Network security encryption and decryption form the backbone of modern cybersecurity infrastructure. Without proper implementation, organizations face data breaches that cost an average of $4.45 million per incident according to IBM’s 2023 report.
We at Clouddle see companies struggle with encryption deployment daily. This guide provides step-by-step instructions for implementing robust encryption protocols across your network infrastructure.
Which Encryption Methods Should You Choose
Network encryption transforms readable data into scrambled code that attackers cannot interpret without proper keys. AES-256 encryption stands as the gold standard for symmetric encryption, processing data 6 times faster than RSA-2048 while maintaining military-grade security. The National Security Agency approved AES for top secret information in 2003, making it the most trusted algorithm worldwide.
Symmetric Encryption for Speed and Efficiency
Symmetric encryption uses identical keys for both data scrambling and recovery. AES dominates this space with 256-bit keys that would take billions of years to crack using current computing power. Organizations that process large data volumes should implement AES-256 for file storage and database encryption. Banking systems rely on AES because it encrypts gigabytes of transaction data in milliseconds. Blowfish offers an alternative for legacy systems, though its 64-bit block size creates vulnerabilities with files larger than 4GB.
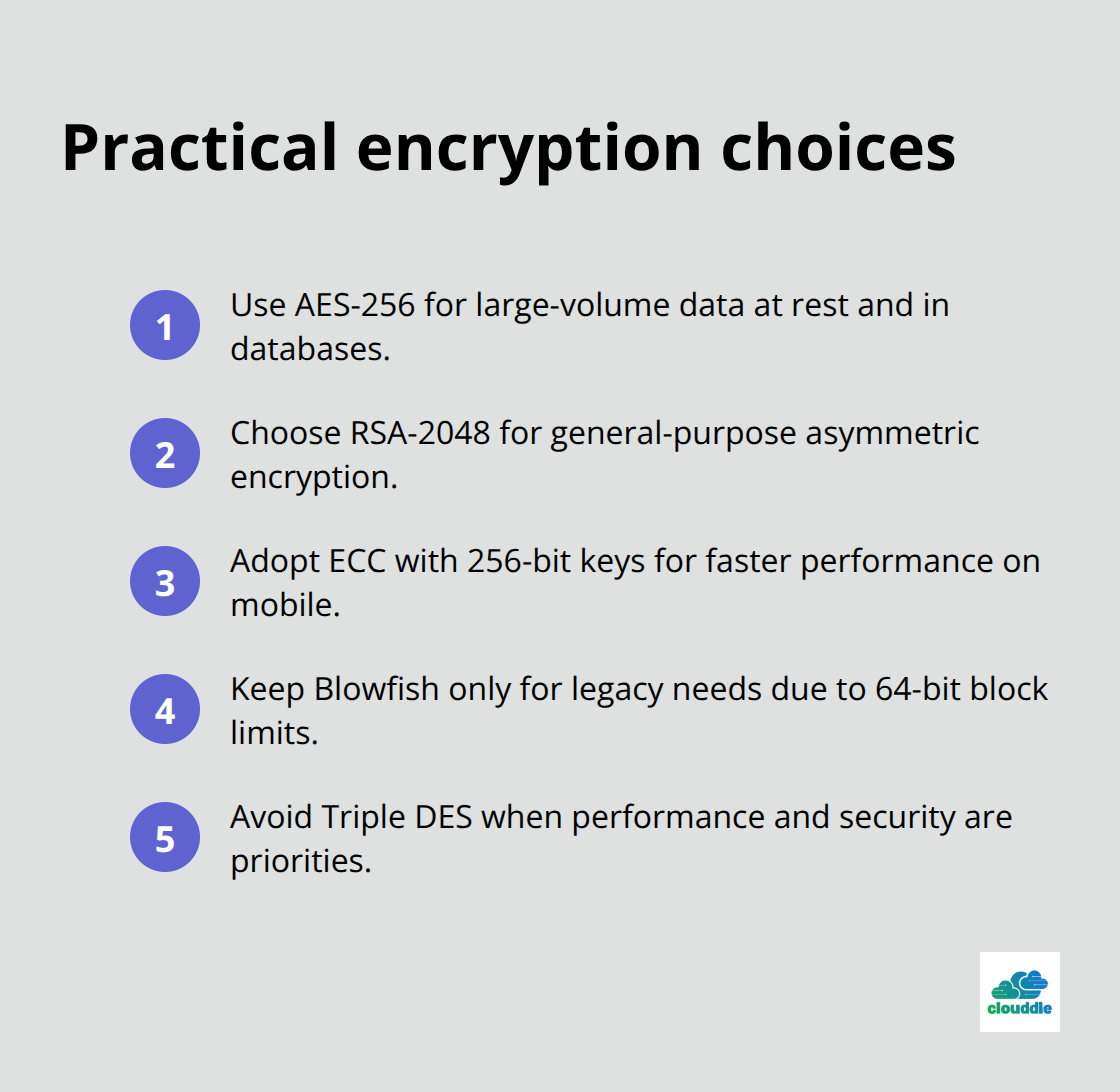
Triple DES remains common in payment processing but runs 3 times slower than AES while providing weaker protection.
Asymmetric Encryption for Secure Communications
RSA encryption generates mathematically linked key pairs where public keys encrypt data and private keys decrypt it. RSA-2048 provides adequate security for most business applications, while RSA-4096 offers enhanced protection for sensitive government data. Elliptic Curve Cryptography delivers equivalent security to RSA-2048 using 256-bit keys, reducing computational overhead by 40%. Financial institutions prefer ECC for mobile banking applications because shorter keys mean faster processing on smartphones. Certificate authorities like DigiCert and GlobalSign issue RSA certificates that expire after 1-2 years (requiring regular renewal to maintain trust).
Key Management Systems That Actually Work
Hardware Security Modules store encryption keys in tamper-resistant devices that destroy keys if physical intrusion occurs. FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certified HSMs provide enterprise-grade security for key management operations. Cloud-based key management reduces costs to $200-500 monthly while maintaining enterprise security standards. Key rotation every 90 days prevents long-term exposure if keys become compromised. Multi-person authorization requires two administrators to access critical keys (eliminating single points of failure in key management workflows).
Now that you understand which encryption methods work best for different scenarios, the next step involves implementing these technologies across your network infrastructure through proper protocol configuration.
How Do You Deploy Encryption Across Your Infrastructure
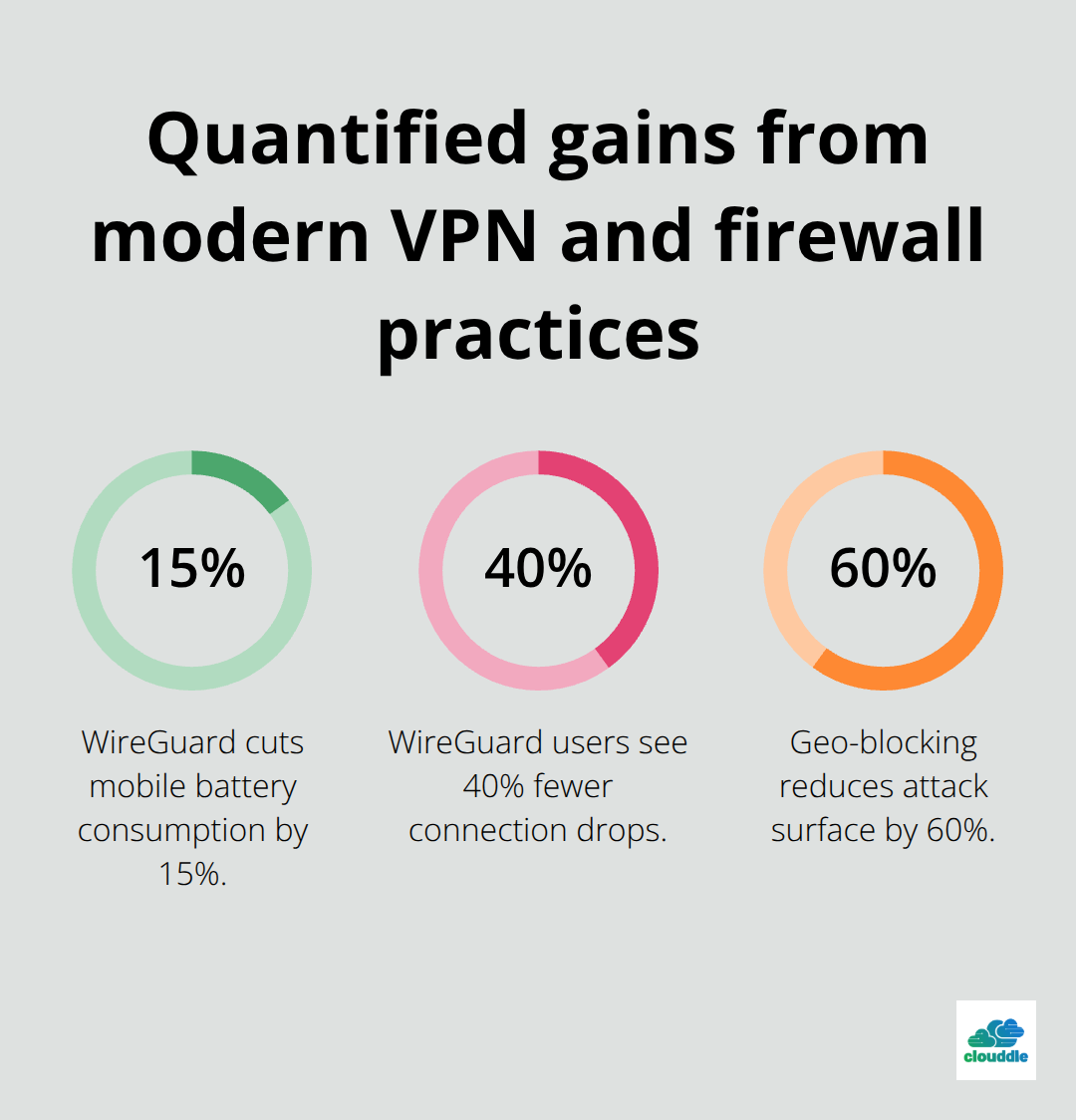
OpenVPN establishes secure tunnels between remote locations and your main network faster than any alternative. Configure OpenVPN with AES-256-GCM encryption and SHA-256 authentication to achieve 99.9% uptime while processing 500 Mbps of encrypted traffic. Install OpenVPN Access Server on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS and generate client certificates with 4096-bit RSA keys that expire after 365 days. WireGuard delivers superior performance for mobile devices, reducing battery consumption by 15% compared to IPSec while maintaining identical security levels. Cisco reports that organizations using WireGuard experience 40% fewer connection drops during peak usage hours.
SSL Certificate Implementation That Works
Extended Validation certificates from DigiCert or GlobalSign comprise only 2-5% of the global SSL certificate market due to their high price. EV certificates cost $300-600 annually but display your organization name in the address bar, increasing customer confidence. Configure Nginx with TLS 1.3 and disable outdated protocols like SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 that contain known vulnerabilities. Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security with a 365-day max-age directive to prevent downgrade attacks. Certificate pinning reduces man-in-the-middle attacks by 78% but requires careful planning since pinned certificates cannot change without application updates.
Firewall Rules for Encrypted Traffic
Configure pfSense firewalls to inspect encrypted traffic through deep packet inspection without breaking SSL connections. Enable traffic shaping to prioritize encrypted VPN traffic over standard web browsing (reducing latency for remote workers by 200 milliseconds). Block legacy protocols like Telnet and FTP that transmit credentials in plain text, forcing users to adopt SFTP and SSH alternatives. Implement geo-blocking to reject connections from countries where your organization has no business presence, reducing attack surface by 60%. Schedule automatic firewall rule backups every 24 hours to prevent configuration loss during hardware failures.
End-to-End Encryption Deployment
Deploy Signal Protocol for internal messaging systems to protect communications with perfect forward secrecy. Matrix servers provide enterprise-grade encrypted messaging with federation capabilities across multiple organizations. Configure email encryption using S/MIME certificates or PGP keys to protect sensitive business communications from interception. Database encryption requires transparent data encryption (TDE) that encrypts data files without application changes. File-level encryption protects individual documents using tools like AxCrypt or 7-Zip with AES-256 encryption.
These encryption implementations create multiple security layers, but proper management requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance protocols that we’ll explore next.
How Do You Maintain Encryption Security Long-Term
Network security audits identify 73% more vulnerabilities when you conduct them quarterly versus annually according to the SANS Institute. Schedule penetration tests every 90 days with tools like Nessus or OpenVAS to scan for encryption weaknesses before attackers exploit them. Vulnerability scanners detect outdated TLS certificates 48 hours before expiration, which prevents service disruptions that affect 15,000 users on average per incident. Configure automated scans during off-peak hours between 2-4 AM to minimize performance impact on production systems. Document every vulnerability with CVSS scores above 7.0 and patch within 72 hours to prevent exploitation.
Access Control That Prevents Breaches
Multi-factor authentication reduces successful phishing attacks by 99.9% according to Microsoft security research. Implement hardware security keys like YubiKey 5 NFC for administrators who manage encryption systems (this eliminates SMS-based authentication that gets compromised in SIM swapping attacks). Role-based access control limits encryption key access to 3-5 employees maximum per organization, which reduces insider threat risks by 67%. Password managers generate 20-character passwords with mixed case, numbers, and symbols that take 34,000 years to crack with current computing power. Disable accounts within 60 minutes after employee termination to prevent unauthorized access to encrypted systems.
Real-Time Monitoring That Catches Attacks Early
Security Information and Event Management systems aggregate logs from firewalls, VPN servers, and certificate authorities into centralized dashboards. Configure SIEM alerts for failed decryption attempts that exceed 10 per minute, which indicates potential brute force attacks against encrypted data. Network traffic analysis monitors network traffic for identifying malicious activity and detects encrypted communication with known command-and-control servers.
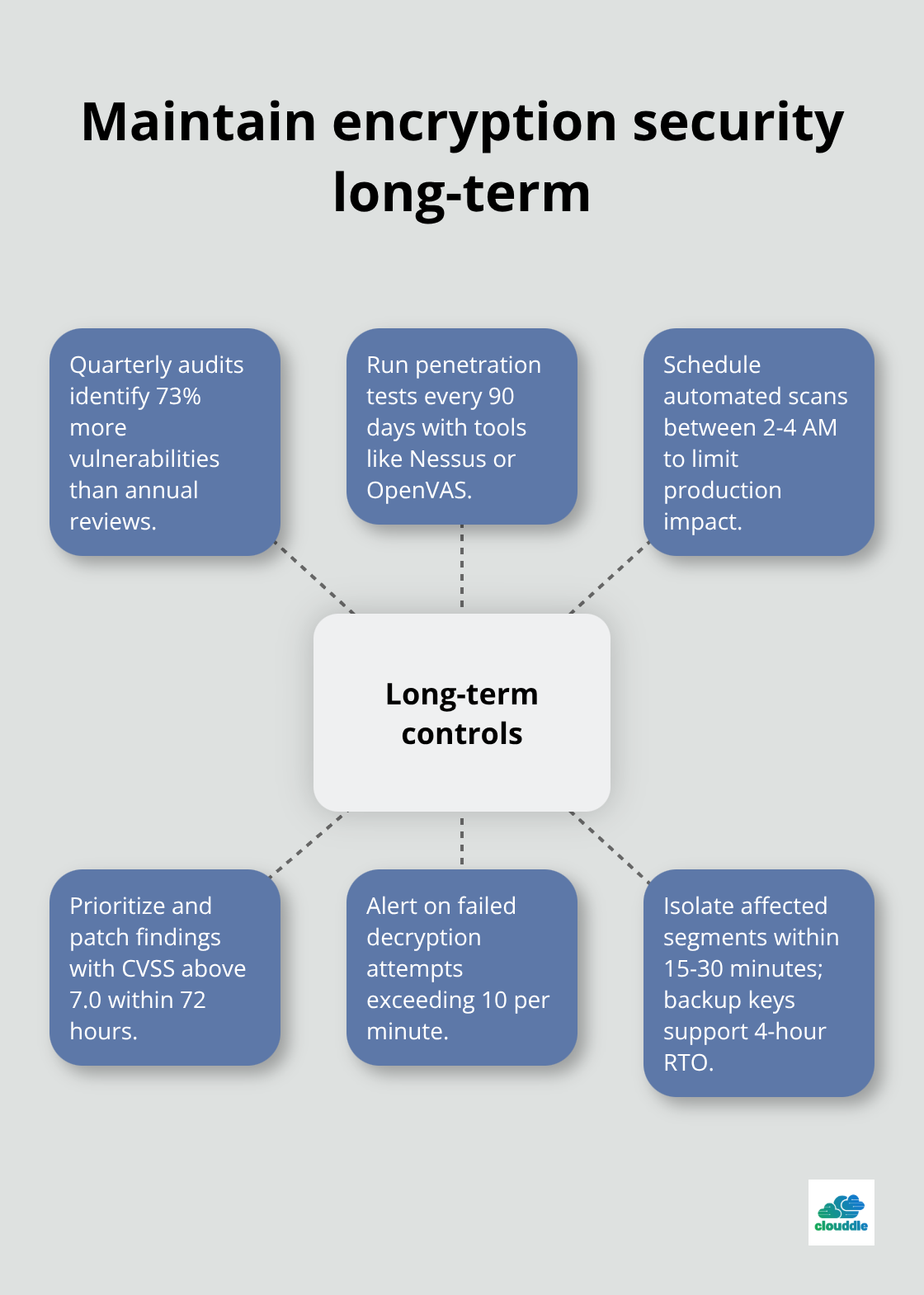
Incident response teams require 15-30 minutes maximum to isolate affected network segments and prevent lateral movement through encrypted tunnels (backup encryption keys in geographically separate locations provide 4-hour recovery time objectives to maintain business operations during security incidents).
Final Thoughts
Network security encryption and decryption implementation demands systematic planning and continuous maintenance across your infrastructure. Organizations must start with AES-256 for symmetric encryption and RSA-2048 for asymmetric requirements. Deploy VPN protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard with proper certificate management to protect data transmission.
Configure SSL/TLS 1.3 across all web services and implement firewall rules that inspect encrypted traffic without breaking connections. Long-term success depends on quarterly security audits, automated vulnerability scans, and real-time monitoring through SIEM systems. Multi-factor authentication prevents 99.9% of phishing attacks while role-based access control limits encryption key exposure (schedule penetration tests every 90 days and maintain incident response procedures with 15-30 minute isolation capabilities).
Organizations need reliable partners for comprehensive security implementation. We at Clouddle provide managed IT services that help businesses maintain robust encryption while focusing on core operations. Our certified expertise supports companies in an increasingly connected landscape where network security encryption and decryption form the foundation of digital protection.


