Ever wonder how a popular website like Amazon or Netflix handles millions of users at once without crashing? A huge part of the magic is network load balancing.
Think of it as a super-efficient traffic manager for your digital services. Instead of sending every single user request to one server—which would quickly get overwhelmed—a load balancer intelligently spreads the work across a whole group of servers. This simple but powerful strategy is the key to preventing slowdowns, avoiding crashes, and delivering a smooth, reliable experience for every user.
Understanding Network Load Balancing Fundamentals

Let’s use a real-world analogy. Imagine a busy grocery store with only one checkout lane open on a Saturday afternoon. The line would quickly snake down the aisles, customers would get angry, and the whole operation would grind to a halt. The single cashier is a classic bottleneck.
Now, picture a store manager stepping in. This manager sees the long line and immediately opens up several more checkout lanes, directing incoming shoppers to the shortest line. That manager is acting just like a network load balancer.
In the digital world, the load balancer is a piece of hardware or software that sits in front of your servers (often called a "server farm"). When a user tries to access your website or application, their request doesn't go directly to a server. Instead, it hits the load balancer first. The load balancer then instantly assesses the health and current workload of all the servers in the farm and forwards the request to the one that can handle it fastest.
The Core Purpose of NLB
At its heart, network load balancing is all about building resilience and scalability into your system. The main goals are to make the best use of your server resources, keep data flowing quickly, and ensure no single machine gets overloaded. It’s a foundational piece of any serious digital operation.
A load balancer is your ultimate safety net. If one of your servers suddenly fails or needs to be taken offline for maintenance, the load balancer knows instantly. It stops sending traffic to the down server and reroutes everything to the healthy ones, keeping your service online without a single hiccup.
This automatic failover is what makes a system truly robust. It's a critical component of the entire digital backbone that powers today's applications. To see how load balancing fits into the broader ecosystem, it's helpful to understand the fundamentals of a modern network. You can learn more about how all the components work together in our guide on what is network infrastructure.
Core Functions and Benefits of Network Load Balancing
To put it all together, a network load balancer performs a few critical jobs that deliver direct, tangible benefits to your IT operations. The table below breaks down these core functions and the advantages they provide.
| Core Function | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Traffic Distribution | Prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, which dramatically improves overall performance and speed. |
| Health Monitoring | Actively checks the status of each server and automatically pulls unresponsive or "unhealthy" ones out of rotation. |
| High Availability | Guarantees your service stays online by instantly redirecting traffic away from failed servers (this is called failover). |
| Scalability | Makes it easy to add more servers to the group to handle growing traffic without causing any downtime or service interruptions. |
Ultimately, implementing NLB is about moving from a fragile, single-point-of-failure setup to a strong, flexible, and highly available architecture that can grow with your needs.
How Network Load Balancing Actually Works

So, how does the "manager" in our coffee shop analogy actually decide which barista gets the next order? It's not random. The load balancer relies on specific rules, called load balancing algorithms, to distribute incoming traffic in the smartest way possible. Think of these algorithms as the playbook the manager uses to keep the whole operation running smoothly.
The goal is to prevent a situation where one server is completely overwhelmed while others are just sitting around. This is the essence of what is network load balancing. Its importance is clear when you look at the numbers: the global market was valued at around $5.5 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit over $20 billion by 2034. This explosive growth is being fueled by the massive expansion of cloud services and internet use. For a deeper dive into the numbers, check out the load balancer market growth at Allied Market Research.
Common Traffic Distribution Methods
While the algorithms can get pretty sophisticated, most are built on a few core strategies. Let's look at two of the most popular ways a load balancer directs traffic:
- Round Robin: This is the simplest method. It sends each new request to the next server in the lineup, just like a dealer handing out cards one by one to each player around a table. When it gets to the end of the list, it just starts over at the beginning.
- Least Connections: This approach is a bit more intelligent. The load balancer checks to see which server currently has the fewest active connections and sends the new request to that one. It's perfect for when some tasks take much longer than others, as it helps balance the actual workload, not just the number of requests.
Ensuring Server Health and Reliability
Splitting up the traffic is just one part of the job. A great load balancer also needs to know if the servers are actually in a good state to handle more work. This is done through a process known as health checks.
The load balancer constantly "pings" each server in its pool, asking a simple question like, "Are you online and ready to work?" If a server fails to respond correctly, the load balancer immediately marks it as unhealthy and stops sending traffic its way.
This constant monitoring is what makes automatic failover possible. If a server suddenly goes offline, the load balancer doesn't miss a beat. It instantly redirects that server's traffic to the other healthy ones in the group, ensuring users never even notice there was a problem. This is the secret to building highly available systems that deliver a seamless experience.
Exploring the Different Types of Load Balancers
Just like a seasoned traffic cop uses different signals and routes to manage rush hour, network load balancers come in a few different flavors. They aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. The three main types you'll encounter are hardware, software, and cloud-based, and knowing the difference is crucial to picking the right one for your setup. Each comes with its own set of trade-offs when it comes to performance, cost, and flexibility.
A hardware load balancer is a purpose-built physical appliance. Think of it as a supercharged piece of kit designed to do one thing exceptionally well: direct network traffic at blistering speeds. These boxes are the workhorses of the networking world, known for raw power and rock-solid reliability. This makes them a great fit for large enterprises with massive, mission-critical performance needs. The catch? That power comes with a hefty price tag, and they need physical space, power, and hands-on maintenance.
Software and Cloud-Based Alternatives
If a dedicated hardware box sounds like overkill, a software load balancer offers a much more flexible approach. This is essentially an application that you can install on standard servers or as a virtual machine. You get much of the same traffic management smarts as a hardware device, but with far more agility. It lets you run things on your own terms, on equipment you already manage.
But let's be honest, the real star of the show these days is the cloud-based load balancer. These are fully managed, pay-as-you-go services from cloud giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud. This model is incredibly popular because it abstracts away all the underlying infrastructure management. You just configure it and let the provider handle the rest.
The market trends tell the same story. Data from 2024 shows AWS alone captures a staggering 75.83% of the market share among the top load balancing platforms. Other players like Citrix and HAProxy are in the mix, but the dominance of cloud solutions is undeniable. For a deeper dive into the numbers, check out this in-depth analysis of load balancing software.
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown of how these three options stack up against each other.
Hardware vs Software vs Cloud Load Balancers
| Attribute | Hardware Load Balancer | Software Load Balancer | Cloud Load Balancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highest possible; dedicated hardware | High, but depends on the underlying server/VM | Excellent and scalable, but managed by the provider |
| Cost | High upfront capital expense (CapEx) | Lower upfront cost; often subscription-based (OpEx) | Pay-as-you-go model (OpEx); can be very cost-effective |
| Scalability | Limited; requires purchasing new physical units | Highly flexible; can scale by adding more virtual instances | Extremely easy; scales automatically with demand |
| Flexibility | Low; fixed functionality and physical constraints | High; can be deployed on any standard hardware or cloud | Highest; integrates seamlessly with other cloud services |
| Management | Requires dedicated IT staff for setup and maintenance | Requires management of both the software and the server it runs on | Fully managed by the cloud provider; minimal overhead |
Ultimately, the best choice depends entirely on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise.
The image below gives a great visual of how different load balancing algorithms can impact performance, showing that a smart method like 'Least Connections' can dramatically cut down on response times.
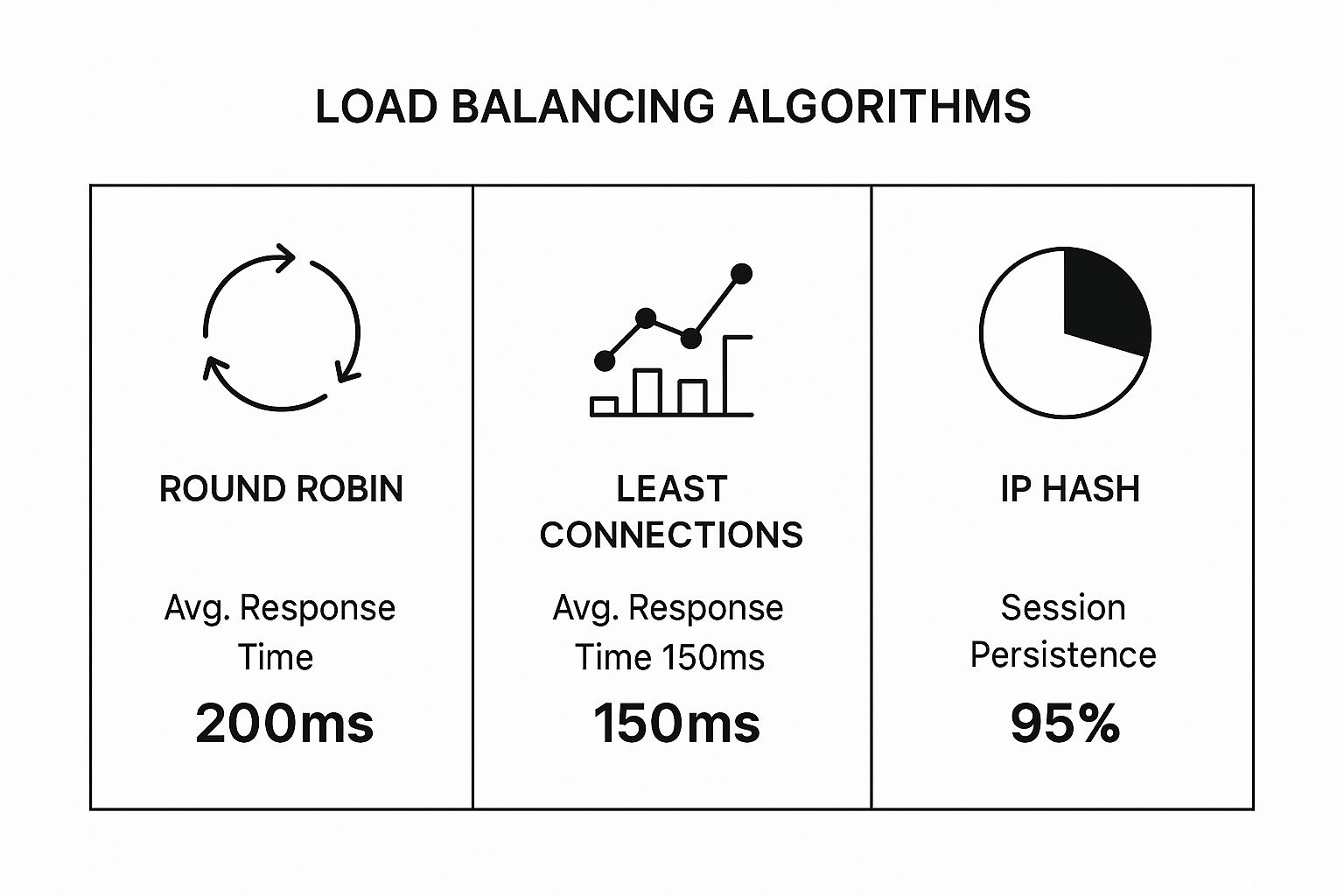
It’s a perfect illustration of the fact that while a simple "Round Robin" approach is easy to implement, choosing a more intelligent algorithm can make a world of difference for your users' experience.
The Tangible Benefits of Network Load Balancing
Putting network load balancing into practice isn't just a technical upgrade; it delivers real, measurable value to your business. The advantages go straight to your bottom line by improving the user experience, stopping expensive downtime, and creating a much more dependable digital backbone for your operations. It’s all about turning a fragile setup into one that can handle anything.
This isn't just about shuffling traffic around. It's about making sure your services are always on and always fast, which is absolutely essential for keeping customers happy and business running smoothly.
Unlocking High Availability and Superior Performance
The biggest win here is a massive boost in reliability. Load balancers are constantly running health checks on every server they manage. If one server goes down or stops responding, the load balancer instantly pulls it out of the rotation.
Traffic is then automatically rerouted to the healthy servers, with no one ever noticing there was a problem. This automatic failover is the key to achieving high availability. It means one server failure won't crash your entire application, saving you from lost revenue and a damaged reputation.
By spreading requests intelligently, a load balancer also gives performance a serious shot in the arm. It makes sure no single server gets overwhelmed, which cuts down on lag and delivers faster response times for everyone.
Enhancing Scalability and Maintenance Flexibility
As your business grows, your traffic will too. Network load balancing offers seamless scalability. You can add new servers to the group on the fly, without any service interruption. The load balancer just starts sending traffic to the new machines as soon as they're online, easily absorbing spikes from a big sale or a successful marketing campaign.
This same flexibility makes routine maintenance a breeze. Need to update a server or take it offline for repairs? No problem. The load balancer will simply route traffic to the other available servers, giving you a perfect window for maintenance with zero downtime.
Here's a quick rundown of the main advantages:
- Boosted Reliability: With automatic failover, your service stays online even if a server fails. This is a core concept we dive into in our guide on what is network redundancy.
- Improved Security: A load balancer can serve as a buffer, shielding your backend servers from direct exposure and helping to fend off certain cyberattacks like DDoS campaigns.
- Greater Flexibility: You can perform critical maintenance and upgrades without ever having to disrupt service or kick users offline.
Load Balancing in Action Across Different Industries

The theory of load balancing is interesting, but seeing it work in the real world is where it really clicks. It’s the unsung hero keeping daily operations afloat everywhere, from a bustling hotel lobby to critical commercial infrastructure. Think of it as the ultimate digital traffic cop, expertly managing data flow to prevent gridlock.
And the demand for these solutions is exploding. The network load balancer market was valued at $6.2 billion in 2024, but it’s expected to shoot up to $13.82 billion by 2029. That incredible growth is fueled by the boom in cloud computing and the ever-present need for better security. If you're interested in the numbers, you can dig into the global load balancer market projections at Research and Markets.
Powering Hospitality and Commercial Real Estate
Picture a big, modern hotel on a Friday night. You have hundreds of guests, and they’re all doing their own thing—streaming movies, jumping on video calls for work, or just scrolling through social media. Without load balancing, the Wi-Fi would grind to a halt, leaving everyone with a spinning wheel of death and a bad taste in their mouth. A load balancer saves the day by intelligently spreading that Wi-Fi traffic across multiple access points and internet lines, so everyone enjoys a fast, reliable connection.
It's a similar story in a large office building with dozens of different companies under one roof. Network load balancing is crucial for serving all those tenants.
It makes sure every business gets the high-speed, secure internet they pay for. This simple act prevents one company’s massive data transfer from bogging down the connection for everyone else, which is key to keeping tenants happy.
Ensuring Stability in Retail Environments
For retailers, network uptime is money. Think about the chaos of Black Friday—point-of-sale (POS) systems and in-store networks are pushed to their absolute limits. If the network goes down, even for a few minutes, it can be a disaster, resulting in lost sales and angry shoppers.
Load balancing acts as a critical safety net. It works behind the scenes to:
- Spread POS traffic over multiple servers so the system doesn't crash under pressure.
- Keep inventory management systems online and accurate.
- Maintain a solid connection for guest Wi-Fi and mobile payment terminals.
By preventing these catastrophic outages, retailers get a very clear answer to what is network load balancing: it’s the technology that safeguards their revenue and protects the customer experience when it matters most.
Bringing in the Pros: Simplifying Network Load Balancing with NaaS
Let’s be honest: setting up and managing network load balancing the old way is a heavy lift. It often means sinking a ton of money into expensive hardware or getting tangled up in complex software configurations. This isn't just a one-time setup, either—it demands specialized IT skills, constant babysitting, and a big upfront budget.
But what if you could sidestep all that hassle? There’s a much simpler way to get the high-performance, reliable network you need.
That's where Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) flips the script. Think of it like hiring a dedicated crew of networking experts who handle everything behind the scenes. Instead of buying and wrestling with your own load balancers, you’re plugging into a managed service that delivers it all as a simple utility.
The NaaS Advantage
This model completely changes the game. The NaaS provider handles all the tough stuff—the infrastructure, the security, the never-ending updates—freeing up your team to focus on what actually grows your business, not just keeping the lights on.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- No More Operational Headaches: Forget about the hands-on management, late-night patching, and frustrating troubleshooting of load balancing gear.
- Expertise on Tap: You instantly gain a team of specialists whose entire job is to keep your network running at peak performance and locked down against threats.
- Predictable, Friendly Costs: This approach moves your spending from a massive upfront capital expense (CapEx) to a manageable, predictable monthly operating expense (OpEx).
At the end of the day, NaaS takes network load balancing from a complex, resource-draining IT project and turns it into a simple, scalable service. It’s how any business can get its hands on enterprise-level networking without the enterprise-level migraine.
Adopting a NaaS model means you can scale your network resources up or down as needed. You’ll have all the capacity you need for your busiest moments without paying for idle hardware the rest of the time.
Want to dive deeper? Check out our complete guide on what is Network-as-a-Service to see how it can bring your infrastructure into the modern era.
A Few Common Questions About Network Load Balancing
As you start to think about what network load balancing can do for your organization, a few practical questions almost always pop up. Getting these details straight is key to understanding where it fits into your overall network strategy.
Is a Load Balancer the Same as a Firewall?
It's a common point of confusion, but while both devices sit in the path of your network traffic, they have completely different jobs. Think of a firewall as your network's security guard. Its entire purpose is to inspect traffic coming in and out, checking it against a strict set of security rules to block anything malicious. Its goal is protection.
A load balancer, on the other hand, is more like a traffic cop or an air traffic controller. It doesn’t inspect traffic for threats; its job is to efficiently distribute legitimate requests across a group of servers. This ensures no single server gets overloaded, which keeps your applications running smoothly for everyone.
The Bottom Line: A firewall protects your network by filtering out bad traffic. A load balancer optimizes performance by distributing good traffic. They aren't interchangeable and, in most professional setups, you'll find them working side-by-side.
Will Adding a Load Balancer Slow Down My Network?
This is a fair question, but the answer is almost always a resounding "no." In fact, it does just the opposite.
While it's technically true that any device you add to a network path introduces a tiny bit of latency, the performance boost you get from smart traffic distribution completely overshadows it. By preventing any one server from becoming a bottleneck, network load balancing is what dramatically improves your network's overall speed and responsiveness. It's the solution to slowdowns, not the cause of them.
How Do I Pick the Right Load Balancing Algorithm?
Choosing the right method really comes down to what you're trying to accomplish and the nature of your servers. There’s no single "best" algorithm for every situation.
For instance, if all your servers are more or less identical and handle simple, uniform requests, a basic Round Robin algorithm often does the trick. It just sends each new request to the next server in line, like dealing cards around a table.
But what if some tasks take longer than others? In that case, something smarter like the Least Connections method is a much better fit. It directs new traffic to whichever server currently has the fewest active connections, which is a great way to ensure the actual workload—not just the number of requests—is spread evenly.
Ready to eliminate network complexity and ensure peak performance without the hassle? Clouddle Inc delivers robust, managed Network-as-a-Service solutions that handle everything for you. Learn more about our NaaS offering and simplify your IT today.


