Network connectivity in cloud computing directly impacts whether your applications run smoothly or grind to a halt. Poor connectivity costs businesses real money through downtime, slower performance, and frustrated users.
At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how the right connectivity strategy transforms cloud operations. This guide walks you through what matters, what breaks, and how to fix it.
Why Network Connectivity Matters
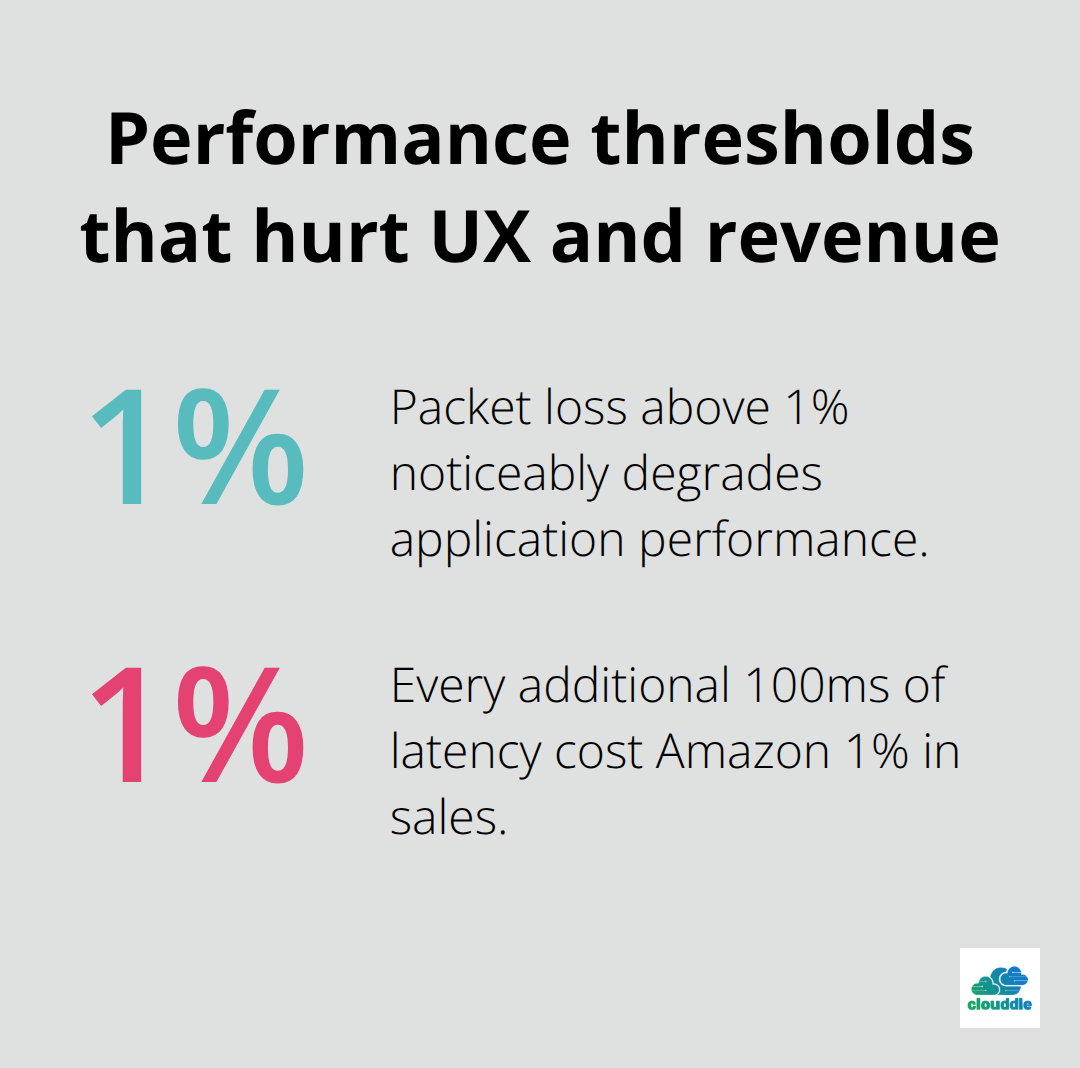
Network downtime costs companies an average of $5,600 per minute according to Gartner research, yet most organizations treat connectivity as an afterthought until something breaks. When your cloud applications lose connection or experience latency spikes, the damage compounds quickly. Every 100ms of latency cost Amazon 1% in sales, according to research from the company. Your users don’t care whether the slowdown originates from application code or network infrastructure-they only know the experience is poor.
Connectivity’s Role in Critical Operations
In hospitality, multi-family dwelling, and senior living environments, connectivity directly determines whether guests enjoy seamless Wi-Fi, residents access essential services reliably, or staff can manage operations efficiently. A single connectivity failure in a senior living facility prevents nurses from accessing patient records or emergency communication systems, creating genuine safety risks beyond simple inconvenience. These aren’t theoretical problems-they represent real operational threats that demand immediate attention.
The Revenue Impact of Network Degradation
Poor cloud connectivity doesn’t just frustrate users; it hemorrhages revenue and operational capacity. When your network degrades, your applications become slower, which drives customers away and damages brand reputation. Bandwidth bottlenecks force you to reduce service quality or turn away traffic, directly limiting growth. Security vulnerabilities in poorly managed networks invite attacks that compromise data and customer trust. Organizations with unreliable connectivity spend disproportionate resources on reactive troubleshooting instead of strategic initiatives.
Building a Financial Case for Investment
The financial case is straightforward: invest in robust connectivity upfront, or pay substantially more through lost productivity, emergency repairs, and customer churn. Businesses that implement Network as a Service solutions eliminate single points of failure and gain unified visibility across their entire network infrastructure. This visibility translates directly into faster problem resolution and fewer incidents that disrupt operations. The cost of prevention always undercuts the cost of crisis management.
Understanding why connectivity matters sets the foundation for what comes next-the specific practices that keep your cloud networks running reliably.
Building Redundancy Into Your Cloud Network
Redundancy separates organizations that experience occasional hiccups from those that suffer catastrophic failures. A single connection to your cloud provider creates a single point of failure-when that connection drops, everything stops. We see this pattern repeatedly: businesses operating on single connections face unplanned downtime that could have been prevented with basic redundancy. Implement at least two independent network paths to your cloud infrastructure, preferably through different providers or different physical routes. AWS recommends using multiple Availability Zones across regions for critical workloads, and the same principle applies to your connectivity layer. If you operate in hospitality or senior living environments where connectivity failures directly impact guest experience or resident safety, redundancy isn’t optional-it’s a baseline requirement. Configure automatic failover so that when your primary connection degrades, traffic shifts to secondary paths without manual intervention. This requires setting up health checks that monitor connection quality in real time, not just whether a link is technically up. A connection can be technically active while delivering terrible performance through packet loss or latency spikes.

Most cloud providers support this through their routing protocols and load balancing services.
Monitor What Actually Matters
Network monitoring tools flood you with data that rarely leads to action. Focus instead on metrics that correlate with real user experience: packet loss percentage, latency percentiles (especially the 95th and 99th), and jitter variance. Cisco research shows that packet loss above 1% degrades application performance noticeably, and most users notice latency above 150ms. Set thresholds that trigger alerts before these performance floors are breached, not after. Integrate your cloud provider’s native monitoring tools with your own infrastructure monitoring to correlate cloud-side issues with connectivity problems. AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations all provide visibility into network performance metrics. The critical insight: correlation matters more than individual data points. When latency spikes simultaneously with increased packet loss and CPU usage, you’re seeing a congestion problem, not three separate issues. Event logging lets you filter by device and event type to reduce noise and focus on actionable data. Set up configurable notifications so your team receives alerts only for problems that require immediate attention, preventing alert fatigue that causes teams to ignore genuine issues.
Choose Your Provider Based on Network Strength
Your cloud provider’s network infrastructure determines whether your best practices even matter. Providers differ dramatically in network redundancy, geographic reach, and peering relationships with other networks. AWS operates in 33 regions globally with multiple Availability Zones per region, while Google Cloud spans 40 regions. Azure covers 60 regions but with varying service availability. If your users concentrate in specific geographic areas, select a provider with strong infrastructure in those regions. Peering relationships matter significantly-providers with extensive peering arrangements deliver better performance to users on smaller ISPs. Ask potential providers directly about their network topology, redundancy architecture, and SLAs for packet loss and latency. A provider offering 99.9% uptime means nothing if that uptime includes periods of terrible performance. Evaluate whether the provider offers tools for visibility into your connectivity quality. A unified organizational view provides single-pane visibility across network health, enabling rapid identification of problems without switching between consoles. This matters because time spent navigating multiple management interfaces is time you’re not solving problems.
Leverage Network Topology for Faster Troubleshooting
Network topology visualization transforms how quickly you identify and resolve connectivity issues. When problems occur, topology maps show you the exact path traffic takes through your infrastructure and pinpoint where failures happen. This visibility eliminates the guesswork that typically consumes hours during outages. Direct navigation from an issue to the specific device and supporting context accelerates root-cause analysis significantly. Rather than checking multiple systems to understand how your network connects, topology tools consolidate this information into actionable views. This approach proves especially valuable in complex environments where multiple cloud regions, on-premises infrastructure, and third-party connections intersect. The faster you locate problems, the faster your team resolves them and restores service to users.
Your provider selection and monitoring foundation now support the next critical layer: addressing the specific connectivity problems that emerge despite your best preventive efforts.
What Actually Breaks Your Cloud Network
Latency spikes and packet loss represent the most common connectivity failures, yet most organizations lack the diagnostic capability to identify which is causing problems. Latency above 150ms becomes noticeable to users, but packet loss above 1% degrades application performance even when latency appears acceptable. These problems often occur simultaneously during congestion events. The critical mistake teams make is treating latency as the only metric worth monitoring. A connection can show acceptable latency while losing packets silently, destroying application reliability without triggering obvious performance complaints.
Measure both metrics at the 95th and 99th percentile, not averages. Average latency of 50ms means nothing if the 99th percentile hits 400ms during peak hours. Combine your cloud provider’s native monitoring with dedicated network monitoring tools to capture packet loss across different times of day and traffic patterns. When you identify elevated packet loss, the cause typically traces to one of three sources: congestion on your network path, misconfigured Quality of Service settings that deprioritize traffic, or physical layer problems on your connectivity circuits. Test each hypothesis systematically rather than guessing. Request packet capture capabilities from your provider-this reveals exactly where packets drop in your infrastructure. Most providers now offer packet capture tools that let you select specific ports and apply filters for deep diagnostics without requiring direct console access.
Congestion Demands Aggressive Capacity Planning
Bandwidth bottlenecks hit suddenly when traffic patterns shift unexpectedly. Organizations consistently underestimate peak traffic requirements, then scramble when seasonal events or unexpected demand spikes overwhelm their provisioned capacity. The solution isn’t simply purchasing more bandwidth; it requires understanding your traffic patterns well enough to predict when congestion will occur.
Analyze historical traffic data across the entire day, week, and year to identify peak periods. Most cloud environments experience traffic concentration during specific windows-morning startup periods, lunch hours, evening usage surges. Size your primary circuits for your 95th percentile traffic demand, not your peak demand. Provisioning for absolute peak traffic wastes money on capacity you use only briefly. Implement load balancing across multiple cloud regions to distribute traffic geographically. AWS Transit Gateway, Azure Load Balancer, and Google Cloud’s internal load balancers all enable traffic distribution that prevents single region saturation.
When congestion occurs despite planning, event logging filtered by device and event type helps isolate whether the problem originates in your network, your cloud provider’s infrastructure, or your application layer. Misconfigured QoS policies frequently cause artificial congestion by deprioritizing legitimate traffic. Audit your QoS settings to confirm they align with your actual traffic priorities-many organizations inherit outdated policies that no longer match their operations.
Latency and Packet Loss Require Systematic Diagnosis
Latency spikes often mask underlying packet loss that causes real damage to application performance. A connection experiencing both problems simultaneously requires different solutions than one experiencing either problem alone. Start your diagnosis by isolating which metric is the primary culprit. High latency with low packet loss typically indicates congestion or routing inefficiency. High packet loss with acceptable latency points toward physical layer issues or QoS misconfiguration.
Use your cloud provider’s network topology visualization to trace the exact path your traffic takes through their infrastructure. This visibility eliminates hours of guesswork during outages. Direct navigation from an issue to the specific device and supporting context accelerates root-cause analysis significantly. Rather than checking multiple systems to understand how your network connects, topology tools consolidate this information into actionable views. This approach proves especially valuable in complex environments where multiple cloud regions, on-premises infrastructure, and third-party connections intersect.
Security Threats Require Layered Defense
DDoS attacks targeting cloud infrastructure have grown dramatically more sophisticated, with the largest attacks now exceeding 3.5 terabits per second according to recent industry reports. Your connectivity security depends on multiple layers working together, not a single firewall blocking all threats. Cloud providers include DDoS protection in their standard offerings, but relying solely on provider-side protection creates blind spots.
Implement rate limiting on your edge infrastructure to drop obviously malicious traffic before it consumes your bandwidth. Configure your cloud provider’s security groups and network access control lists to permit only necessary traffic patterns. Most organizations over-provision permissions, allowing connections they never actually use. Review your security rules quarterly and remove any that aren’t actively needed. Hybrid connectivity introduces additional attack surface-if you connect on-premises infrastructure to cloud resources, secure that connection with a VPN or dedicated circuit rather than exposing it to the public internet.
Encrypt all traffic crossing network boundaries. The computational overhead of encryption is negligible compared to the risk of unencrypted data exposure. Monitor for unusual traffic patterns that indicate potential attacks: sudden traffic spikes from specific sources, connections to unexpected destinations, or protocol patterns that don’t match your normal operations. Your network topology visualization tools help tremendously here-they show you exactly which traffic flows are normal and which represent anomalies worthy of investigation.
Final Thoughts
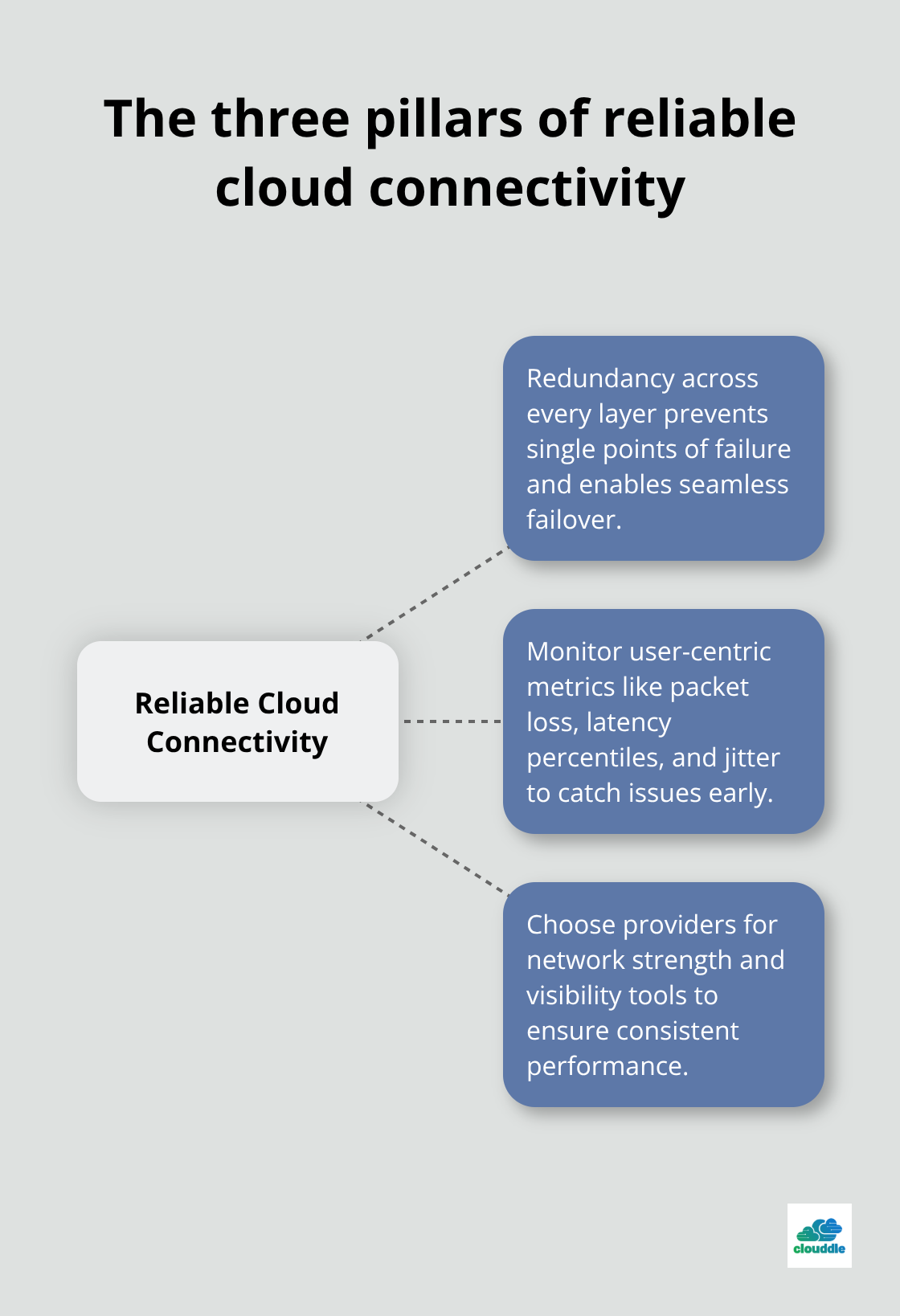
Network connectivity in cloud computing demands ongoing attention and systematic monitoring rather than a one-time fix. Organizations that maintain reliable cloud networks treat connectivity as a strategic priority, not a technical detail. Your foundation rests on three pillars: redundancy across every network layer, monitoring metrics that affect user experience, and selecting cloud providers based on their infrastructure strength and visibility tools.
When problems emerge, your diagnostic capability determines how quickly you resolve them. Network topology visualization, packet capture tools, and event logging filtered by device type transform troubleshooting from hours of guesswork into minutes of targeted investigation. The faster you identify root causes, the faster your team restores service and prevents revenue loss.
For organizations in hospitality, multi-family dwelling, and senior living environments, connectivity failures carry particular weight because poor network performance directly impacts guest experience, resident safety, and staff efficiency. At Clouddle, we provide managed networking solutions designed specifically for your operational requirements, combining reliability with simplicity through our Network as a Service approach. This commitment to the practices outlined here transforms your operations from reactive firefighting into proactive optimization.


