Network security risks have increased by 600% since 2020, with cyberattacks costing businesses an average of $4.45 million per breach according to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report.
At Clouddle, we see organizations struggling daily with evolving threats that can cripple operations within minutes. The key lies in proactive identification and swift mitigation strategies.
This guide covers the most dangerous vulnerabilities facing networks today and provides actionable steps to protect your infrastructure before attackers strike.
What Are the Most Dangerous Network Threats Today?
Malware Infections That Paralyze Operations
Ransomware attacks have become the primary weapon of choice for cybercriminals, with the average ransom reaching $2.73 million in 2024, almost an increase of $1 million from 2023. These attacks specifically target unpatched software vulnerabilities, which makes Windows 7 systems and other legacy platforms particularly vulnerable. The financial impact extends far beyond ransom payments, as downtime from ransomware creates substantial operational costs. What makes this threat particularly devastating is that organizations face significant challenges in complete data recovery, though 97 percent of organizations whose data had been encrypted got it back.

Unauthorized Access Through Weak Authentication
Insider threats and compromised credentials account for a significant portion of security breaches, with companies now sharing confidential information with numerous third parties. Traditional password-based authentication has proven insufficient against sophisticated attackers who exploit human error, which causes 95% of all cybersecurity breaches. Remote work environments have amplified this risk, as employees frequently access company networks through unsecured home connections and personal devices.
DDoS Attacks That Cripple Network Resources
Distributed Denial of Service attacks have evolved beyond simple traffic floods to sophisticated multi-vector assaults that can render entire network infrastructures inaccessible. Modern botnets, which consist of compromised IoT devices and unprotected computers, generate attack volumes that can overwhelm even well-protected networks. These attacks often serve as smokescreens for more serious intrusions and allow attackers to exploit vulnerabilities while IT teams focus on restoring service availability.
The next step involves implementing systematic approaches to detect these threats before they can cause damage to your network infrastructure.
How Do You Detect Network Threats Before They Strike?
Effective threat detection requires continuous monitoring tools that track network traffic patterns and identify anomalies in real-time. SIEM systems like Splunk and IBM QRadar collect and analyze log data from multiple sources, which provides centralized visibility into potential security incidents. Network packet analyzers such as Wireshark and SolarWinds NPM monitor data flow and detect suspicious activities that traditional firewalls might miss. These tools should monitor bandwidth usage, connection attempts, and user behavior patterns to establish baseline activities and flag deviations that indicate potential breaches.
Automated Vulnerability Scanners
Organizations must deploy automated vulnerability scanners like Nessus, OpenVAS, and Qualys VMDR to identify security weaknesses before attackers exploit them. These tools perform comprehensive scans of network infrastructure, web applications, and connected devices to detect unpatched software, misconfigurations, and exposed services. Regular scan schedules should run weekly for critical systems and monthly for less sensitive infrastructure. Penetration testing through services like Rapid7 or Cobalt provide deeper analysis when they simulate real-world attack scenarios and validate whether identified vulnerabilities can actually be exploited.
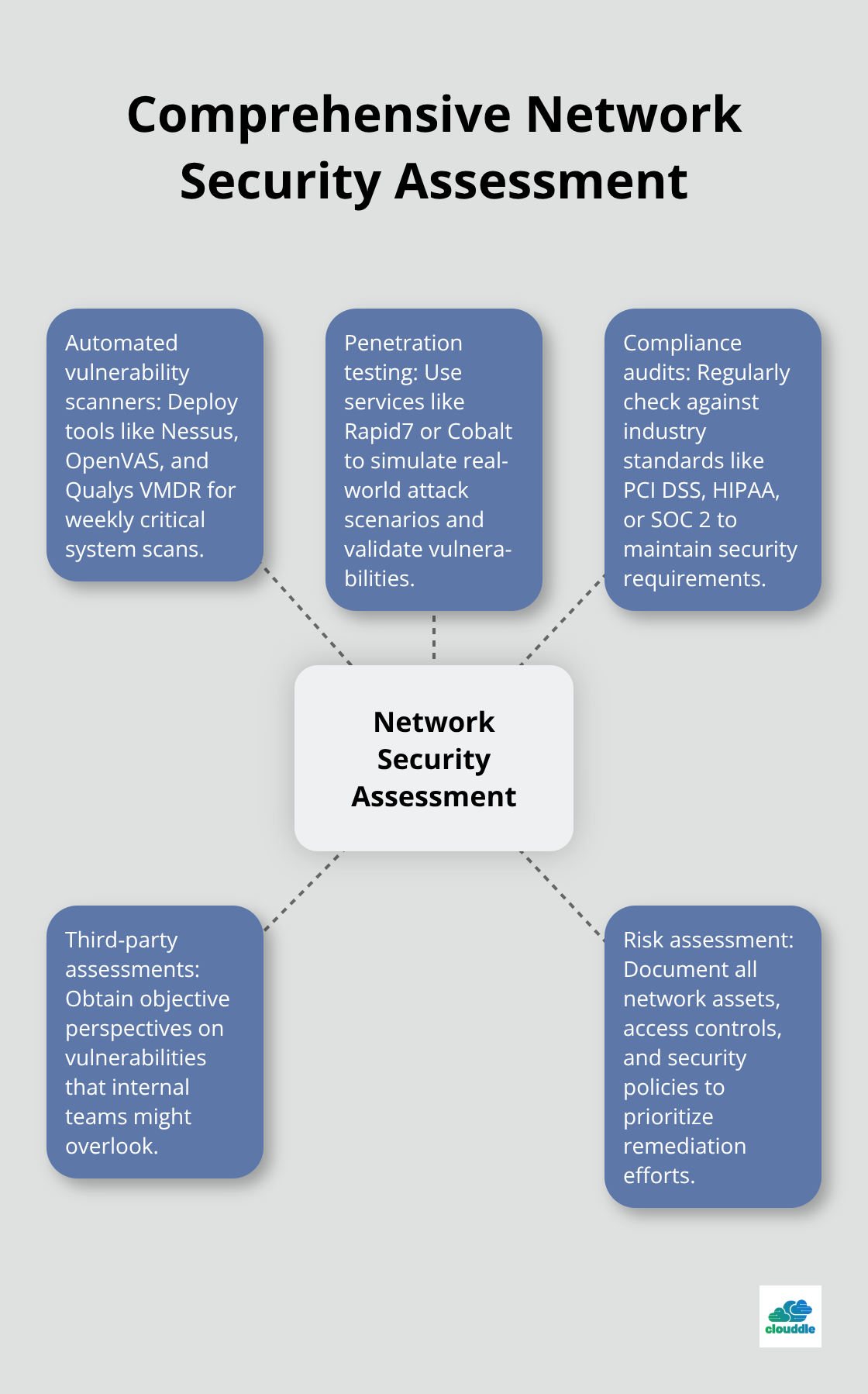
Compliance Audits and Risk Assessment
Security audits that use frameworks like NIST SP 800-53 and ISO 27001 provide structured approaches to evaluate current security posture and identify gaps in protection. Third-party security assessments offer objective perspectives on vulnerabilities that internal teams might overlook due to familiarity with existing systems (especially legacy systems that receive less attention). Regular compliance checks against industry standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or SOC 2 help maintain security requirements and avoid regulatory penalties. Documentation of all network assets, access controls, and security policies enables thorough risk assessments and helps prioritize remediation efforts based on potential business impact.
Once you identify these threats and vulnerabilities, the next step involves implementing comprehensive security measures that prevent attackers from exploiting weaknesses in your network infrastructure.
What Security Measures Actually Stop Network Attacks?
Multi-Factor Authentication Deployment
Multi-factor authentication reduces breach risk according to Microsoft security research, making it the most effective single security control organizations can implement. Deploy MFA on all administrative accounts first, then extend coverage to standard user accounts that access sensitive systems. Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator, and hardware tokens like YubiKey provide robust second-factor verification that stops credential-based attacks. Configure MFA for VPN access, email systems, cloud applications, and administrative interfaces to create multiple security barriers. Organizations should avoid SMS-based authentication due to SIM swapping vulnerabilities and instead use app-based or hardware token solutions.

Automated Patch Management Systems
With over 30,000 new security vulnerabilities identified in 2024 representing a 17% year-over-year increase, many organizations still rely on manual update processes that leave critical gaps. Microsoft WSUS, Red Hat Satellite, and Automox provide centralized patch management that automatically tests and deploys security updates across entire network infrastructures. Set up automatic patches for critical security updates within 72 hours of release, while you schedule regular maintenance windows for non-critical patches. Legacy systems that run Windows 7 or older operating systems require immediate replacement or isolated network segments with additional monitoring (especially in healthcare and financial sectors). Maintain detailed inventories of all software assets and their current patch levels to identify vulnerable systems quickly.
Security Training Programs That Work
Security awareness training reduces phishing susceptibility by 70% when conducted monthly rather than annually, according to Proofpoint research. Implement simulated phishing campaigns through platforms like KnowBe4 or Cofense to test employee responses and provide immediate feedback. Focus training on how employees recognize social engineering tactics, secure password practices, and proper incident reporting procedures. Measure training effectiveness through click-through rates on simulated attacks and track improvement over time. Role-specific training for IT administrators, finance teams, and executives addresses the unique threats each group faces and provides targeted protection strategies (particularly important for remote work environments).
Final Thoughts
Network security risks continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace, with organizations facing increasingly sophisticated threats that can devastate operations within minutes. The strategies outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive framework for identifying vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them and implementing effective countermeasures that actually prevent breaches. Proactive security management has become non-negotiable in today’s threat landscape.
Organizations that wait for incidents to occur face average costs of $4.45 million per breach, while those implementing continuous monitoring, automated patch management, and multi-factor authentication significantly reduce their risk exposure. The 600% increase in network security risks since 2020 demonstrates that reactive approaches no longer suffice. Companies must prioritize multi-factor authentication across all systems, establish automated vulnerability scanning schedules, and conduct monthly security awareness training for all employees.
At Clouddle, we understand that managing comprehensive network security requires specialized expertise and resources that many organizations lack internally. Our managed IT and security services provide 24/7 monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities that protect your infrastructure while allowing you to focus on core business operations. Regular compliance audits using frameworks like NIST SP 800-53 help maintain security posture and identify emerging gaps before they become critical vulnerabilities.


