Network security private communications in a public world has become a top priority for businesses of all sizes. Cyberattacks increased by 38% in 2023, with public networks serving as prime hunting grounds for malicious actors.
We at Clouddle see companies struggle daily with protecting their digital assets while maintaining operational efficiency. The cost of a single data breach now averages $4.45 million globally.
What Makes Public Networks So Dangerous
Public networks expose businesses to sophisticated attack methods that traditional security measures cannot stop. Man-in-the-middle attacks target unsecured public Wi-Fi connections, which allows attackers to intercept communications between devices and servers. Packet sniffing tools capture unencrypted data transmissions, while rogue access points mimic legitimate networks to steal credentials. Evil twin attacks create fake hotspots with names identical to trusted networks, which trap users who connect automatically.
Financial Services Face Maximum Risk
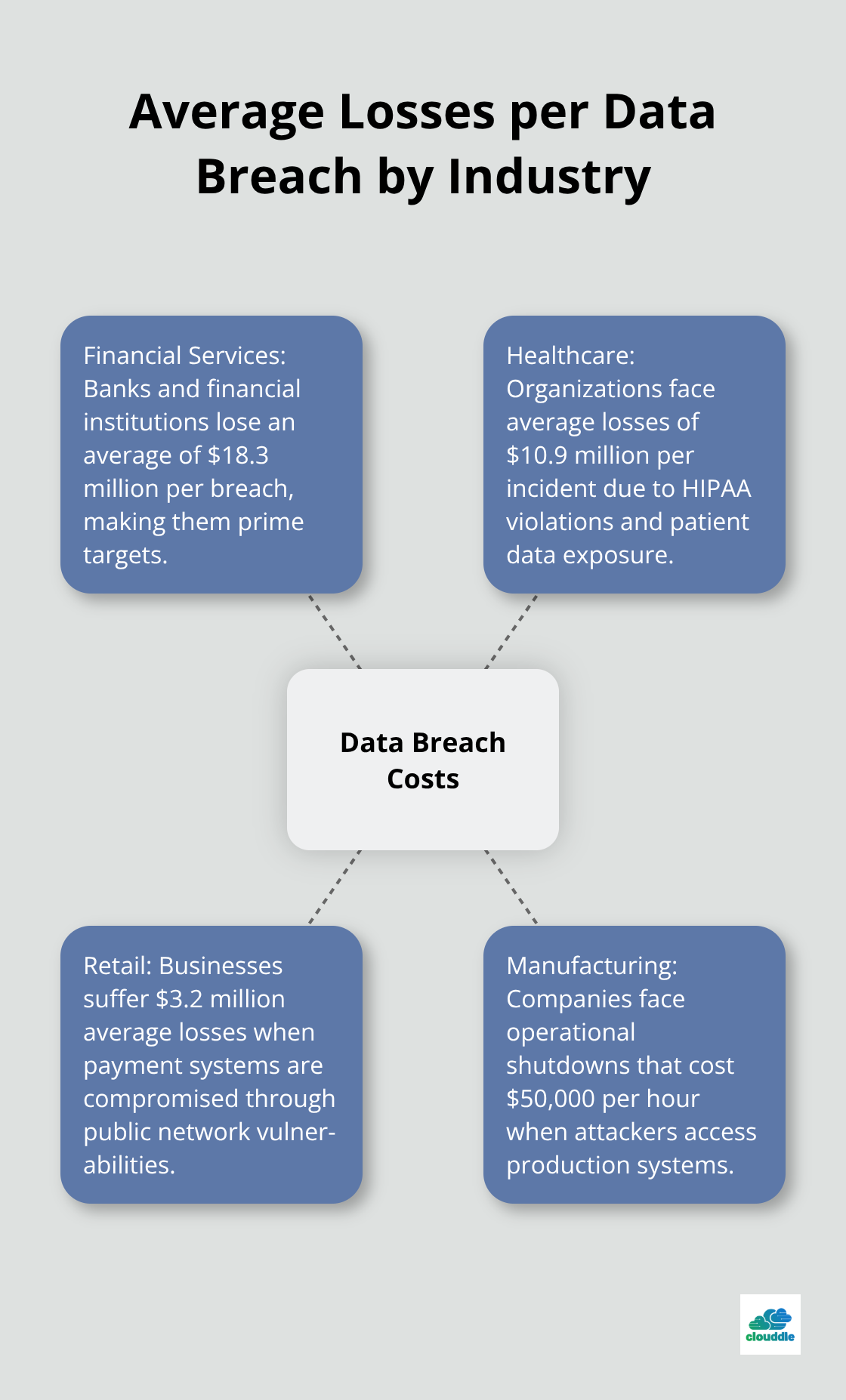
Banks and financial institutions lose an average of $18.3 million per breach based on IBM Security data, which makes them prime targets on public networks. Healthcare organizations follow closely at $10.9 million per incident due to HIPAA violations and patient data exposure. Retail businesses suffer .2 million average losses when payment systems get compromised through public network vulnerabilities. Manufacturing companies face operational shutdowns that cost $50,000 per hour when attackers access production systems through unsecured connections.
Operational Disruption Costs More Than Data Theft
Network breaches force 73% of affected companies to halt operations for 24-72 hours according to Ponemon Institute research. Customer trust erosion results in 31% revenue decline within six months post-breach for retail businesses. Recovery expenses include forensic investigations (which average $240,000), legal fees that reach $1.4 million, and regulatory fines up to $50 million for GDPR violations. Reputation damage persists for 2-3 years, with stock prices that drop 15% on average after major security incidents.
Attack Methods Continue to Evolve
Cybercriminals now deploy AI-powered tools that automate network reconnaissance and exploit detection. Social engineering attacks combine with technical vulnerabilities to bypass multiple security layers simultaneously. Vulnerability exploitation through web applications has increased substantially as a critical path to breaches. These sophisticated threats require equally advanced defensive strategies that go beyond basic firewall protection.
Which Security Technologies Actually Stop Modern Attacks
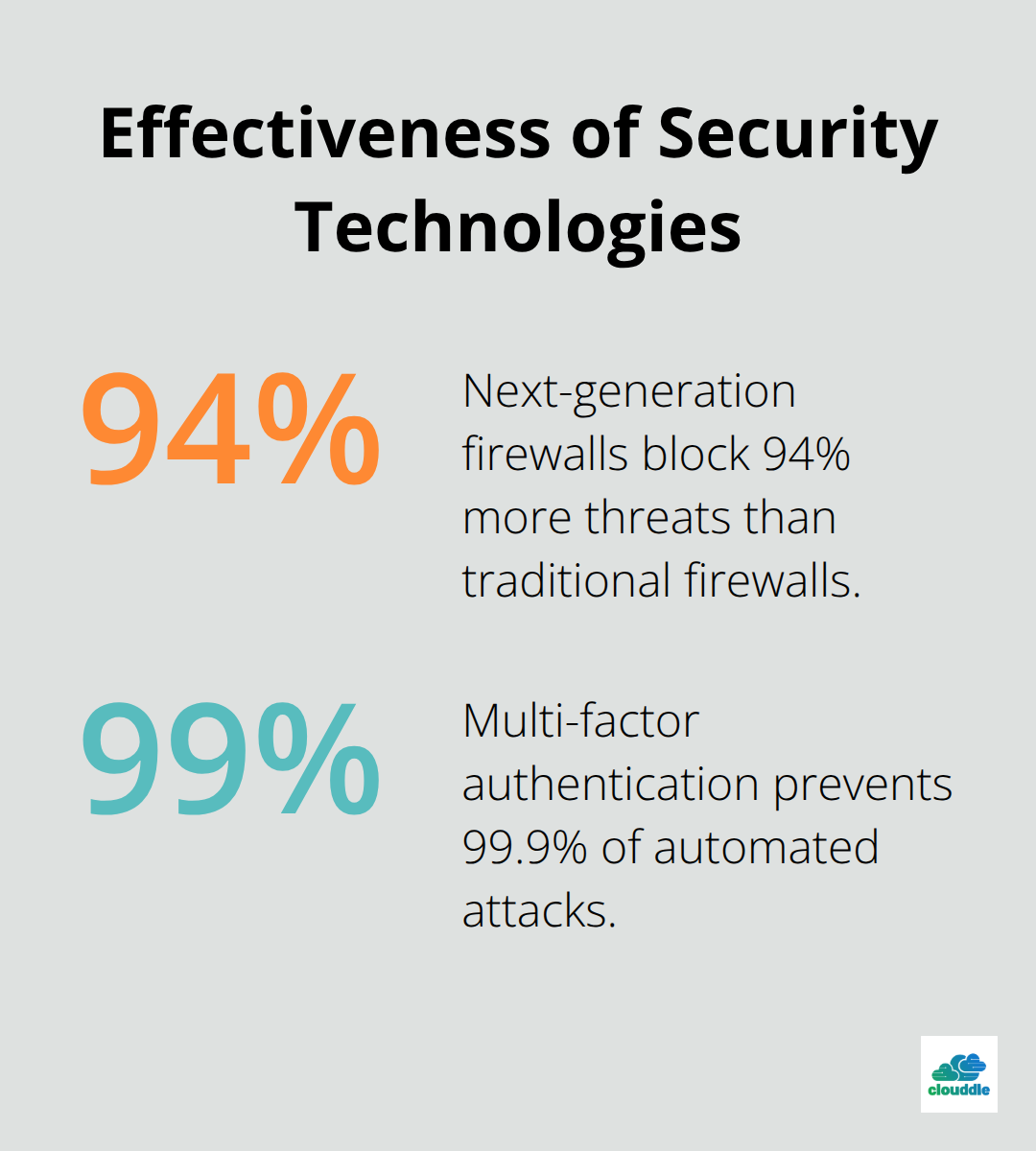
Modern networks need defense systems that adapt to real-time threats rather than static protection models. Next-generation firewalls with deep packet inspection block 94% more threats than traditional firewalls according to Fortinet research. Intrusion prevention systems that use behavioral analytics detect zero-day attacks within 4.2 seconds on average. Network segmentation reduces breach impact by 76% when attackers penetrate perimeter defenses, and endpoint detection systems stop 99.7% of malware before execution when properly configured.
Access Controls That Actually Work
Multi-factor authentication prevents 99.9% of automated attacks according to Microsoft security data, but implementation matters more than adoption. Hardware security keys provide stronger protection than SMS codes, which criminals intercept in 67% of attempted bypasses. Privileged access management systems limit administrative credentials to 2-hour windows and require re-authentication for sensitive operations. Zero-trust architecture validates every connection attempt regardless of network location, which eliminates the 23% of breaches that originate from insider threats.
Vulnerability Management That Prevents Breaches
Weekly vulnerability scans identify 89% of exploitable weaknesses before attackers find them, while monthly assessments miss critical windows that cybercriminals exploit. Automated patch management reduces exposure time from 67 days to 3 days for high-severity vulnerabilities (a significant improvement over manual processes). Penetration tests every quarter reveal configuration errors that scanners miss, and red team exercises test incident response capabilities under realistic attack scenarios. Companies that conduct security audits monthly experience 58% fewer successful breaches than those with annual assessments.
Network Monitoring That Catches Threats Early
Continuous network monitoring detects suspicious activity within minutes rather than the industry average of 287 days. Behavioral analytics establish baseline patterns for normal network traffic and flag deviations that indicate potential breaches. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems correlate data from multiple sources to identify coordinated attacks that single tools miss. Automated threat response systems can isolate compromised devices within 30 seconds of detection.
These technical safeguards form the foundation of network protection, but technology alone cannot defend against all attack vectors. Human factors play an equally important role in maintaining security posture.
How Do You Keep Network Security Strong Over Time
Security technologies provide the foundation, but maintaining protection requires ongoing human effort and systematic processes. Companies that train employees monthly see 70% fewer successful phishing attacks compared to those with annual training sessions according to Proofpoint research. Effective programs focus on real-world scenarios rather than generic presentations, with simulated phishing tests that identify vulnerable staff members within specific departments. Interactive workshops that demonstrate actual attack methods produce 4x better retention rates than passive video training modules.

Staff Training That Actually Changes Behavior
Security awareness programs work best when they target specific job roles with relevant threats. Finance teams need training on business email compromise attacks, with average reported losses of $19,372 per incident based on FBI data. IT staff require advanced education on social engineering techniques that bypass technical controls in 82% of successful breaches. Regular phishing simulations should escalate in complexity, starting with obvious fake emails and progressing to sophisticated spear-phishing attempts that mimic legitimate business communications. Companies that conduct weekly micro-training sessions achieve 90% better security compliance than those with quarterly programs.
Recovery Plans That Work When Disasters Strike
Backup strategies must account for ransomware attacks that target backup systems directly (which happens in 75% of successful encryption incidents according to Veeam research). The 3-2-1 backup rule requires three copies of critical data stored on two different media types with one copy kept offline or air-gapped from network access. Recovery time objectives under 4 hours prevent most operational disruptions, while backup testing every 30 days identifies corruption before emergencies occur. Companies with automated failover systems restore operations 6x faster than those that rely on manual processes during crisis situations.
Monitoring Systems That Catch Problems Fast
Continuous monitoring requires human analysts to interpret automated alerts, as 85% of security tools generate false positives that overwhelm response teams. Security operations centers with 24/7 staffing detect breaches within 200 days on average, while companies without dedicated monitoring take 287 days according to IBM research. Incident response playbooks must include specific escalation procedures, communication templates, and recovery steps that teams can execute under pressure. Regular tabletop exercises test response capabilities every quarter and reveal gaps that standard monitoring cannot identify.
Network Maintenance That Prevents Vulnerabilities
System administrators must apply security patches within 72 hours of release to prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities. Automated patch management systems reduce human error and maintain consistent security posture across all network devices. Network configuration reviews every month identify misconfigurations that create security gaps (often overlooked during routine operations). Firmware updates for network hardware close security holes that attackers exploit to gain initial access to corporate systems.
Final Thoughts
Network security private communications in a public world demands a comprehensive approach that combines advanced technology with human vigilance. The statistics speak clearly: companies with next-generation firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring reduce breach risks by over 75% compared to those that rely on basic protection. Success requires more than the installation of security tools.
Weekly vulnerability scans, monthly staff training, and quarterly penetration tests create the systematic approach that stops modern attacks. Organizations that implement these practices experience 58% fewer successful breaches while they maintain operational efficiency. The complexity of today’s threat landscape makes professional security management essential rather than optional.
We at Clouddle understand that businesses need comprehensive technology solutions that integrate networking, security, and monitoring without massive upfront investments. Companies that conduct security audits within 30 days, implement automated patch management, and establish 24/7 monitoring capabilities protect their operations effectively. Those that delay these measures face average breach costs of $4.45 million (while proactive organizations safeguard their revenue streams).


