Network security in healthcare has become a critical concern in recent years. Cyber threats targeting medical institutions are on the rise, putting patient data and lives at risk.
At Clouddle, we understand the unique challenges healthcare organizations face in protecting their networks and sensitive information. This blog post will explore effective strategies and advanced technologies to enhance network security in the healthcare sector.
Why Healthcare Is a Prime Target for Cyber Attacks
The Unprecedented Surge in Cyber Threats
Healthcare organizations face an alarming increase in cyber threats. While specific statistics may vary, recent reports indicate a significant rise in healthcare data breaches and cyberattacks. This trend highlights the urgent need for robust network security measures in the healthcare sector.
The Gold Mine of Healthcare Data
Cybercriminals target healthcare organizations primarily due to the immense value of medical data. Patient records contain a wealth of personal information (including social security numbers, addresses, and financial details). Experts suggest that medical data can be significantly more valuable than credit card information on the black market, making healthcare an irresistible target for malicious actors.
Vulnerabilities in Connected Medical Devices
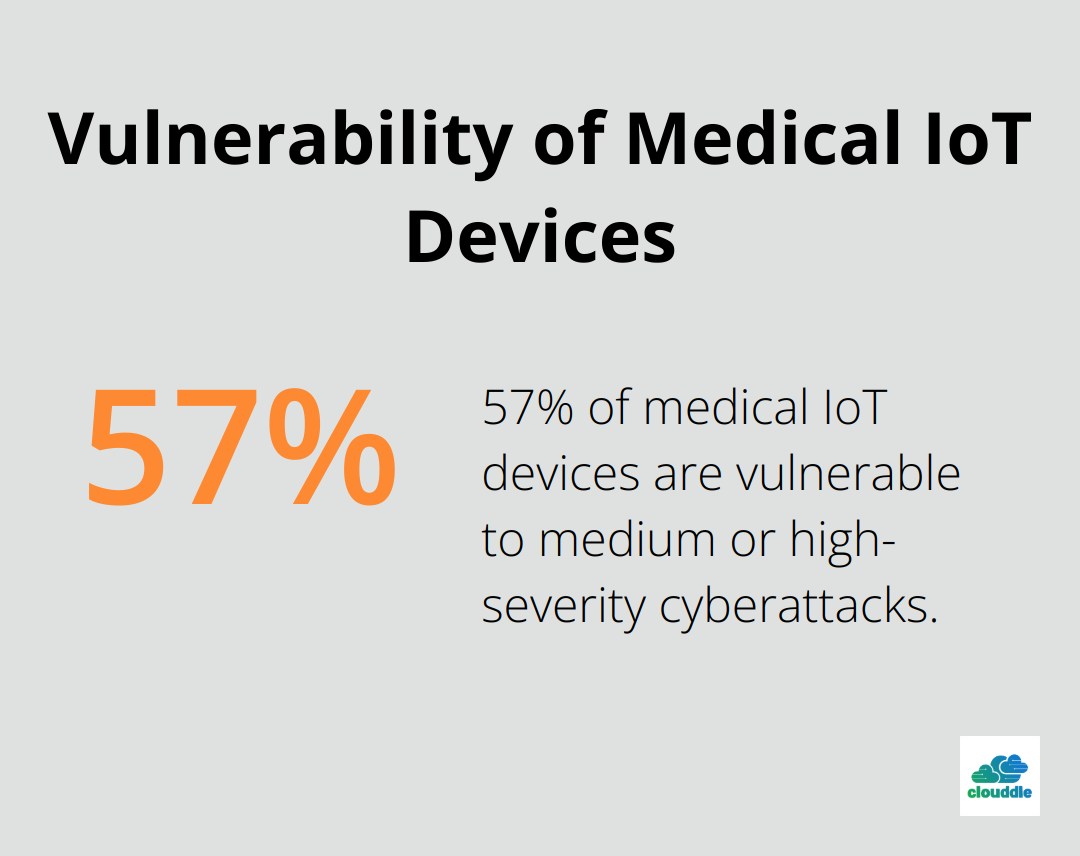
The proliferation of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices introduces new security risks. A study by Cynerio found that nearly 57% of medical IoT devices are vulnerable to medium or high-severity cyberattacks. These connected medical devices often run outdated software or lack proper security protocols, serving as potential entry points for cybercriminals.
Navigating Complex Compliance Requirements
Healthcare organizations must adhere to a complex web of regulations, including HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties. For example, HIPAA violations can lead to fines of up to $1.5 million per year for each violation category. This regulatory landscape adds another layer of complexity to healthcare cybersecurity efforts.
The Human Element: A Persistent Vulnerability
Despite technological advancements, human error remains a significant security risk. In 2024, cybersecurity professionals reported that 88% of healthcare workers opened phishing emails. This statistic underscores the critical need for ongoing cybersecurity training and awareness programs in healthcare organizations.
The healthcare sector’s unique challenges and vulnerabilities make it a prime target for cyber attacks. To address these risks effectively, organizations must implement comprehensive security solutions that protect networks, safeguard patient data, and maintain compliance with evolving regulations. In the next section, we will explore best practices for enhancing healthcare network security.
How Can Healthcare Organizations Fortify Their Network Security?
Healthcare organizations face an urgent need to protect their networks and sensitive patient data from escalating cyber threats. Implementing robust security measures is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical step in safeguarding patient trust and organizational integrity.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication stands as one of the most effective ways to enhance network security. Healthcare organizations should require at least two forms of identification before granting access to sensitive systems or data. This could include a combination of:
- Something the user knows (e.g., a password)
- Something they have (e.g., a security token)
- Something they are (e.g., a fingerprint)
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Security audits play a crucial role in identifying vulnerabilities before exploitation. The Department of Health and Human Services recommends conducting these audits at least annually. However, the rapidly evolving threat landscape may necessitate more frequent assessments. These audits should include penetration testing, where ethical hackers attempt to breach systems to uncover weaknesses.
Prioritize Employee Training
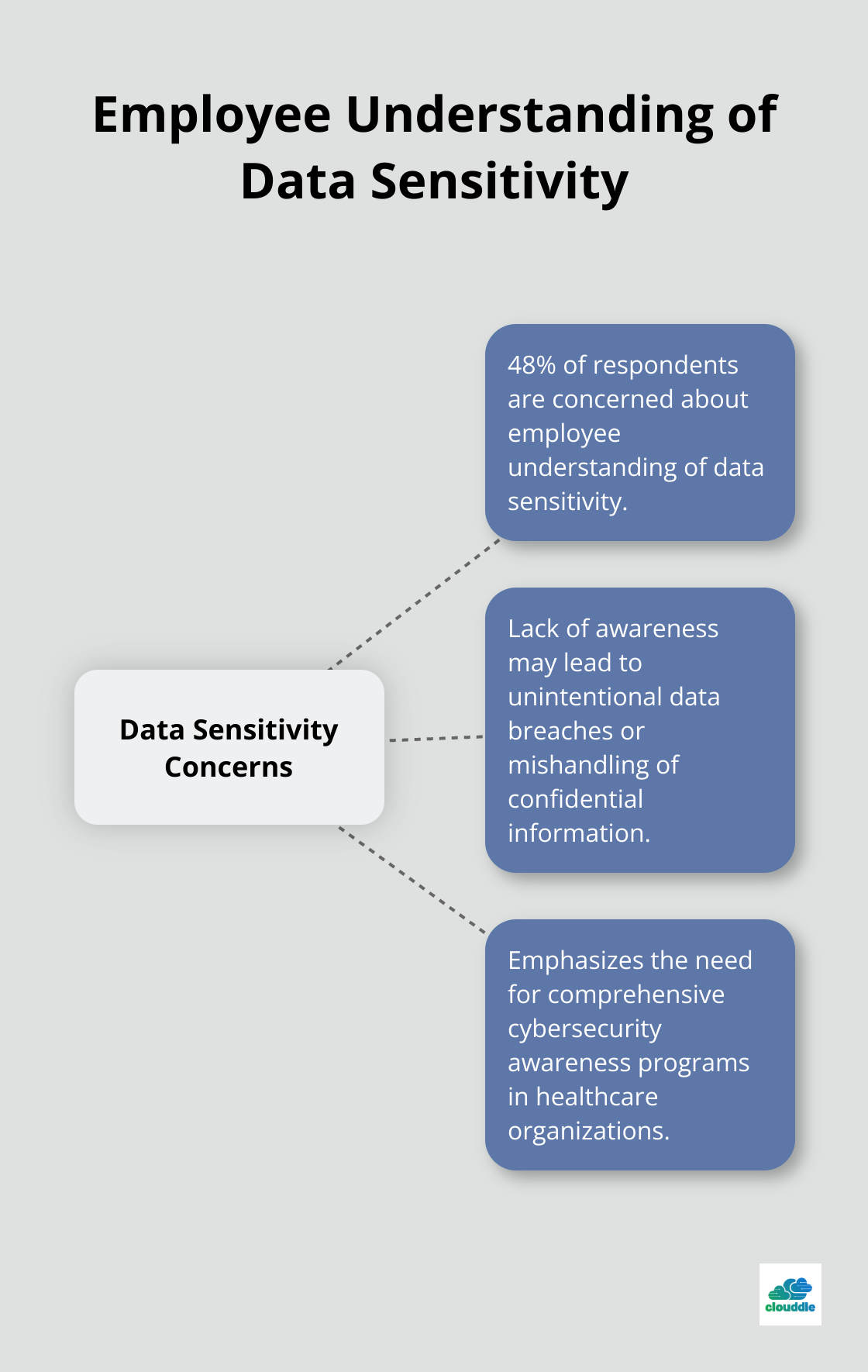
Human error remains a significant vulnerability in healthcare cybersecurity. About half of respondents (48 percent) are concerned or very concerned that employees do not understand the sensitivity and confidentiality of data shared. To combat this, organizations must invest in comprehensive cybersecurity awareness programs. These programs should cover:
- Recognition of phishing attempts
- Proper handling of sensitive data
- Importance of strong password practices
Training should occur regularly and receive updates to address new threats.
Encrypt All Sensitive Data
Encryption serves as a powerful tool in protecting patient data, both at rest and in transit. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends using AES-256 bit encryption for sensitive healthcare data. This level of encryption (virtually unbreakable with current technology) provides a strong defense against data breaches.
Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments. This practice limits the potential damage of a breach by containing it to a specific segment. Healthcare organizations should separate critical systems (such as those handling patient data) from less sensitive areas of the network. This approach can significantly reduce the impact of a potential cyber attack.
The implementation of these practices can significantly enhance a healthcare organization’s network security posture. However, cybersecurity requires an ongoing process of monitoring, updating, and adaptation. As we explore advanced technologies for healthcare network protection in the next section, we’ll discover how cutting-edge solutions can further bolster these foundational security measures.
How Advanced Technologies Protect Healthcare Networks
Advanced technologies play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive patient data and critical systems in healthcare cybersecurity. These cutting-edge solutions offer healthcare organizations powerful tools to detect, prevent, and respond to sophisticated cyber threats.
Next-Generation Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Traditional firewalls no longer suffice to protect healthcare networks from advanced threats. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) and intrusion detection systems (IDS) provide more comprehensive protection. NGFWs offer deep packet inspection, application-level filtering, and integrated threat intelligence. The global next-generation firewall market size was estimated at USD 4.33 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 10.99 billion by 2030.

Healthcare organizations should consider NGFWs with features such as:
- Application awareness and control
- User identity integration
- SSL/TLS inspection
- Threat intelligence feeds
Intrusion detection systems complement NGFWs by monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities. Modern IDS solutions use machine learning algorithms to improve threat detection accuracy and reduce false positives.
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) revolutionize healthcare cybersecurity. These technologies enable faster threat detection, automated response, and predictive analytics. AI-driven systems have been useful in identifying ransomware attacks as they occur, minimizing the risk of major data loss and operational disruptions.
Healthcare organizations can leverage AI and ML in several ways:
- Anomaly detection: AI algorithms identify unusual patterns in network traffic or user behavior that may indicate a security breach.
- Automated threat response: ML-powered systems automatically isolate infected devices or block malicious traffic, reducing response times.
- Predictive analytics: AI analyzes historical data to predict potential vulnerabilities and recommend proactive security measures.
Secure Cloud Solutions for Healthcare Data
Cloud computing offers healthcare organizations scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage and management. However, it’s important to choose cloud providers that offer robust security features and comply with healthcare regulations.
When selecting a cloud solution, healthcare organizations should prioritize:
- End-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest
- Strong access controls and multi-factor authentication
- Regular security audits and compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, HITRUST)
- Data residency options to meet regulatory requirements
Network Segmentation and Microsegmentation
Network segmentation is a critical security strategy for healthcare organizations. Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments limits the spread of potential breaches and protects critical assets.
Microsegmentation applies fine-grained security policies at the individual workload level. This approach is particularly valuable in healthcare environments with diverse connected devices and applications.
Benefits of microsegmentation in healthcare include:
- Improved visibility into network traffic
- Reduced attack surface
- Enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements
- Better protection for legacy medical devices
As cyber threats continue to evolve, healthcare organizations must stay ahead of the curve by adopting these advanced technologies. The combination of next-generation firewalls, AI-powered threat detection, secure cloud solutions, and advanced network segmentation techniques significantly enhances cybersecurity posture and protects sensitive patient data.
Final Thoughts
Network security in healthcare protects patient data and organizational integrity. Healthcare organizations face unique challenges, from valuable patient information to vulnerable medical devices. The strategies we discussed form a robust defense against evolving cyber threats, but enhancing cybersecurity requires continuous adaptation.
Clouddle understands the complexities of network security in healthcare. Our managed IT and security services help healthcare organizations navigate these challenges effectively. We combine cutting-edge technology with industry expertise to enable healthcare providers to focus on patient care while we handle network security intricacies.
Healthcare organizations must prioritize cybersecurity as a fundamental aspect of their operations. It safeguards patient trust, ensures operational continuity, and maintains regulatory compliance. Implementing comprehensive security measures and partnering with experienced providers allows healthcare organizations to build resilient networks capable of withstanding current and future cyber challenges.


