right conditions. Cat5e, on the other hand, tops out at 1 Gbps. Cat6 also has a more robust internal design to combat interference, making it the smarter, more reliable choice for modern networks.
Cat5 vs Cat6: A Quick Comparison for a Better Network
Picking the right Ethernet cable is one of those foundational decisions that dictates your network’s speed and reliability for years to come. While they might look nearly identical on the outside, Cat5e (Category 5 enhanced) and Cat6 (Category 6) are built very differently, and that difference creates a serious performance gap.
This initial comparison will give you a clear, high-level look at what separates these two common standards. Getting this right is crucial, whether you’re wiring a brand-new building, upgrading an aging office network, or just want to make sure you’re getting the full speed you pay for from your internet provider. While Cat5e can still get the job done for basic needs, Cat6 has firmly taken its place as the go-to standard for any new installation.
The real differentiators are bandwidth (how much data can be sent at once), supported data rates, and how well the cable resists electronic "noise" or interference, which is technically known as crosstalk.

Key Specification Comparison Cat5e vs Cat6
To truly see the difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable, a direct side-by-side look at the specs is the best way to cut through the noise. The table below breaks down the core technical details that really matter for property managers, IT professionals, and anyone making a long-term cabling decision.
| Specification | Cat5e | Cat6 |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 1 Gbps (1,000 Mbps) at 100 meters | 1 Gbps at 100 meters; 10 Gbps up to 55 meters |
| Bandwidth | Up to 100 MHz | Up to 250 MHz |
| Crosstalk | Standard protection | Reduced crosstalk due to tighter twists and a spline |
| Conductors | Thinner 24 AWG copper wires | Thicker 23 AWG copper wires for better performance |
| Best Use Case | Home networks with < 1 Gbps internet, basic office use | New installations, smart homes, business networks, PoE |
| Future-Proofing | Limited; sufficient for current Gigabit needs | Excellent; supports emerging multi-gigabit speeds |
As you can see, the specs don't lie. Cat6 is simply a more capable cable.
The real game-changer is Cat6’s ability to handle 10 Gigabit Ethernet over practical distances (up to 55 meters or 180 feet). This capability, combined with its 2.5x greater bandwidth, provides critical headroom for future network demands.
For any new build or significant network upgrade, the small extra cost for Cat6 cabling pays for itself over the long haul. It ensures your physical infrastructure won't be the bottleneck when you eventually upgrade to faster internet or add more demanding devices. While Cat5e is perfectly fine for today's typical gigabit speeds, Cat6 gets your network ready for what's next.
The Evolution of Ethernet Cabling
To really appreciate the performance jump from Cat5e to Cat6, it helps to look at how we got here. Each new cable category wasn’t just a random upgrade; it was a direct response to the exploding demands of network technology. The journey from Cat5 to Cat6 tells a story of innovation born from necessity.
The original Cat5 standard, which came on the scene in the mid-90s, was built for a world just getting its feet wet with networking. It supported speeds up to 100 Mbps with a bandwidth of 100 MHz. Back then, that was plenty for basic file sharing and the early days of the internet.
But technology has a habit of moving fast. As applications grew more sophisticated and files got bigger, the need for faster, more dependable connections became obvious.
The Rise of Cat5e and Gigabit Speeds
The first big step forward was Cat5e (Category 5 enhanced). Standardized in 2001, its main purpose was to reliably support Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) across the full 100-meter channel. It pulled this off by tightening manufacturing standards to cut down on crosstalk—the signal interference that can bleed between wire pairs inside the cable.
This improvement made Cat5e the go-to workhorse for homes and offices for more than a decade. It was the perfect match for a world embracing high-speed internet, online gaming, and streaming video. For a long time, it was the definition of reliable connectivity.
Cat5e wasn't a total reinvention, but a smart refinement. By improving the twist rates of the copper pairs and holding manufacturers to stricter testing rules, it could handle ten times the speed of its predecessor without a fundamental redesign.
This refinement was a game-changer, but the digital world kept accelerating. The explosion of HD video, the shift to data-heavy cloud services, and the rise of Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices started to push Cat5e to its limits. Networks didn't just need more speed; they needed more capacity.
Why Cat6 Was a Necessary Innovation
This is where Cat6 comes in. Standardized in 2002, just a year after Cat5e, it was designed with an eye on the future. The engineers knew that just hitting the 1 Gbps mark wasn't going to be enough for long. The next challenge was handling multi-gigabit speeds and much heavier data loads.
Cat6 was engineered from the start to be a better cable. It brought several key physical upgrades to the table:
- Higher Bandwidth: It cranked up the maximum frequency from 100 MHz to 250 MHz. This effectively widened the "data highway," allowing more information to flow simultaneously.
- Stricter Crosstalk Limits: It introduced much tougher specs for reducing signal interference, which is absolutely critical for keeping data clean at higher speeds.
- Support for 10GBASE-T: For the first time, a common twisted-pair cable could handle 10 Gbps speeds, though it was limited to shorter runs of up to 55 meters.
The development of Cat6 was a direct answer to the writing on the wall. It wasn't just another small step forward; it was a foundational shift needed to power the next generation of business applications, smart building tech, and high-density Wi-Fi networks. The difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable is a perfect reflection of this technological leap.
Performance Deep Dive: Bandwidth, Speed, and Crosstalk

To really grasp the difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable, we have to look past the plastic jacket and into the electrical performance. The real story is told by three key metrics: bandwidth, speed, and how well each cable handles signal interference, or "crosstalk." These are what define a cable's true capability out in the field.
Think of bandwidth, measured in megahertz (MHz), as the width of a data highway. A cable with more bandwidth has more lanes, allowing more data to travel at once without creating a traffic jam.
Here, Cat6 establishes a commanding lead. It’s a serious upgrade, rated for frequencies up to 250 MHz, whereas Cat5e tops out at just 100 MHz. That’s a 150% jump in capacity, meaning Cat6 is built to handle a much heavier flow of information from the get-go.
From Megahertz to Megabits: What It Means for Speed
That wider data highway directly translates to faster potential speeds. Both Cat5e and Cat6 can easily handle Gigabit Ethernet (1,000 Mbps or 1 Gbps), the standard for most modern networks, over the full 100-meter (328-foot) cable run. For everyday office and home use, Cat5e is often perfectly adequate.
But the extra bandwidth in Cat6 unlocks a whole other tier of performance. Under the right conditions, Cat6 can push data at a blistering 10 Gbps. This incredible speed is possible on shorter runs—officially up to 55 meters (around 180 feet). In these situations, Cat6 is literally ten times faster than its predecessor, giving you a massive advantage for high-demand connections.
This is a game-changer in a commercial setting. Think about connecting a busy server to your core switch or linking network closets between floors. These are prime examples where a 10 Gbps Cat6 link can eliminate bottlenecks. While Cat5e simply can't do it, Cat6 gives you a practical path to multi-gigabit speeds where they matter most. You can explore our guide to better understand network throughput and its real-world impact.
Taming the Noise: How Cat6 Beats Crosstalk
Speed isn't everything. A reliable connection depends on clean, error-free data transmission. The primary threat to that signal integrity inside an Ethernet cable is crosstalk.
Crosstalk is the unwanted "bleeding" of signals between the different wire pairs twisted together inside the cable. Imagine four people having separate phone calls in a tiny room—their voices would overlap and interfere, making it hard to understand anyone clearly. Crosstalk does the same thing to your data, leading to errors that force re-transmissions and slow everything down.
Cat6 was specifically designed to combat this issue with a couple of key physical improvements:
- Tighter Twists: The pairs of copper wires in a Cat6 cable are twisted more tightly than in Cat5e. This simple-but-effective manufacturing change makes the cable inherently more resistant to signal noise, both from other pairs (crosstalk) and from outside electrical interference (EMI).
- Internal Separator (Spline): Most Cat6 cables contain a thin plastic divider, known as a spline, that runs down the middle. This physically isolates the four wire pairs, preventing them from interfering with each other. This is a feature you just won't find in Cat5e cables.
The Key Takeaway: The one-two punch of higher bandwidth and far better crosstalk reduction means Cat6 delivers a signal that is cleaner, more stable, and much more reliable. This is crucial for applications that can’t tolerate data errors, like HD video conferences, VoIP calls, and large file transfers.
Using tools for real-time network performance monitoring can really bring these differences to life, showing you the tangible impact of a more stable physical layer. Ultimately, Cat6 doesn't just run faster; it maintains its integrity under pressure, giving you a consistently better network experience.
Comparing Physical Construction and Design
The performance leap from Cat5 to Cat6 isn't just about numbers on a spec sheet; it's rooted in serious physical engineering. To really get why Cat6 delivers a cleaner, more reliable signal, you have to look inside the cable. The differences in their internal architecture are what allow Cat6 to handle much higher frequencies and speeds without data-corrupting noise.
At a glance, a Cat5e and Cat6 cable might look the same. But cut one open, and the story changes completely.
Thicker Copper and Better Signal Flow
One of the most immediate physical differences is in the copper conductors. Cat6 cables simply use thicker wires, and that makes a huge difference.
- Cat6 Conductors: Built with 23 American Wire Gauge (AWG) copper wires.
- Cat5e Conductors: Use slightly thinner 24 AWG copper wires.
The AWG scale is inverse—a smaller number means a bigger wire. The thicker copper in Cat6 reduces electrical resistance, letting the signal travel farther with less weakening. It also means Cat6 is better at handling heat, a critical advantage for Power over Ethernet (PoE) where the cable delivers both data and electricity to devices like security cameras or Wi-Fi access points.
The Spline: A Key Differentiator
Maybe the single most important upgrade in a Cat6 cable is something Cat5e doesn't have at all: an internal separator called a spline. This is a plastic piece running right down the middle of the cable, creating separate channels that keep the four twisted wire pairs isolated from each other.
It's a simple but brilliant bit of engineering designed to fight crosstalk. By keeping the pairs physically apart, the spline dramatically cuts down on signals bleeding from one pair to another—a major source of network errors at high speeds. This physical isolation is a huge reason Cat6 maintains signal purity all the way up to 250 MHz.
The Impact of the Spline: This internal divider makes Cat6 cables more rigid and a bit thicker. That extra durability is great, but it can also make the cable trickier to bend around tight corners or terminate into jacks and plugs during an installation.
Tighter Twists and Enhanced Shielding
Beyond the spline, Cat6 cables also pack more twists per inch into their copper pairs compared to Cat5e. This tighter twist rate is another deliberate design choice that fortifies the cable against both internal crosstalk and external electromagnetic interference (EMI) from things like power lines or fluorescent lights.
Both cable types come in unshielded (UTP) and shielded (STP) versions, but the manufacturing standards for Cat6 are far stricter. This means even a standard UTP Cat6 cable offers a higher baseline of noise rejection right out of the box.
This combination of thicker wires, a physical spline, and tighter twists is what gives Cat6 its definitive edge. Each element builds on the others to create a more robust and stable path for your data. These principles of physical integrity are foundational to any high-performance network, which is why understanding the basics of structured cabling is so important for long-term reliability. The superior construction ensures that Cat6 isn't just a faster cable—it's a fundamentally more dependable one. You can read more about these construction differences on Truecable.com.
Deciding Between Cat5e and Cat6 for Your Needs
All the technical specs in the world don't mean much until you apply them to your own situation. Choosing the right cable isn't about picking the "best" one on paper; it's about matching its capabilities to your specific environment, budget, and future plans. For many, Cat5e is still perfectly fine. For others, settling for anything less than Cat6 would be a major oversight.
The whole decision really boils down to one simple question: are you working with an existing network, or are you putting in brand-new wiring?
This decision tree cuts right to the chase.
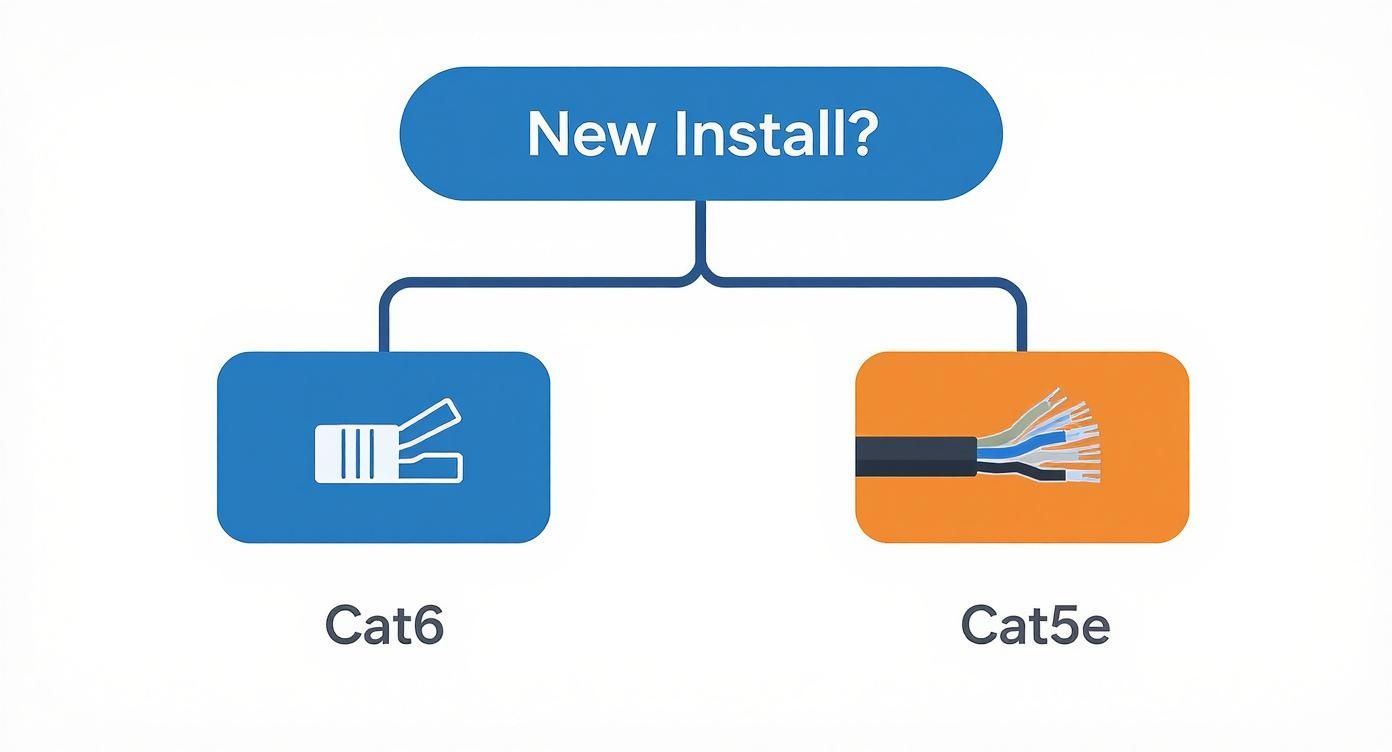
The takeaway is clear: for any new project, Cat6 is the industry standard and the way to go. For existing, less demanding networks, Cat5e can still pull its weight.
The Home Network Scenario
For most homes, the debate often comes down to your internet plan. If your service is 1 Gbps or less, your existing Cat5e wiring can absolutely handle it. The cable won't be a bottleneck, and you'll get the full speed you pay for. Tearing out your walls to upgrade is rarely worth the cost or hassle.
But the conversation shifts if you're a power user, have a sophisticated smart home, or you're already renovating with the walls open.
- Smart Homes: A modern smart home isn't just a few lightbulbs anymore. It's dozens of devices—security cameras, smart speakers, thermostats, locks—all fighting for bandwidth. Cat6 provides a much more stable and robust backbone for these crowded networks.
- Power Users: If you're a gamer, content creator, or someone running a home server, you'll feel the difference. Cat6 offers the extra headroom you need for massive local file transfers and applications where every millisecond of latency counts.
- New Installations: This is the easiest call to make. If you're building a new house or have the walls open for any reason, install Cat6. The small bump in material cost is nothing compared to the labor expense of re-pulling cable a few years down the road when multi-gigabit internet is the new normal.
The rule of thumb for home use is simple: Don’t rip out working Cat5e for a sub-gigabit connection. But if you’re running any new cable, choose Cat6 to set your home up for the next decade.
The Modern Business Environment
In a commercial setting, the choice is much clearer. Cat6 isn't just an upgrade anymore; it’s the baseline standard for any new business installation. The daily demands of an office or commercial property far outstrip what a typical home needs, making the superior capabilities of Cat6 essential.
Think about these common business scenarios where Cat6 is a must-have:
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): Devices like VoIP phones, security cameras, and wireless access points often get their power straight from the Ethernet cable. The thicker 23 AWG copper wires in Cat6 handle that electrical load more efficiently, with less heat, ensuring your critical devices run reliably.
- High-Density Wi-Fi: An office with dozens of employees needs multiple high-performance Wi-Fi access points. Cat6 provides the multi-gigabit backhaul needed to keep those access points from becoming data choke points, delivering a smooth wireless experience for everyone.
- Data-Intensive Workflows: Any business that moves large files around—design firms, video production studios, medical offices—will see an immediate benefit. Cat6 supports 10 Gbps speeds over shorter distances, which is perfect for linking workstations to a central server.
For any business owner or IT manager, choosing Cat6 is an investment in productivity. It builds a network infrastructure that can handle growth and new technologies without needing a costly and disruptive overhaul down the line. And once you've standardized on Cat6, it's worth looking ahead at even more advanced options like Cat6 vs Cat8 cabling for your most critical, high-demand network links.
Weighing Installation Costs and Future-Proofing
When you get past the technical specs, the choice between Cat5e and Cat6 really boils down to three things: what it costs today, how easy it is to install, and whether it will still be useful years from now. At first glance, Cat5e looks like the easy winner on price, but the real story is a bit more complicated when you consider the total investment.
The cable itself is only part of the equation. Sure, Cat6 cable usually costs about 20-30% more per foot than Cat5e. But don't forget the other hardware—keystone jacks, patch panels, and connectors for Cat6 are also a bit pricier.
The Installation Process
You'll use the same tools to terminate both cables, but working with Cat6 requires a bit more finesse. The copper wires in Cat6 are thicker (23 AWG), and it has a plastic spine running down the center to prevent signals from interfering with each other. This construction makes the cable tougher and more rigid.
That stiffness can make pulling Cat6 through conduit or navigating sharp turns a real challenge. Getting those thicker wires properly seated in a jack also takes more precision to get a clean, reliable connection. It’s not a showstopper for a pro, but this physical difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable can add a little more time to the installation.
The biggest line item in any cabling job is almost always the labor, not the cable itself. The cost to run wire through walls and ceilings is the same whether you're pulling Cat5e or Cat6. This is the single most compelling reason to plan for the future.
Investing in What's Next
This is the most important factor: choosing a cable isn't a decision for next year, it's a decision for the next decade. The wiring you install today will likely be in service for 10-15 years, and we all know how quickly technology evolves.
Cat5e is fine for the 1 Gbps internet speeds most people have now, but that’s its absolute limit. As multi-gigabit internet plans become standard, a Cat5e network will become an immediate bottleneck, throttling the very speeds you’re paying for.
Opting for Cat6 is a strategic move. By spending a little more now, you're laying a foundation that's ready for what comes next.
- Ready for Multi-Gigabit Speeds: Cat6 can handle 2.5 Gbps, 5 Gbps, and even 10 Gbps over shorter runs, so your network won't hold you back when faster internet services arrive.
- Better Wi-Fi Performance: Newer standards like Wi-Fi 6 need a super-fast wired connection to the access point to deliver top wireless speeds. Cat6 provides that essential multi-gigabit backhaul.
- Avoids a Rip-and-Replace Nightmare: The cost and headache of tearing open walls to replace outdated Cat5e wiring is astronomical compared to the small initial savings. For any new build or major renovation, Cat6 is the only logical choice.
Choosing to future-proof with Cat6 protects your investment and keeps your property up-to-date. To see how these factors add up, it's worth understanding the complete network cable installation cost to appreciate why thinking ahead delivers the best long-term value.
Common Questions About Cat5 and Cat6 Cables
Even after you've waded through all the technical specs, some very practical questions always pop up when it's time to actually buy and install new cabling. Let's tackle some of the most common points of confusion to make sure you get this right.
Getting these details straight means you'll pick the right cable without overspending or accidentally creating a bottleneck for yourself down the road.
Can I Use a Cat6 Cable on a Cat5e Network?
Yes, absolutely. The standards were designed to be backward-compatible, so you can plug a Cat6 cable into a network built with Cat5e jacks and switches without a problem.
The catch? Your network's performance will always be limited by its weakest link. In this case, even with a superior Cat6 cable, the entire connection will drop down to Cat5e speeds, which maxes out at 1 Gbps.
Should I Upgrade Existing Cat5e Wiring to Cat6?
For most homes and many small businesses with internet plans of 1 Gbps or less, there’s really no compelling reason to rip out perfectly good Cat5e wiring. Your existing cables can already handle those speeds just fine, so an upgrade won't give you any noticeable performance boost.
However, the story changes completely if you're starting fresh.
If you're doing any new construction, a significant renovation, or have plans to jump to multi-gigabit internet, installing Cat6 is the only logical choice. The slightly higher material cost is a tiny price to pay for future-proofing your entire network infrastructure.
Do I Need Different Tools to Install Cat6?
The fundamental tools of the trade—your crimper, stripper, and punch-down tool—are the same for both Cat5e and Cat6. The actual process of terminating the cable hasn't changed.
But here’s where you need to pay attention: the components themselves are different. The physical difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cable is significant; Cat6 wires are thicker and often have a plastic spine (spline) running down the middle to separate the pairs. Because of this, you must use Cat6-rated keystone jacks and RJ45 connectors. Using Cat5e ends on a Cat6 cable will result in a poor fit, unreliable connections, and a failure to perform at Cat6 speeds.
Ready to build a network that’s prepared for the future? Clouddle Inc specializes in designing and installing high-performance structured cabling solutions for commercial properties, hospitality, and multi-family residences. Ensure your infrastructure can handle tomorrow’s demands by visiting Clouddle's website to learn about our Network-as-a-Service offerings.


