Think about your network for a moment. Is it ready for what's next? Network scalability is all about your network's ability to handle more traffic, more users, and more data without slowing down or breaking. It's the difference between a system that supports your business as it grows and one that crumbles right when you need it most.
Understanding Network Scalability and Why It Matters

Let's use a simple analogy. Imagine a small, quiet country road. It works perfectly for the handful of cars that pass through each day. But what happens when a new stadium is built right next to it? On game day, that road becomes a parking lot. That’s an unscalable network.
A scalable network is more like a modern highway system. It’s designed from the ground up with growth in mind. It has the capacity to add new lanes, interchanges, and smart traffic controls as the city around it expands. This foresight is the heart of what is network scalability: building for tomorrow's traffic, not just today's.
The Real-World Impact of Poor Scalability
When a network can't keep up, the fallout is swift and painful. A system that wasn't built to handle a sudden rush will inevitably fail, creating serious headaches for your business.
Here are a few common problems you'll see:
- Website Crashes: You launch a huge Black Friday sale, and the flood of visitors takes your site down completely. Lost sales, angry customers.
- Poor User Experience: Think slow-loading pages, glitchy apps, and constant timeouts. This kind of frustration sends customers straight to your competitors.
- Reduced Productivity: When internal systems get sluggish, your team's workflow grinds to a halt, hitting your bottom line where it hurts.
A network that can't scale isn't just a technical problem—it's a direct roadblock to growth. It physically stops you from serving more customers, entering new markets, or seizing big opportunities.
The Growing Need for Scalable Architectures
It's no surprise, then, that businesses are investing heavily in getting this right. The global market for network engineering services—the very expertise needed to build these robust systems—was valued at USD 48.38 billion and is expected to climb to USD 104.16 billion by 2034.
This massive growth shows just how critical scalable infrastructure has become. As data volumes explode and new technologies emerge, having a network that can adapt is non-negotiable. You can find more insights about the network engineering market on Precedence Research.
To simplify these concepts, here’s a quick breakdown of what makes a network truly scalable.
Key Elements of Network Scalability at a Glance
| Component | What It Means in Practice | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Having enough bandwidth and processing power to handle current and future traffic loads without bottlenecks. | Prevents slowdowns during peak hours, ensuring a smooth user experience and consistent service delivery. |
| Flexibility | The ability to easily add new resources, services, or users to the network without a major overhaul. | Allows the business to quickly adapt to market changes, launch new products, or expand operations. |
| Redundancy | Building in backup systems and failover paths so that if one component fails, the network keeps running. | Minimizes downtime, protecting revenue and maintaining customer trust even when things go wrong. |
| Performance | Maintaining low latency and high throughput, even as the number of users and data requests increases. | Guarantees that applications remain responsive and fast, which is critical for customer satisfaction and employee productivity. |
Ultimately, these elements work together to create a network that doesn't just survive growth—it enables it.
2. Choosing Your Growth Path: Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling
When your network starts feeling the strain of increased demand, you’re at a crossroads. It’s a lot like deciding how to handle a growing family’s transportation needs. Do you trade in your trusty sedan for a much bigger, more powerful SUV? Or do you just buy a second car and keep the first one?
This simple choice is the perfect analogy for the two fundamental ways to scale your network: vertical scaling (getting the bigger SUV) and horizontal scaling (adding another car).
Understanding the pros and cons of each path is absolutely critical. The decision you make will directly impact your budget, your network's flexibility, and how easily you can handle future growth without starting from scratch.
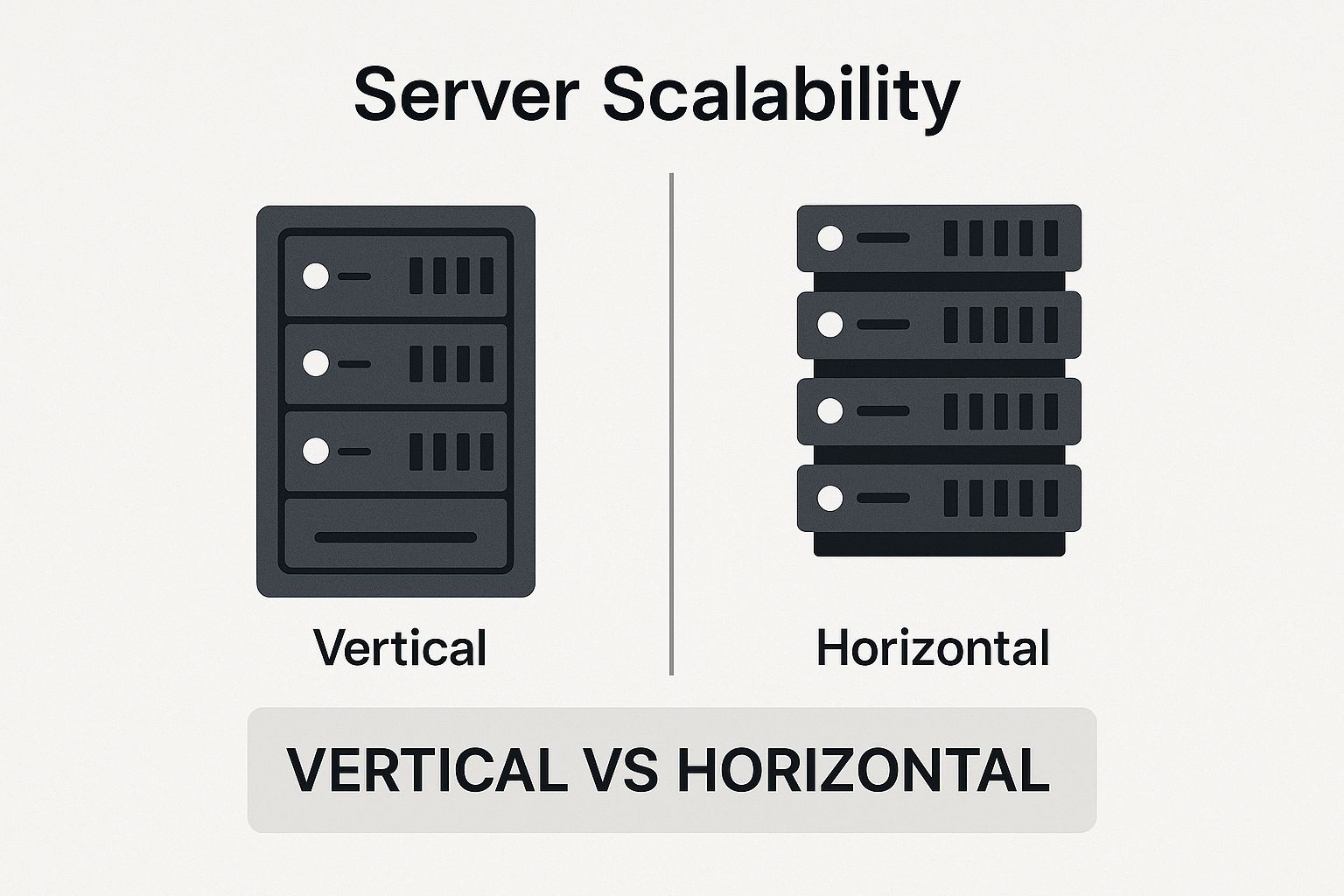
As you can see, vertical scaling is all about concentrating power in one place, while horizontal scaling is about distributing it. This fundamental difference has huge implications for resilience and flexibility.
Scaling Up With Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, often called "scaling up," is the "bigger SUV" approach. You take an existing server or network device and beef it up with more powerful components. Think of it as giving your machine a serious upgrade—more CPU cores, a massive boost in RAM, or faster storage.
This method can feel straightforward at first. After all, you’re still just managing one machine, which simplifies things. For certain applications, like a massive, monolithic database that needs immense raw processing power, scaling up can provide a direct and noticeable performance kick.
But there’s a catch.
You can only cram so much horsepower into a single server. Eventually, you'll hit a hard limit, either because of physical constraints or because the next upgrade costs a small fortune.
At some point, scaling up further becomes impractical or just plain impossible.
Scaling Out With Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, or "scaling out," is the "add another car" strategy. Instead of making one machine more powerful, you add more machines to your network. The workload is then spread across this entire fleet of servers. This is the bedrock principle that makes modern cloud computing possible.
This approach brings some serious advantages to the table:
- Better Fault Tolerance: If one server in your cluster goes down, it's not a catastrophe. The others just pick up its share of the work, and your service stays online.
- Incredible Flexibility: You can add or remove smaller, commodity servers as demand fluctuates. This is far more cost-effective than being stuck with a single, oversized server that’s underused most of the time.
- Near-Infinite Growth: Unlike the hard ceiling of a single machine, you can theoretically keep adding servers to a horizontal cluster almost indefinitely.
This model shines for applications built for a distributed world, like web servers and microservices. Modern solutions often abstract away the complexity; for instance, many are turning to Network as a Service (NaaS) to get this kind of on-demand scalability without the management headache.
Comparing Horizontal and Vertical Scaling Strategies
To help you decide which scaling method best fits your network's needs and business goals, here’s a side-by-side comparison.
| Attribute | Horizontal Scaling (Scale-Out) | Vertical Scaling (Scale-Up) |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Add more machines to the network pool. | Add more resources (CPU, RAM) to a single machine. |
| Cost | Often lower initial cost using commodity hardware. Can become complex to manage at a large scale. | Can be very expensive for high-end hardware. You pay for peak capacity even if unused. |
| Limit | Practically limitless; you can keep adding more machines. | Limited by the maximum capacity of a single server. |
| Fault Tolerance | High. Failure of one node doesn't bring down the entire system. | Low. A single point of failure; if the server goes down, the service is unavailable. |
| Flexibility | High. Easy to scale up or down by adding/removing machines based on demand. | Low. Scaling often requires downtime and can be a difficult, disruptive process. |
| Best For | Web servers, microservices, distributed databases, modern cloud-native apps. | Monolithic applications, large databases, systems that cannot be easily distributed. |
Ultimately, there’s no single "right" answer. The best path depends entirely on your specific applications, your budget, and how you expect to grow. In fact, many sophisticated systems blend the two, using a hybrid approach where individual servers are scaled up to a point, and then the entire cluster is scaled out with more of these powerful nodes.
Warning Signs Your Network Is at Its Limit
Long before a network completely gives out, it starts sending up flares. These distress signals are easy to ignore at first, but doing so is like putting a piece of tape over your car's check engine light. You might make it a few more miles, but a breakdown isn't a matter of if, but when. Learning to spot these signs is the first step to getting ahead of a major failure.
The most common red flag is a predictable slowdown. Does your e-commerce site grind to a halt during a flash sale? Do your internal apps become unusable at the end of every quarter? When performance dips during peak hours, you're watching your network hit its capacity ceiling in real-time. This isn't just an annoyance; it's a direct threat to productivity and your customers' experience.
Lag and Lost Connections
Go a level deeper than just general slowness and look for latency and application timeouts. Latency is simply the time it takes for data to get from point A to point B. When it creeps up, you get that awkward, painful lag on video calls or an extra few seconds of waiting for a page to load.
Even more serious are frequent application timeouts. This is what happens when a server gets so swamped with requests it just starts dropping them. If your team is constantly complaining about getting booted from a system or staring at error messages, your infrastructure is screaming for help.
This is exactly why businesses are pouring money into their networks. The global enterprise networking market is already valued at around USD 215.45 billion and is on the rise, underscoring just how critical it is to build systems that don't crumble under pressure. You can dive deeper into the growth of enterprise networking in recent industry reports.
High latency and constant timeouts aren't just technical glitches—they're a direct signal that your network can't handle its current workload. This translates into a terrible user experience that can quickly damage customer loyalty.
Strained Server Resources
Finally, take a hard look at the health of your servers. If their CPU and memory are consistently maxed out, you're living on the edge. A server that’s always running at 80-90% capacity just to handle normal traffic has absolutely no wiggle room for a sudden surge. It's an outage waiting to happen.
Keep a close eye on these three vital signs:
- High CPU Utilization: This tells you the server's brain is overworked and can't keep up with the processing demands.
- Memory Exhaustion: Once the RAM is full, the system resorts to using much slower disk space, and performance falls off a cliff.
- Increased I/O Wait: This is a classic bottleneck where the CPU is sitting idle, waiting for the storage drive to catch up.
When these metrics are constantly in the red zone, it's a clear signal that your network needs a scalability plan—before a small slowdown turns into a full-blown catastrophe.
Overcoming Common Network Scaling Challenges
Throwing more servers at a growth problem might feel like a quick fix, but true network scalability is about navigating a minefield of potential issues. If you don't tackle these hurdles head-on, you'll find that even with more hardware, performance can still grind to a halt. It's the difference between a network that’s built for growth and one that's always a step away from collapse.
One of the sneakiest and most dangerous traps is the single point of failure (SPOF). This is any one piece of your system—a router, a server, even a single database—that can take the whole operation down with it if it fails. Think of a busy restaurant with only one credit card machine. When it goes down, sales stop, no matter how many chefs are in the kitchen. The exact same thing can happen in your network.
That's why resilient architectures are designed with redundancy built-in from the ground up. The goal is to make sure no single component can cause a system-wide outage. It’s a foundational principle for building a network that can handle the unexpected without your users ever noticing a thing.
The Art of Balancing the Load
As you start adding more servers to handle more traffic (that’s horizontal scaling), you suddenly need a really smart traffic cop to direct all the incoming requests. This is what load balancing is all about. A load balancer's job is to spread traffic out evenly across your servers, making sure no single machine gets slammed.
Without good load balancing, you could have ten servers running, but find that 90% of your traffic is hitting just one or two of them. This creates a nasty bottleneck, leaving the rest of your expensive hardware sitting idle while your users complain about slowdowns.
An effective load balancing strategy is the key to unlocking the true power of horizontal scaling. It ensures that every resource you add is actually used, maximizing performance and preventing hotspots from forming in your network.
The Database Bottleneck Problem
More often than not, the biggest roadblock to scaling isn't the web servers or the network gear—it's the database. You can spin up dozens of web servers, but if they all have to funnel their requests through a single, overworked database, you haven’t actually solved the problem. The database becomes the choke point that throttles the entire system.
Scaling a database is a tricky business and usually requires some specialized tactics, like:
- Read Replicas: You can create copies of your database that only handle read requests. This takes a huge load off the main database, freeing it up to focus on writes.
- Sharding: This involves splitting a massive database into smaller, faster, and more manageable chunks, which are then spread across multiple servers.
- Caching: Storing frequently accessed data in a super-fast memory layer (like Redis or Memcached) dramatically cuts down on how often you need to hit the database.
This is where network capacity planning becomes absolutely critical for spotting these potential bottlenecks before they bring you down. To learn more, take a look at our guide on strategic network capacity planning to help you stay ahead of demand. By getting in front of these challenges, you can build a network that grows stronger, not just bigger.
Proven Best Practices for Scalable Network Design

If you want a network that can actually keep up with your business, you can't just react to problems as they happen. You have to design for growth from day one. Thinking ahead prevents those painful, expensive overhauls down the road and turns your infrastructure into a growth engine, not a bottleneck. This means embracing a few core principles that build flexibility right into the foundation.
A powerful starting point is to decouple your services. Instead of one giant, tangled application where every piece depends on the others, a microservices architecture breaks things down. Think of it like building with LEGOs instead of carving a statue from a single block of marble.
When your user login service gets hammered with traffic, you can just scale that one "brick" without ever touching the payment or inventory systems. This modular approach not only makes your system more resilient but also far easier to manage as it expands.
Design for Failure and Automate Everything
Here’s a hard truth: in a scalable network, things will break. The trick is to build a system that expects failure and doesn't fall apart when it happens. This "design for failure" philosophy is all about building in redundancy and automatic failover mechanisms from the ground up.
Automation is what makes this resilience possible. Trying to manually configure servers or roll out updates is slow, inconsistent, and a recipe for human error—it simply doesn't work at scale.
This is where Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools come in. With IaC, you can:
- Define your entire network setup in simple, version-controlled files.
- Spin up new resources with perfect consistency every single time.
- Set up auto-scaling rules that automatically add or remove servers based on live traffic.
This hands-off approach is the only way to achieve the kind of elasticity modern applications demand.
A scalable network isn't just about throwing more hardware at a problem. It's about building an intelligent system that can manage itself, adapt to change, and recover from failures without someone needing to intervene.
Tap into Cloud Elasticity and Monitor Relentlessly
Cloud platforms were practically built for this stuff. They give you the tools to scale horizontally with incredible efficiency through elasticity—the power to grab resources when you need them and let them go when you don't. This pay-as-you-go model is a game-changer, saving you from buying and maintaining expensive hardware just to handle occasional traffic spikes.
But you can't manage what you can't see. That’s why robust monitoring isn't a "nice-to-have"; it's a necessity. Good monitoring gives you the data you need for smart capacity planning, helping you spot bottlenecks long before your users do. You can’t build a scaling strategy without first understanding what is network monitoring and making it a priority.
The demand for these practices is exploding. The global network optimization market is on track to jump from USD 5.5 billion to USD 25.0 billion by 2035. This massive growth, detailed in reports on the network optimization market, is a direct result of rising network complexity and the flood of data from cloud and IoT devices.
When you bring together a modular design, aggressive automation, cloud elasticity, and deep visibility, you're creating a blueprint for a network that's not just bigger—it's smarter.
Your Network Scalability Questions Answered
As you start thinking about what network scalability actually means for your business, a few practical questions always seem to pop up. Moving from theory to practice means getting straight answers to the things that can trip you up. This section is all about tackling those common queries, cementing the core ideas, and giving you direct guidance for making smarter infrastructure decisions.
Getting these details right is the difference between simply knowing the definition of scalability and being ready to build a system that can actually handle growth. Let's clear up some of the most important points that come up when planning for the future.
What Is the Difference Between Network Scalability and Performance?
It’s incredibly common to mix these two up, but they measure completely different things. Think of performance as how fast and responsive your network is right now, with its current traffic. Scalability, on the other hand, is all about its ability to keep that great performance even as the workload gets much, much bigger.
A network might be blazing fast with 100 users but grind to a halt the moment 10,000 users log on. That network has good performance at a specific moment, but its scalability is terrible.
A truly scalable network is designed from the ground up to handle that jump from 100 to 10,000 users without breaking a sweat. In short, performance is a snapshot; scalability is your roadmap for the future.
This distinction is critical. A system that feels speedy today could easily be built on a foundation that will crumble under the pressure of tomorrow's success.
How Does Cloud Computing Improve Network Scalability?
Cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud were practically built for scalability. Their secret weapon is elasticity—the power to automatically add or subtract resources like servers and bandwidth in direct response to real-time demand. This is a world away from the old model of buying a mountain of expensive physical hardware just to handle peak traffic that might only happen a few times a year.
The cloud makes sophisticated horizontal scaling accessible to just about anyone. It comes with a toolbox of features that do the heavy lifting for you:
- Managed load balancers to intelligently spread traffic across multiple servers.
- Auto-scaling groups that spin up new servers when traffic spikes and shut them down when it’s quiet, all without a human touching a thing.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing, which means you stop paying massive upfront costs for hardware you might not even need yet.
This model rips out so much of the manual work and complexity that once made scaling a massive engineering headache, letting businesses react to customer demand in an instant.
Should a Small Business Worry About Network Scalability?
Absolutely. While a small business obviously doesn't need the same beastly infrastructure as a global corporation, putting scalability on the back burner is a recipe for serious pain later on. The architectural choices you make in the early days have a funny way of sticking around for a very long time.
Making smart, simple choices from day one—like picking a database technology known to scale well or designing your application to be stateless—can save you from a hugely expensive and disruptive overhaul right when your business is taking off. A lack of scalability often becomes a growth-killing bottleneck at the very moment you start to find success.
Think of it this way: planning for scale early is a direct investment in your company's future potential. It ensures your tech can keep up with your ambition.
What Role Does Automation Play in Scaling a Network?
Automation is the engine that makes modern scalability run. The old-school approach of a system administrator manually provisioning servers, configuring software, and deploying updates is just too slow, inconsistent, and error-prone to work at any real scale.
Today, tools like Terraform and Ansible let you define your entire infrastructure as code (IaC). This means you can create new resources in minutes with perfect, repeatable consistency. More importantly, it’s the key to autoscaling, where the system itself watches for traffic changes and adds or removes resources on its own. Without automation, true elasticity and efficient horizontal scaling are pretty much impossible. It turns a reactive, manual task into a proactive, self-healing system.
Ready to build a network that grows with your business without the management headaches? Clouddle Inc offers Network-as-a-Service solutions that deliver the scalability, security, and support you need to focus on what you do best. Explore our managed services and build your future-proof infrastructure today.


