IT projects fail at alarming rates, with studies showing that 70% exceed their budgets or timelines. The importance of IT project management has never been more apparent as businesses rely heavily on technology initiatives.
At Clouddle, we see organizations struggle daily with poorly managed IT implementations that drain resources and delay critical business objectives. Effective project management transforms these challenges into successful outcomes.
What Makes IT Project Management Actually Work
Successful IT project management starts with ruthless scope definition that eliminates ambiguity before it destroys your timeline. The Project Management Institute reports that only 52% of organizations create proper scoping documents, yet this single step determines whether your project succeeds or becomes another statistic. Define exactly what gets built, what stays out, and who makes scope change decisions. Document every requirement with measurable acceptance criteria and get stakeholder signatures on the final scope. Teams that skip this step face scope creep that derails projects, with IT project success rates between 28 to 35%.
Resource Planning That Prevents Disaster
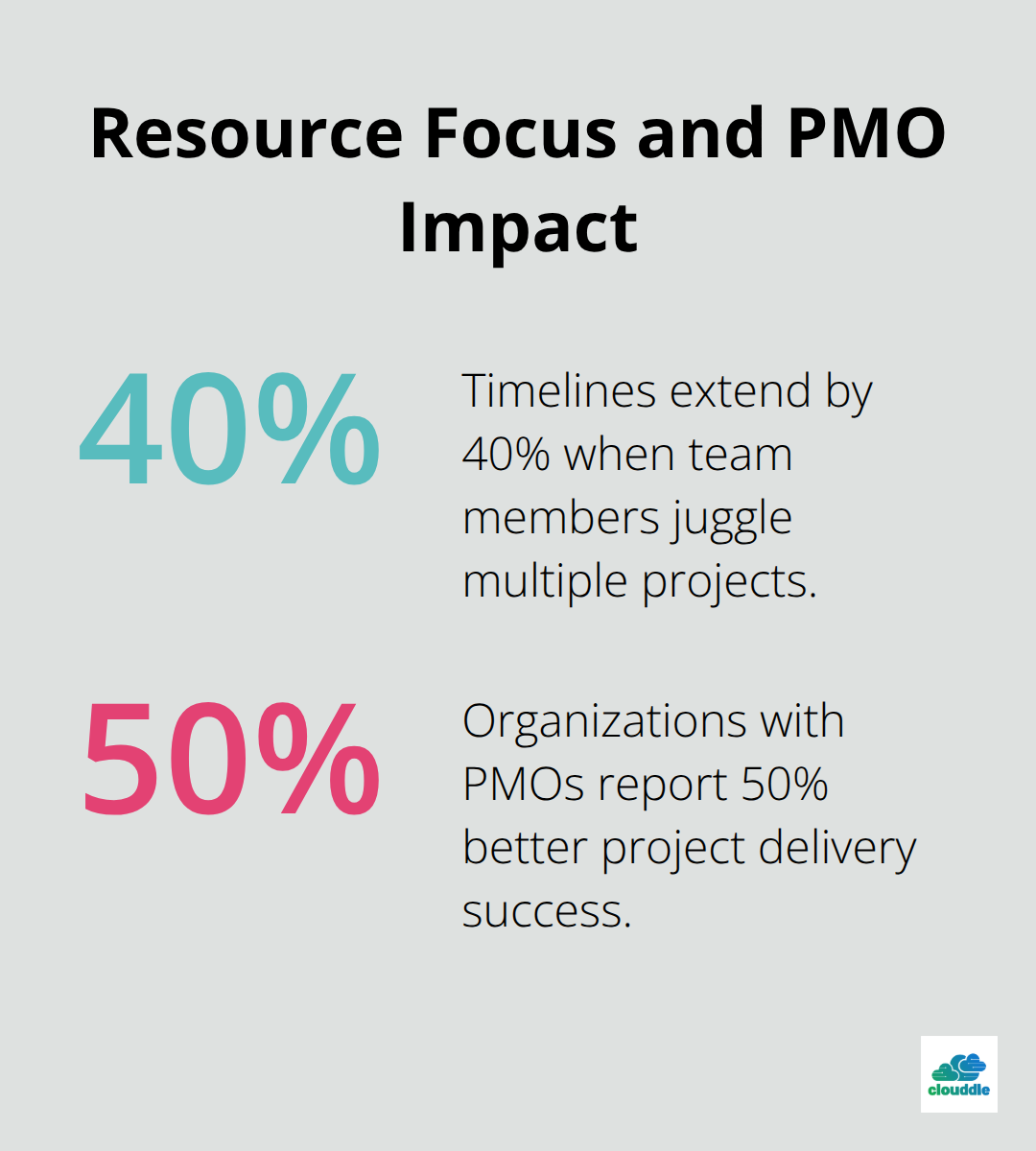
Resource allocation failures kill more IT projects than technical challenges ever will. Assign specific team members to defined roles with clear accountability metrics rather than hope generalists will figure it out. The average IT project team member works on 3.2 projects simultaneously, which creates focus problems that extend timelines by 40%. Dedicate your best developers to single projects and protect their time from excessive meetings. Track resource utilization weekly and reassign team members immediately when bottlenecks appear. Organizations with dedicated Project Management Offices report 50% better project delivery success because they manage resources systematically rather than reactively.
Risk Management Through Data
Identify project risks with historical data from similar implementations rather than generic risk templates that miss real threats. The average IT project faces 27% cost overruns, but teams that conduct weekly risk assessments reduce this to 12% (according to PMI studies). Create risk registers that track probability and impact scores for technical integration challenges, vendor delays, and skill gaps. Assign risk owners who monitor specific threats and execute mitigation plans when triggers occur. Test your backup plans before you need them and maintain vendor relationships that provide emergency support when primary solutions fail.
Communication Frameworks That Work
Establish clear communication channels that prevent the breakdowns where ineffective communications is the primary contributor to project failure one third of the time. Schedule weekly status meetings with defined agendas and require written updates from all team leads. Use project management tools that centralize documentation and track progress in real-time rather than rely on email chains that lose critical information. Create escalation paths that route issues to decision-makers within 24 hours and document all major decisions with timestamps and rationale. Teams with structured communication protocols complete projects 23% faster than those without formal frameworks.
These foundational elements set the stage for addressing the specific challenges that plague most IT implementations.
Common IT Project Management Challenges and Solutions
Budget overruns plague IT projects because teams underestimate integration complexity and change request frequency. The Standish Group reports that only 29% of IT projects finish on time, on budget, and with required features, while the average cost overrun reaches 27% according to PMI data. Combat budget creep with weekly budget reviews that track actual expenses against forecasts and establish change control boards that evaluate every modification request with cost impact analysis. Set aside 20% contingency funds for unexpected technical challenges and vendor delays, then protect this buffer with executive approval requirements for access. Organizations that monitor expenses weekly reduce cost overruns to 12% compared to those that track monthly. Implementing IT cost saving strategies helps maintain budget discipline throughout project lifecycles.
Timeline Disasters Start With Poor Estimates
Timeline delays stem from optimistic plans that ignore dependency chains and resource conflicts between concurrent projects. Teams consistently underestimate testing phases (40% shortfall) and integration work (60% shortfall), according to Nucleus Research findings. Create realistic timelines with 25% buffer added to development estimates and 50% to integration phases, then track progress through daily standups that identify blockers within 24 hours. Use critical path analysis to identify tasks that directly impact project completion dates and assign your strongest team members to these activities. Map all external dependencies including vendor deliveries, third-party integrations, and regulatory approvals, then build alternative paths when primary vendors face delays.

Technology Integration Problems That Kill Projects
Technology compatibility issues destroy project momentum when teams discover integration problems during development rather than planning phases. Legacy system constraints account for 45% of technical project failures because teams assume modern solutions will connect seamlessly with existing infrastructure. Conduct technical feasibility assessments before project kickoff that test API connections, data format compatibility, and security protocol alignment between all systems. Build integration prototypes during planning phases that validate critical data flows and identify authentication challenges early. Document every integration point with fallback procedures and maintain vendor support contracts that provide emergency assistance when primary integrations fail during deployment. Consider outsourced IT solutions when internal teams lack specialized integration expertise.
These challenges demand systematic approaches that transform project chaos into predictable success through proven methodologies and stakeholder engagement strategies.
Best Practices for Successful IT Project Implementation
Agile methodologies eliminate the project failures that plague traditional waterfall approaches. Teams deliver functional software every two weeks instead of waiting months for complete systems. The Wellingtone study shows that 24.6% of companies have adopted agile practices, yet agile projects have a 42% success rate compared to Waterfall’s 13% success rate.
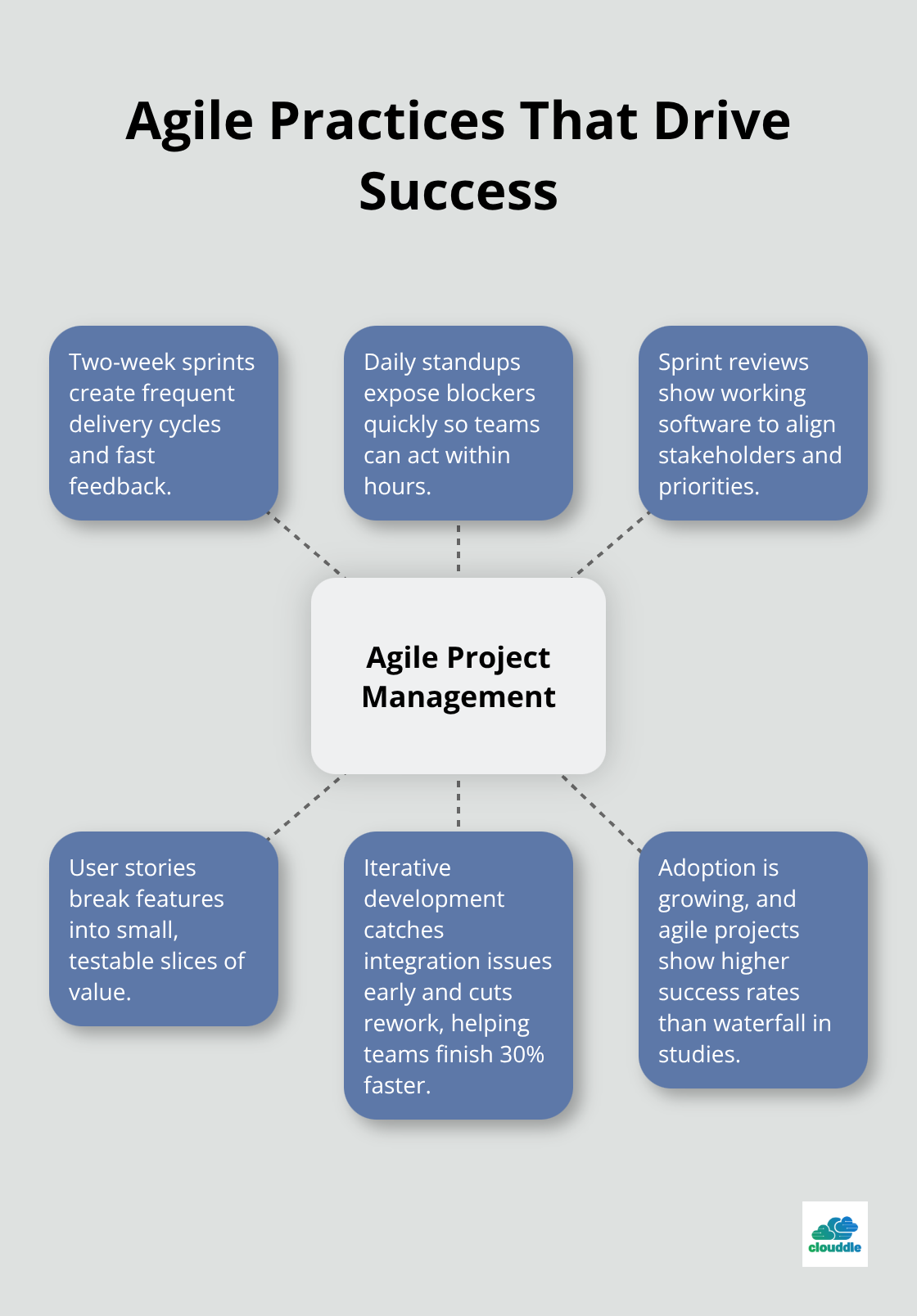
Teams implement two-week sprints with daily standups that identify blockers within hours rather than weeks. Sprint reviews show stakeholders actual functionality instead of theoretical progress reports. Large features break down into small user stories that deliver measurable value, with priorities based on business impact rather than technical preferences. Teams that embrace iterative development complete projects 30% faster because they catch integration problems early when fixes cost less than major rework cycles.
Stakeholder Engagement Through Live Demonstrations
Stakeholder engagement fails when teams provide status reports instead of functional demonstrations that show real progress toward business objectives. Weekly demo sessions let stakeholders interact with actual features rather than review PowerPoint slides about theoretical functionality. PMI research indicates that organizations that prioritize stakeholder communication achieve 73% higher project success rates, yet 47% of companies lack real-time access to project performance indicators. Stakeholder feedback loops capture requirements changes within 48 hours, and change control processes evaluate impact before implementation. All decisions get documented with timestamps and rationale, then meeting summaries distribute within 24 hours to prevent miscommunication that derails project momentum.
Quality Assurance Protocols That Prevent Production Failures
Quality assurance requires systematic testing protocols that validate functionality before deployment rather than hope integration works in production environments. Automated testing suites run with every code commit and maintain test coverage above 80% for critical system components. Project management helps teams organize, track, and execute work within a project, but only when teams test continuously rather than batch testing at project end. Testing environments mirror production systems exactly, then user acceptance testing executes with actual business users who validate requirements against real workflows. Rollback procedures restore previous versions within 30 minutes when deployment issues occur, and vendor support agreements provide emergency assistance during critical system failures.
Final Thoughts
The importance of IT project management becomes evident when you examine the dramatic difference between successful and failed implementations. Organizations that apply systematic project management practices achieve 73% higher success rates while they reduce cost overruns from 27% to 12%. These improvements translate directly into competitive advantages through faster time-to-market, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Effective IT project management transforms business operations when it eliminates the chaos that destroys productivity and wastes resources. Teams complete projects 30% faster with agile methodologies, while proper resource allocation prevents the focus problems that extend timelines by 40% (according to industry research). Companies gain predictable project outcomes that support strategic planning and budget forecasting.
Start to improve your project management processes when you implement weekly risk assessments and establish clear communication protocols. Document all requirements with measurable acceptance criteria and create dedicated project teams that focus on single initiatives. Consider partnering with technology solution providers that offer managed IT services and 24/7 support to handle complex integrations while your teams focus on core business objectives.


