Network protocols are the backbone of modern digital communication, but they can also be a weak link in your security chain. At Clouddle, we’ve seen firsthand how understanding these protocols is essential for maintaining robust cybersecurity.
This blog post will explore common network protocols, their vulnerabilities, and best practices for securing them. We’ll provide practical tips to help you strengthen your network’s defenses against potential threats.
Network Protocols Demystified: The Building Blocks of Digital Communication
Network protocols form the foundation of our digital world. These rules govern data movement across networks, ensuring seamless communication between devices. Understanding these protocols can significantly enhance a company’s security strategy.
TCP/IP: The Internet’s Core
TCP/IP serves as the internet’s backbone. This protocol suite ensures data packets reach their destination accurately and in the correct order. Businesses depend on this protocol suite as it underpins most network applications.
HTTP and HTTPS: Web Communication Cornerstones
HTTP powers the web, while HTTPS adds encryption for enhanced security. This shift has dramatically reduced data interception risks during transmission.
FTP: File Transfer Workhorse
FTP facilitates file transfers between networked computers. However, standard FTP lacks data encryption. Security experts recommend using SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) instead, which incorporates SSH encryption for file transfers.
SMTP: Email’s Backbone
SMTP stands as the standard protocol for sending emails. However, it remains vulnerable to spam and email spoofing. Implementation of additional security measures like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can reduce email-based threats.
DNS: The Internet’s Directory
DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses. While essential for web navigation, it’s a frequent target for attacks. In 2024, ICANN generated a new trust anchor for the DNS root which is planned to become active in 2026, highlighting the ongoing efforts to enhance DNS security.
Understanding these protocols marks the first step towards robust network security. The next section will explore the vulnerabilities associated with these protocols and how attackers exploit them. This knowledge will equip you to better protect your digital assets and maintain a secure network infrastructure.
Network Protocol Vulnerabilities Exposed
The Insidious Nature of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks pose a severe threat to network security. In these scenarios, attackers intercept communication between two parties, potentially eavesdropping on or altering the exchanged data. A report by Positive Technologies reveals that 63% of companies are vulnerable to MitM attacks due to insufficient protection of data transmission channels.

ARP spoofing exemplifies a common MitM attack. An ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a Man in the Middle (MitM) attack that allows attackers to intercept communication between network devices. To mitigate this risk, organizations should implement ARP spoofing detection tools and use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for sensitive communications.
The Devastating Impact of Denial of Service Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can cripple networks by overwhelming them with traffic or exploiting protocol weaknesses. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) reported a 151% increase in DoS attacks in 2024 compared to the previous year.
TCP SYN flood attacks (a notable example) exploit the TCP handshake process. A SYN flood attack is a type of network-based denial-of-service (DoS) attack in which an attacker overwhelms a target system by sending a large number of SYN packets. Organizations should implement SYN cookies and rate limiting on their network devices to defend against such attacks.
Protocol-Specific Vulnerabilities: A Moving Target
Each network protocol has its unique set of vulnerabilities. The DNS protocol, for instance, is susceptible to cache poisoning attacks, where malicious actors inject false information into a DNS cache. ICANN reported a 22% increase in DNS-related attacks globally in 2024.
To protect against DNS vulnerabilities, organizations should implement DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) and regularly update their DNS software. Additionally, using a reputable DNS filtering service can block known malicious domains.
HTTP/2, despite its performance benefits, has shown vulnerabilities to rapid reset attacks. In 2024, a critical flaw in HTTP/2 implementation led to widespread DDoS attacks affecting major cloud providers. Organizations must stay vigilant about protocol-specific vulnerabilities and apply patches promptly when they become available.
Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards will significantly enhance a network’s resilience against potential threats. The next section will discuss best practices for securing network protocols and maintaining a robust security posture.
How to Fortify Your Network Protocols
Encryption: Your First Line of Defense
Encryption plays a vital role in today’s threat landscape. A 2024 IBM Security report revealed that encrypted data breaches cost organizations 29% less than unencrypted breaches. Implement TLS 1.3 for all web traffic to enhance speed and security. For email, use STARTTLS to encrypt SMTP connections. Switch from FTP to SFTP or FTPS for file transfers to ensure data confidentiality during transit.
Patch Management: Stay Ahead of Threats
Unpatched vulnerabilities provide easy access for hackers. The Ponemon Institute found that 52% of data breaches were caused by malicious attacks. Set up an automated patch management system to keep your protocols up-to-date. Apply critical patches within 24 hours of release. Implement non-critical updates during your next maintenance window (no later than two weeks after release).
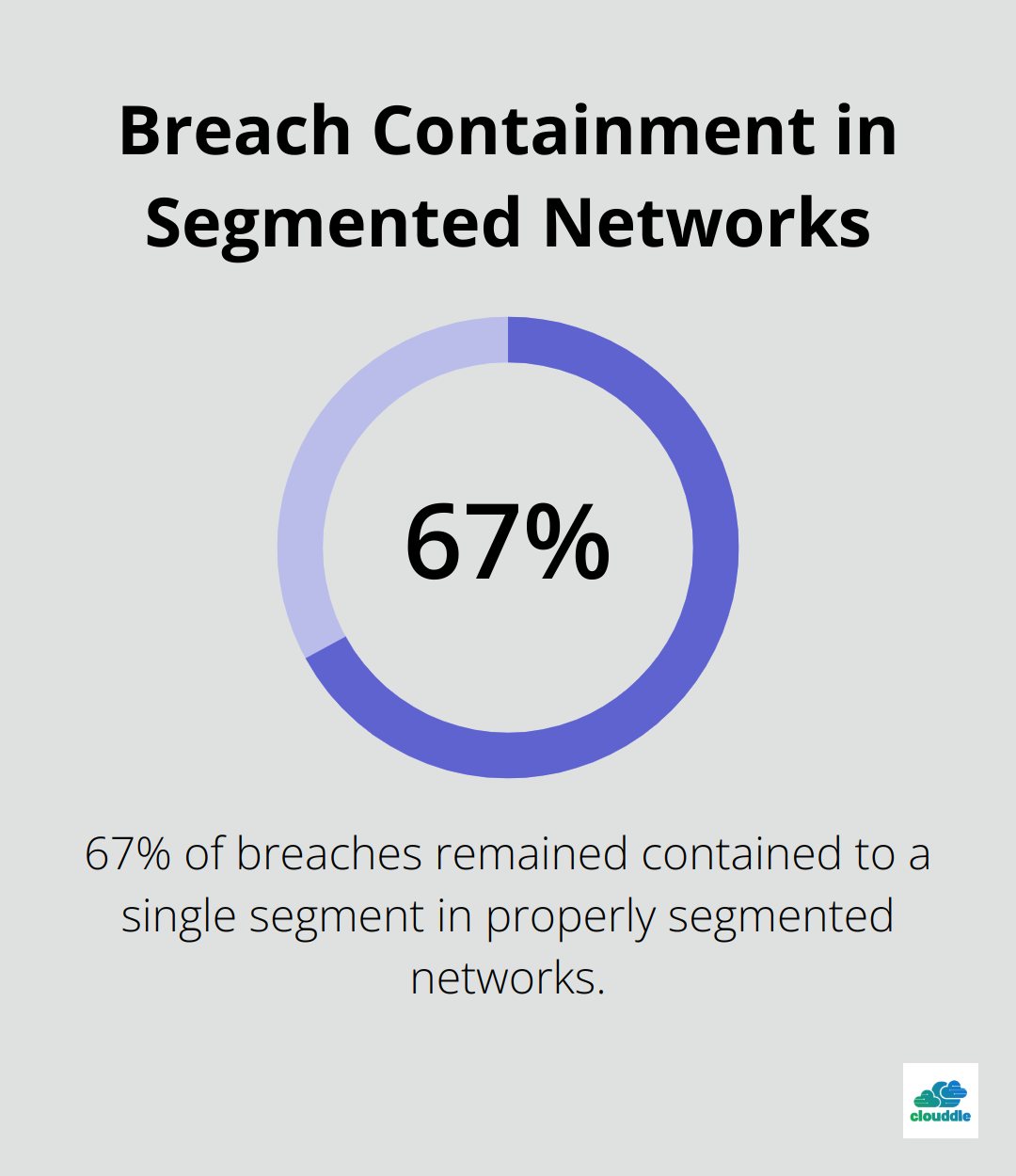
Network Segmentation: Limit Potential Damage
Network segmentation serves as a critical security strategy. The 2024 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report showed that 67% of breaches remained contained to a single segment in properly segmented networks. Implement VLANs to isolate different parts of your network. Use firewalls between segments to control traffic flow. Place IoT devices on a separate network segment for enhanced security.
Continuous Monitoring: Detect Issues Early
You can’t secure what you can’t see. Implement a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to monitor your network protocols in real-time. Gartner reports that organizations using SIEM tools detect threats 2.7 times faster than those without. Set up alerts for unusual protocol behavior (e.g., unexpected DNS queries or abnormal SMTP traffic). Review these logs daily to catch potential issues.
Employee Training: Build a Human Firewall
Your employees act as your first line of defense. The 2024 Proofpoint State of the Phish report revealed that 75% of organizations worldwide experienced a successful phishing attack. Conduct regular training sessions on secure protocol usage. Teach employees to recognize phishing attempts, especially those exploiting email protocols. Run simulated phishing exercises to test their knowledge. Try to achieve a 95% success rate in identifying and reporting these attempts.

Final Thoughts
Network protocols and security form the foundation of our interconnected world. Organizations must understand these protocols to protect their digital assets effectively. Implementing strong encryption, vigilant patch management, network segmentation, continuous monitoring, and employee training creates a robust defense strategy against cyber threats.
The future of network protocols will involve quantum-resistant cryptography, zero-trust architectures, and AI-powered threat detection. These advancements will reshape how we approach network security in the coming years. Clouddle’s Network as a Service (NaaS) solution combines networking, entertainment, and security services to help businesses navigate these complexities.
As cyber threats evolve, staying informed about network protocols and security best practices becomes essential. Organizations can safeguard their operations and data in an increasingly connected world by implementing the strategies discussed in this post. Partnering with experienced providers will help businesses confidently navigate the complex landscape of network security.


